blog 2nd March Keeping order inprisons e.t.c
advertisement

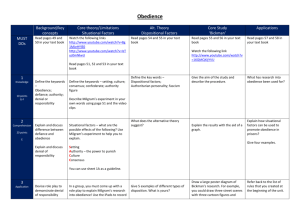
Applications of Research into Obedience Keeping Order in Institutions and Situations Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform What method did Bickman use in his investigation? a. b. c. a laboratory experiment a field experiment a questionnaire Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform What method did Bickman use in his investigation? a. b. c. a laboratory experiment a field experiment a questionnaire Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform Which of these uniforms did he not test? a. b. c. a guard’s uniform a milkman’s uniform an army officer’s uniform Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform Which of these uniforms did he not test? a. b. c. a guard’s uniform a milkman’s uniform an army officer’s uniform Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform Which of these tasks were participants not asked to do? a. b. c. walk down one side of the pavement pick up litter give some money to a stranger Bickman’s (1974) investigation into the power of uniform Which of these tasks were participants not asked to do? a. b. c. walk down one side of the pavement pick up litter give some money to a stranger Findings of Bickman’s study 89% 57% Obedience Rate (%) 33% Type of Uniform Keeping Order in Institutions BATs Apply research into obedience by finding out how to keep order in schools, prisons and the armed forces (C+) Revision for mini test next week Blog quiz Activities on p60 of text book How can we apply what we have learnt about Obedience? Most groups in Society have a HIERARCHY? What does this mean? Giving orders, making business decisions, exercising discipline Taking orders, following instructions, obeying or else ‘fired’ Most Authority Low obedience to others below Least Authority Obedience to everyone higher up See Supermarket example on p57 Keeping Order in Prisons Read p 58 and fill in the worksheet. Use of Uniform Gives guards power and status Easier for guards to give orders as they do not feel responsible for their actions Prisoners lose identity – easier to control/distinguish BUT - Prisoners may take less responsibility for their actions and become disobedient Use of Punishment Punishments for breaking rules in prison – prisoners more likely to obey Solitary confinement Loss of privileges Consensus Can encourage obedience Can encourage disobedience – must prevent ’ganging up’ amongst prisoners Can lead to riots Prisoners kept apart most of time, or monitored closely when in groups Keeping Order in Schools Schools need a level of Obedience to make them function properly Draw a hierarchy triangle for this school … Keeping Order in Schools Government South Glos Council Mr Cook – Headteacher Deputy Heads – JA and AT Assistant Heads Heads of Lower, Middle and Upper School Heads of Faculty/Subject Teachers, Support Staff, Cleaners e.t.c Students Behaviour Policy You have10 minutes – we will share these Read the Grange School Behaviour for Learning Policy Look at ‘Doing Research’ p59 In your group write 5 questions you could ask the teacher you have invited They need to be open questions How will you record what is said? Think about Ethics, politeness, and http://www.army.mod.uk armed forces website – ‘joining the army’ – ‘Discipline values and standards’ Keeping Order in the Armed Forces Use the computer to do activity 4.9 Jot down all the ways in which the document encourages obedience in potential recruits. Plenary What were your main findings from the interview with a teacher? Compare your answers with other groups. It will be nice to thank the teachers and let them know what you got out of this, and how it enhanced your understanding of obedience in schools Homework Revision for mini test next week see p 60 You may take your exercise book home Blog quiz – try the quiz