Religions
advertisement

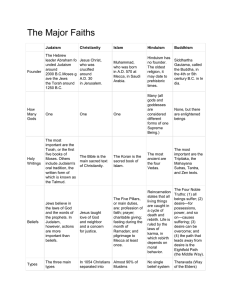
RELIGION THE BIG 5 WHAT ARE THE BIG FIVE RELIGIONS? • • • • • Judaism – 14 million - .2% Buddhism – 500 million – 7% Hinduism – 1 billion – 15% Christianity – 2.2 billion – 32% Islam – 1.6 billion – 23% JUDAISM • Judaism is the oldest of the monotheistic faiths. It affirms the existence of one God, Yahweh, who entered into covenant with the descendants of Abraham, God's chosen people. • These holy writings are known as the Torah, specifically the five books of Moses, but most broadly conceived as the Hebrew Scriptures (traditionally called the Old Testament by Christians) and the compilation of oral tradition known as the Talmud (which includes the Mishnah, the oral law). HEBREWS AND JUDAISM • Hebrews lived in a region between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea called Canaan (modern day – Palestine) • Majority of Hebrew history comes from the first five books of the Bible, the Torah according to Jews and the most sacred of Judaism • Abraham was the leader of the Hebrews and they believed in monotheism, a belief in a single god whom they called Yahweh • This was in direct contrast to all other groups in the region who were polytheists, worshipping many gods usually referring to a specific place they lived • Hebrews proclaimed Yahweh was the one and only God, who had power over all people everywhere – there were no images created of God because Hebrews did not believe he was a physical being • Abraham established a covenant with Yahweh – Abraham promised to obey Yahweh and Yahweh promised to protect Abraham and his descendants MOSES AND THE EXODUS • According to the Bible, Hebrews migrated to Egypt because of drought and famine • Although they were welcomed at first, eventually the Hebrews were forced into slavery • Moses lead the Hebrew people out of Egypt between 1200 and 1300 BC because God commanded him to – this time is called “the Exodus” and remembered during the festival of Passover • When the Hebrews were crossing the Sinai Peninsula, Moses climbed Mount Sinai to pray and returned with two stone tablets on which Yahweh had written the Ten Commandments • The Ten Commandments were the basis for civil and religious laws of Judaism • Religious teachers called prophets taught that Hebrews had a duty to worship God and live justly with one another • Hebrews were eventually became the Jews and their religion was Judaism • This emphasis on right conduct and the worship of one God is called ethical monotheism—a Hebrew idea that has influenced human behavior for thousands of years through Judaism, Islam, and Christianity ZOROASTRIANISM • Empires will conquer Israel, the Kingdom of the Jews throughout history including the Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Greeks and Romans • During the reign of the Persian Empire around 600 BC, a prophet by the name of Zoroaster appeared • Zoroastrianism taught earth was a battle between good and evil, all humans have a part in this struggle • He said there was only one god and he would judge each individual and their part in this struggle • This religion mostly died out after Muslims conquered the region in the 600s, but important elements including the concept of Satan and angels can be traced to Zoroaster which are found in Judaism, Christianity and Islam • Avesta– Ancient Scriptures of Zoroastrianism • Led by priests BUDDHISM • After living a life of isolation, wandering in the forests for six years, Siddhartha Gautama (b. 563 – 483 BC) found enlightenment by meditating under a fig tree for 49 days • He took the name Buddha for “enlightened one” and explained the four main ideas of his enlightenment called, The Four Noble Truths • He accepted the ideas of reincarnation, but rejected the idea of polytheism and the caste system CONT’D • The ultimate goal for Hindus and Buddhists is a perfect state of understanding and a break from the chain of reincarnation • A turning point in the establishment of Buddhism was when Ashoka a great ruler during the Mauryan dynasty converted to Buddhism, he built stupas or shrines for the life of Buddha and he sent missionaries throughout the Mediterranean world. DIFFUSION OF BUDDHISM • Despite Buddhism origins in India, not many solely practiced Buddhism because the ideas between Buddhism and Hinduism were so similar • Missionaries began travelling throughout Asia after Buddha’s death to spread his faith • Also, many of the converts to Buddhism were laborers and crafts people, these merchants were critical in carrying Buddhism to Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, island of Sumatra and following the Silk Road to China, from China or Korea and Japan. CONT’D • Trade made Buddhism the most widespread religion of East Asia • Trade was the key element in not only the spread of goods across the known world, but also essential in the cultural diffusion of ideas HINDUISM • Aryans and non-Aryans in India blended their beliefs and gods until sometime between 750 and 550 BC • Hinduism has no specific founder nor a single set of ideas • Hinduism strengthened the caste system—if you were a upper-class male (Brahmin, warrior, or merchant) it was good karma earned in a former life • Being born a women, a laborer, or an untouchable was bad karma or results of bad deeds in a former life CONT’D • The beliefs of Hinduism and the caste system dominated life—food, dress, associations • The Golden Age of India was from 320-550 AD, this was the reign of the Gupta Empire • Strong central government fostering peace and prosperity within the strict caste system • Math & Science achievements – concept of zero, decimal system based on the number 10, created number writing system which became Arabic numbers • Medicine – Herbal remedies for illness, form of plastic surgery for facial injuries, vaccination for small pox (China – 10th c, Europe – 17th c) • Art & Literature – built stone temples to Hindu gods, Buddhist shrines called stupas, fables and folktales written in Sanskrit, became the basis of Ali Baba and the Forty Thieves and Aladdin and his Magic Lamp CHRISTIANITY • Around 63 B.C. the Roman Empire took control of Judea, the home of the Jews • A Jew named Jesus was born around 4 to 6 B.C.— around the age of 30 he began his ministry and people believed him to be the Messiah or savior of the Jewish people • His influence and following threatened the Roman and Jewish authorities, Jesus was sentenced to be crucified for defying Roman authority • After his death, Jesus’ followers continued to practice and spread his teachings throughout the Roman Empire CONT’D • From 70 A.D. to 135 A.D.—Judea consistently rebelled against Roman authority until the Jews lost and most were driven into exile • The dispersal of the Jews was known as the Diaspora • As the Roman Empire began to decline Christians were persecuted as scapegoats for economic and political problems • Christians were sacrificed as martyrs, people who are willing to sacrifice their lives for the sake of a belief or a cause A WORLD RELIGION • By the 3rd century there were millions of Christian followers in the Roman Empire • In 312 A.D. the Roman Emperor, Constantine converted to Christianity an ended the persecution of Christians • By 380 A.D.—Theodosius made Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire ISLAM • TO BE CONTINUED…