LAW 737 ISLAMIC BANKING AND TRANSACTIONS
advertisement

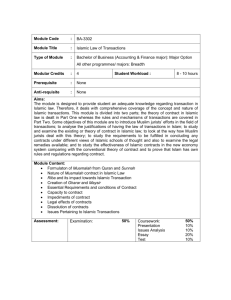
LAW 737 ISLAMIC LAW OF TRANSACTIONS QUESTION 9: GHARAR - THE DIFFERENT VIEW OF JURISTS PRESENT BY: MUNA FARHANA BT. HALIM NORHANISAH BT. JOHAR NUR LIYANA BT. MOHD. ANUAR INTRODUCTION “The prophet prohibited the pebble sale and the gharar sale” Abu Hurayra What is Gharar? • Gharar has many definitions which can be summarised under 4 headings:- Hanafi and Shafi’e - Zahiri - Most Jurists (Jumhur) - Al-Sarakhsi • Hanafi and Shafi’e - Gharar means doubtfulness or uncertainty. - Ibn Abidin defines Gharar as ‘uncertainty over the existence of the subject matter of sale’. • Zahiri - Gharar means ignorance. - Ibn Hazm defines ‘Gharar in sale occurs when the purchaser does not know what he has bought and the seller does not know what he has sold” • Most Jurists (Major) - means combination of both ignorance and uncertainty. - accepted by the majority (Jumhur). • Al-Sarakhsi - defines ‘Gharar in contract or transaction occur when the consequences are concealed or unknown’ to the contracting parties. • Gharar occurred when:1) The consequences are totally concealed. 2) The probability of existence is equal to the probability of non-existence. 3) The non-existence of the subject matter outweighs its existence Prohibition of Gharar • Reliable sources have reported through a number of the Prophet’s companions that the Prophet (S.A.W) has forbidden Gharar in trading. • The Hadith is considered as one of the cardinal principles of sale's law and the groundnorm of all rules governing Gharar contract. • Muslim Jurists agree that excessive Gharar is prohibited as it impairs the validity of the contract. Types of Gharar • Gharar is divided into two namely: (i) Gharar saghir - minor or slight gharar. (ii) Gharar kabir -major or excessive gharar. •The gharar that causes a contract to be invalid is major gharar. • In general terms major or excessive gharar is: - an uncertainty which is so great that it becomes unacceptable, or - it is so vague that there is no means of quantifying it. • More specifically excessive gharar arises out of one of the following: - Asset or merchandise does not exist. - Asset or merchandise cannot be delivered. - Asset or merchandise is not according to specifications. Prohibition of Gharar • The examples agreed upon excessive Gharar: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. The “Pebble” “touch” and “toss” sale. Selling the unborn animal without its mother. Selling the fetuses and embryos. Selling fruit before its emergence. Selling the find of the diver in advance. Selling the unborn animal (Habal-al-Habalah). Selling the object of unknown identity without the buyer having the right to specify it. Selling an object of unknown genus. Deferment of the price to an unknown future date. GHARAR AND THE INVALIDITY OF A CONTRACT • Gharar in a contract can refer to: (i) uncertainty towards the existence of the subject matter. (ii) uncertainty towards the possession/ ownership of the subject matter. (iii) uncertainty towards the price. (iv) uncertainty towards the payment of the price. (v) ignorance (jahalah). THE VIEW OF ISLAMIC JURISTS: PAST AND PRESENT VIEW OF PAST ISLAMIC JURISTS • HANAFI SCHOOL - AI-Sarakhsi - Gharar as something with unknown consequences. - AI-Kasani - Gharar that refers to suspicion. Gharar is the potential risk faced by a person, with a 50% possibility that the goods mayor may not eventually exist (syak). To AI-Khasani, gharar is the suspicion that a good may not exist. • For the Hanafi mazhab, such a trade is lawful because the buyer is given the right to make a choice after he has viewed the goods. This view is based on the Prophet s.a.w. hadith: من اشترى شيئا لم يره فهو بالخيار إذا رآه Meaning: "Whosoever buys something that has not been viewed, he has khiyar (choice to buy or reject) after viewing it". • SYAFIE SCHOOL - Gharar as khatar (of high risks). AI-Shirazi - Gharar as something whose condition and consequence are unknown. AI-Ramli - Gharar is something that has two assumptions, positive and negative, with the negative being bigger. AI-Sharqawi and AI-Qalyubi Gharar as something whose consequence is unknown and has two assumptions, positive and negative, the negative outweighing the positive. • ZAHIRI SCHOOL • Gharar also means ignorance and this can be when the subject matter of sale is unknown. This view is adopted by the Zahiri School alone. - Ibn Hazm ‘Gharar in sale occurs when the purchaser does not know what he has bought and the seller does not know what he has sold.’ VIEW OF PRESENT ISLAMIC JURISTS • MUSTAFA AL-ZARQA' : - Gharar is a fraud through words or deeds to attract someone to perform aq’d. - Divided Gharar into 2 forms:i) Gharar Qauli ii) Gharar Fi'li VIEW OF PRESENT ISLAMIC JURISTS - Gharar qauli a fraud committed verbally by a seller relating to price and method. For example, a seller says to a buyer: "The same product can be found elsewhere but we offer the lowest price." These words attract a buyer to perform 'aqd with the seller. VIEW OF PRESENT ISLAMIC JURISTS - Gharar fi’li a fraud committed by a seller relating to the features of the product, by his action. For example, a shepherd who wants to make his goat saleable by displaying a l arge pouch of milk. This would attract the buyer to assume the goat produces a lot of milk when it does not. VIEW OF PRESENT ISLAMIC JURISTS • MUHAMMAD BELTAJI - It is impossible for the buyer and seller to avoid gharar completely. - 3 requirements in declaring something as gharar that can be excused: i. The gharar is minor and small. ii. Such trading is needed by society. iii. The gharar cannot be avoided without masyaqqah(hardship) that is recognised by Syara'. THE EXTENT OF PERMISSIBLE GHARAR • Gharar is prohibited by the law but to certain extent,it is permissible. • Some of the examples to show that it is permissible under minor gharar such as:– – – – – – Salam Ijara Jua’la Shirka Mudaraba Bay al-Istisna Permissible Gharar • Salam - a sale contract where delivery is delayed until a prefixed future time. - “Believers! When you contract a debt for a fixed period put it in writing“ (Al-Baqarah:282) - prefixing the future date of delivery will render the contract to be valid. Permissible Gharar • Ijara - a contract of hire or lease for a service or for a use of certain moveable and immoveable property for a consideration. - "... one of the girls said: father! take this man into your service (ista 'jir-hu), men who are strong and honest are the best that one can hire (khayra man ista'jar-ta)“. (Al-Qasas : 26) Permissible Gharar • Ju 'ala - a contract for a reward made to the world at large for returning of a lost property. - This contract is risky and uncertainty because the reward is not paid to the offeree until the work is completed, the nature of the work is not certain and precise and no condition of pre-payment is permitted. - “they said: we have lost the king’s cup, and he who brings it shall have a camel-load...” (Surah Al-Yusuf:72 ) Permissible Gharar • Shirka - A contract of partnership to engage in trading or enterprise in the view of sharing the profit secured from the trading or enterprise. - Because of the amount of profit and the nature of presentation and surety ship are not precisely known causing the contract containing the element of gharar. - "they (the heirs) are the sharers (shuraka') of one third“. (Al-Imran:24) Permissible Gharar • Mudaraba - the capital is the combination between cash and effort. - the contract is void because the work done by the entrepreneur is not precise and the profit is not guaranteed and unknown. - In order to make this contract effective the capital and the distribution of profit must be made certain. Permissible Gharar • Bay' al-istisna' - a contract to manufacture, where a customer will place an order to an artisan to make a specific kind of article like shoes, furniture, and the like for a price paid in full or none at the inception of the contract. - contract of a nonexistent – void - This contract was allowed because the people are in the extreme need of it. CONCLUSION Ibn Juza’in stated that:- gharar is prohibited by the hadith and sunnah. - it must be avoided as it render the gharar in contract as null and void. - unless gharar is very minor gharar, it is tolarable. CONCLUSION • Form of gharar or uncertainty prohibited in the Islamic is a vindication of the viability and infallibility of the Islamic injunctions that are derived from the Holy Qur’an and the Tradition of the Prophet. • But to the certain extent, it is permissible under the Islamic law as if it is a minor gharar. “This is a kind of reminder that Man needs the guidance of his creator as he fulfils his role as a vicegerent of God on earth and without this guidance he is always subject to being lead a stray by his whims and desires or the limitation of his mind and experiences as attested to by the many failures of our time in all spheres of life”. Thank you.