Lsn 17 Christianity
advertisement

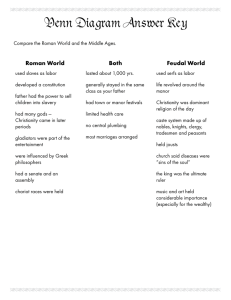
Christianity Lesson 17 ID & SIG: • Calvin, epistles, Gentiles, Hermensen (Arminius), Jesus, Luther, New Testament, Paul (Saul), Pharisees, Reformation, salvation by faith, spread of early Christianity, St. Augustine Jesus • Born sometime before 4 B.C. in Bethlehem – Virgin birth as the Son of God (Luke 1:34-35) • John the Baptist began preaching before Jesus and Jesus began his ministry with a message of repentance similar to John’s • Called Twelve Apostles to assist him Jesus’ Ministry • Met resistance from Jewish authorities who considered his claims to be the Messiah blasphemy and Roman authorities who considered his call for “the kingdom of God” to be a political threat • Jews brought Jesus before the Roman authorities who acquiesced to the Jews’ demands to crucify Jesus Resurrection • Jesus’ followers proclaimed he had risen from the dead and that his death and resurrection served as a sacrifice to offset their sins – Now they too can survive death and live eternally in heaven • Jesus’ followers called him “Christ” which means “the anointed one” and they became known as Christians (Acts 11:26) New Testament • Christians compiled a body of writings including accounts of Jesus’ life, reports of his followers’ works, and letters outlining Christian teachings • Becomes known as the “New Testament” and Christians refer to the Jews’ Hebrew scriptures as the “Old Testament” Salvation • Jesus’s teachings did not replace the Jewish law but transcended it • Salvation for Christians would come by faith rather than by adherence to the law • How does this impact keeping order in a society? Saul • The Christians were subjected to persecutions from Jews who disagreed with the new faith • One of the chief persecutors was Saul – Zealous Pharisee – Held the people’s coats while Stephen was being stoned (Acts 4:58) • Was on his way to Damascus to see whether there is any Christian influence in the synagogue there when God encountered him – “Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me?” (Acts 9:4) Paul • God made Saul “a chosen vessel unto me, to bear my name before the Gentiles, and kings, and the children of Israel” (Acts 9:15) – Came to be known as Paul – Greatest theologian of the early Church – Apostle to the greatest sphere of Christian missionary expansion– to the Gentile world to the west Paul’s Mission Trips Epistles Paul’s Method • The cities in which Paul established churches were politically, culturally, and economically important • They were also located on the main thoroughfares of the Roman Empire, ensuring mobility of the message • Christianity would radiate from these major cities to others and eventually to the countryside Factors Aiding the Spread of Christianity • Paul wrote in Greek – The conquests of Alexander had introduced Greek as the common language from Italy to India (We’ll study Alexander in Lesson 18) • Roman system of good roads and the lack of piracy or serious crime (Pax Romana) – Allowed Paul to travel and preach throughout Asia Minor, Thrace, Greece, and Italy Factors Aiding the Spread of Christianity • Presence of the synagogue – Gave Paul a forum to preach, dispute with the Jews, and attract converts • Roman toleration of religion – Paul and the other missionaries were able to freely debate the cause of Christianity, provided they said nothing subversive to Rome’s political authority Factors Aiding the Spread of Christianity • Degenerate nature of Roman society – Rome’s idle, lascivious aristocracy amused itself with such pursuits as mortal combat for entertainment and created a spiritual void that needed to be filled • Broad Appeal – Open to lower classes, urban populations, and women – Accorded honor and dignity to individuals who did not enjoy high standing in Roman society Result • Less than 300 years after the crucifixion, Christianity became the most dynamic and influential religion in the Mediterranean basin • In 380 A.D., Theodosius proclaimed Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire Institutional Church • In the absence of organized leadership, the earliest Christians had generated a wide range of sometimes conflicting doctrines • To standardize the faith, Christian leaders instituted a hierarchy of church officials – The bishop in Rome and patriarchs in Jerusalem, Antioch, Alexandria, and Constantinople – As Roman imperial authority crumbled, the bishop of Rome (known as the pope) emerged as the spiritual leader of Christians communities in the western part of the empire Evolving Doctrine • In 325 A.D., Constantine called the Council of Nicea which brought together Christian leaders to consider the views of the Arians – Arians taught that Jesus was a mortal man rather than God Himself – Arianism was condemned as heresy • (We talked about this in Lesson 6) Nicean Creed We believe in one God the Father, the Almighty, maker of heaven and earth, of all that is, seen and unseen. We believe in one Lord, Jesus Christ, the only Son of God, eternally begotten of the Father, God from God, Light from Light, true God from true God, begotten, not made, of one Being with the Father; through him all things were made. For us and for our salvation he came down from heaven, was incarnate of the Holy Spirit and the Virgin Mary and became truly human. For our sake he was crucified under Pontius Pilate; he suffered death and was buried. On the third day he rose again in accordance with the Scriptures; he ascended into heaven and is seated at the right hand of the Father. He will come again in glory to judge the living and the dead, and his kingdom will have no end. We believe in the Holy Spirit, the Lord, and the giver of life, who proceeds from the Father and the Son, who with the Father and the Son is worshiped and glorified, who has spoken through the prophets. We believe in the one holy catholic (Christian) and apostolic church. We acknowledge one baptism for the forgiveness of sins. We look for the resurrection of the dead, and the life of the world to come. Amen. Added Philosophical Sophistication • The earliest Christians had come from the ranks of ordinary people • Their doctrine seemed unsophisticated to intellectual elites • Until the 3rd Century Christianity grew as a popular religion of salvation favored by the masses • During the 4th Century, intellectual elites began to give it a reasoned doctrine of intellectual substance St. Augustine of Hippo (354-430) • Well educated and conversant with all the leading intellectual currents of his day • Converted to Christianity in 387 • Worked to reconcile Christianity with Greek and Roman philosophical traditions, especially Platonism • Tried to articulate Christianity in terms that were familiar to educated classes • Wrote Confessions and The City of God Martin Luther • In 1517, Martin Luther distributed his Ninety Five Thesis which was a public challenge to debate the Church practice of selling indulgences – Indulgences were a type of pardon that excused individuals from doing penance for their sins and facilitated entry into heaven – Church officials thought indulgences were great– encouraged believers to reflect piously on their behavior and served as a large source of income Reformation • In 1520, Pope Leo X excommunicated Luther • Though expelled from the Church, Luther still considered himself a Christian and he began to attract followers • The movement spread from Wittenberg, throughout Germany, to Switzerland, and throughout western Europe – The printing press was instrumental in spreading the word • The dissidents became known as “Protestants” because they were protesting against the established order Other Reformers • John Calvin – Converted to Protestantism in the 1530s and left France for Switzerland to escape persecution – Founded a model Protestant community in Geneva which also served as a missionary center – Advanced the doctrine of predestination – Great influence on Presbyterianism Other Reformers • Jacob Hermensen (Latinized Arminius) – Revolts against strict Calvinism in favor of free will – Argues that people must make an active choice to be saved – Profoundly influenced John Wesley and Methodism Next • Group led discussion