American Revolution - Social Circle City Schools
advertisement

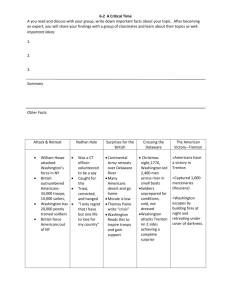
The Colonial Army Strengths: Their cause – fighting for freedom on their own land. Had to transport supplies a short distance Had good military leaders like Washington Familiar with terrain and used guerilla warfare learned from the natives. Defensive strategy = hang on! "There! His Majesty can now read my name without glasses. And he can double the reward on my head!" -- John Hancock British Army Strengths Well trained and disciplined professional army 400% larger army More $$ Best Navy in the world Manufacturing Strategy Colonial Army Outlast Defend and drag war out 2. Guerilla tactics learned from natives 3. Need alliance : France 4. Don’t surrender 1. British Army Divide and Conquer Use loyalists, take land, encourage slave revolts 2. Split the North and South 3. Blockade = no trade 1. George Washington The American Symbol 1. Build an army from militias 2. Build and maintain support 3. Recruit volunteers “Discipline is the soul of an army. It makes small numbers formidable; procures success to the weak, and esteem to all” - George Washington Crossing the Delaware From 1776 -1777, most of the battles ended in British victory In need of victory, Washington decided to attack the Hessian army at Trenton, New Jersey Christmas night. – If a victory was not met it was very possible the revolution would end that year in failure. Contracts from the soldiers were almost up and moral was down. It was stormy and cold that night, but he and 2,400 men successfully crossed the icy Delaware river. At 8am the next morning, Washington and his men led a surprise attack securing victory at the Battle of Trenton! 1777 - The Year of the Hangman The British started the year by mounting a major effort to end the rebellion. Their strategy was to bring troops from Canada to join forces with General Howe in New York. From there, this British army, commanded by John Burgoyne, would isolate the important region of New England from the rest of the colonies. 5,000 British and 3,000 German Mercenaries assembled in Canada during the winter of 1776 -1777. They became ravaged by disease and couldn’t even bury their own men in the frozen ground. Burgoyne led his men towards New York at a slow pace (2-3 miles a day at times) because Colonials cut down trees in their path and attacked them along the way. By October 1777, Burgoyne’s army was down to less than 6,000 men. Part of Burgoyne’s plan would failed when General Howe failed to meet him in New York. He was preoccupied conquering Philadelphia. Gaining France’s Aid Gaining the aid of France was essential for the US in their war for independence – Finances, navy, weapons … With the help of two men and the need for revenge, France would eventually join the war. Benjamin Franklin gains the help of France In 1776 Benjamin Franklin went to France as America’s first ambassador. – His goal was to gain their aid in the war against England Franklin was very popular in France. He learned their language quickly, dressed modestly, and was very adept at politics and persuasion. Marquis de Lafayette A French aristocrat. He left France against the king’s orders to help the Americans. Inspired by America’s cause, he volunteered to help the army without pay. He became a great, respected commander in the field. Served with Washington and became friends. Help persuaded French government to send aid and eventually troops to America. Battle of Saratoga As Burgoyne is moving south from Canada towards New York they became intercepted by the Colonial Army commanded by Gates. Colonial Army – 12,000 men Surrounding them at the battle of Saratoga Burgoyne surrendered to Gates on October 17, 1777 The battle of Saratoga was important turning point in the war. By winning the battle it helped convince the French to join our side as an ally. The French were eager to strike back at their longtime enemy, the British. The French Join the War Before officially entering the war, the French secretly gave weapons to the Americans. After the victory at Saratoga, the French decided to officially enter the war on the side of the Colonials. They signed a commercial treaty and military alliance with the U.S. on Feb 6, 1778. Both sides agreed to not end military action until Britain officially recognized America’s independence. France’s goal was to get revenge on the British for the Seven Years War and weaken them. The French provided naval support to the Colonists. This navy not only engaged British ships but also helped protect American trade abroad. French entry in the war emboldened other countries to challenge Britain for trade rights in America. Russia, Denmark, Sweden, Austria, Portugal, Prussia, and Sicily joined the League of Armed Neutrality to protect their trade rights in America. Many historians believe that America’s independence would not have been possible without the help of France. Winter at Valley Forge While Burgoyne was making his way towards New York, British general William Howe moved his army towards Philadelphia to destroy Washington’s army. (Remember Howe is supposed to meet Burgoyne in New York) Washington’s army met the British, fought hard but lost and retreated with 1,200 soldiers killed or injured. In comparison, the British lost about 600 men. The British Conquered Philadelphia and settled in comfortable winter quarters. Congress fled to York, Pennsylvania and the Continental Army established winter quarters outside Philadelphia at Valley forge. That winter was particularly cold. 2,500 of Washington’s men died from cold, disease, or starvation. Another 2,000 deserted. Many of the men didn’t have shoes and left bloody footprints as they marched through the snow. The army seemed as though it was on the brink of total collapse. "If the army does not get help soon, in all likelihood it will disband." – General George Washington General Charles Cornwallis British General, second in command. Won many victories in the South In 1780 he invaded North Carolina and attempted to control the south. In 1781, he marched North to seek a decisive battle in Virginia and to cut off supplies going to the Carolinas. Lack of loyalist support made it difficult for him to conquer Virginia. General Clinton ordered Cornwallis to take a fort at Yorktown. Cornwallis followed orders and waited there for reinforcements. Battle of Yorktown This was the last major battle of the war. The battle was fought from September 28 - October 19, 1781 The situation The British Cornwallis and his army of 8,000 men waited at Yorktown, building defensive positions. Waiting for reinforcements. Had to secure access to the sea for supplies and possible escape. The French and Americans: The French landed an army of 7,800 men. A large French fleet had also arrived. Seeing an opportunity to take advantage of the British situation at Yorktown, the allies (France and America) devised a plan. Washington faked preparations to attack British controlled New York. Meanwhile, he secretly sent an army to Yorktown. The French Navy moves in and defeats the British navy thus cutting off Cornwallis from the sea. Washington’s Army of 8,800 Americans met with Marquis de Lafayette’s army of 7,800 French. Cornwallis’ army of 8,000 men were cut off and surrounded. Cornwallis had nowhere to go and the British army in New York could not reinforce him fast enough. Outnumbered, outgunned, and surrounded… Cornwallis eventually surrendered on October 19, 1781. “Oh god, It’s all over.” – Lord North, British prime minister Treaty of Paris 1783 The surrender at Yorktown marked the end of major fighting but skirmishes continued for another year. King George III wanted to continue the war but most of parliament felt that enough men and money had been invested in keeping America in the empire. King George III The Peace negotiations took place in Paris. Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, and John Jay represented on behalf of America. The peace treaty was singed by all parties on September 3, 1783. In the deal, the negotiators got most of everything they hoped for, except for Canada. Britain also restricted American access to the Gulf of Mexico, a source of diplomatic friction for years. John Jay hoped to end the slave trade in the treaty but nothing was said about it. New boundaries created by the Treaty of Paris. Keep in mind… nobody consulted the many Indian tribes about these boundaries.