Fungal infections
advertisement

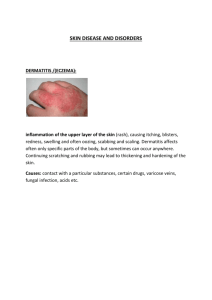
Fungal infections Cutaneous: dermatophytes, pityriasis versicolor, candidiasis. Subcutaneous: mycetoma Systemic: histoplasmosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis Dermatophytes=ringworm=tinea • 3 genera: trichophton, microsporum, epidermophyton. • All give similar clinical picture. • Invade keratin only. • Zoophilic and anthropophilic. • Clinical features depend on the site Tinea pedis * predisposing factors: swimming pools, occlusive footwear. * Clinically: interdigital scaling or Diffuse scaling of sole or Recurrent vesicles of the sole Tinea unguium • Toe nail more common than finger nail • Free edge becomes yellow or whitish, the infection then spread proximally with darkening of the nail plat and thickening of the nail plate and subungual hyperkeratosis Tinea corporis • Erythematous scaly plaque, grow peripherally and clear centrally annular configuration • =active border • Close inspection ----- vesicles and pustules Tinea cruris • Affects inguinal fold • Erythematous plaque, scale, active border, not affects scrotum. close inspection -----vesicles and pustules • Differential diagnosis: *Flexural psoriasis: look for other sites of predilection of psoriasis *candidiasis: satellite papules, pustules *seborrheic dermatitis: look for other sites of predilection of psoriasis Tinea faciei • Erythematous annular plaque- face • Diff. diag.: * seborrheic derm.: nasolabial, eyebrows, eyelashes, ears * Rosacea: bilateral erythema, telangiectasia Tinea capitis • Patch of hair loss, scales, easily epilated hair. • Usually children • Zoophilic spp.: Intense inflamm., boggy swelling, pustules = kerion • Diff. diag.: alopecia areata: no inflamm. trichotillomania: psych. upset, broken hair Investigations • Skin scraping, nail clipping, hair plucking + KOH • Culture on sabouraud’s dextrose agar • wood’s light ----- green fluorescence in some cases of T. capitis Treatment • Topical imidazoles ex. Clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole ----- Few patches of T corporis, facei, cruris and pedis. • Systemic therapy ex. Griseofulvin, terbinafine, imidazoles ex. Fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole ------Tinea capitis, T. unguium, T.incognito, wide spread T. corporis, pedis and feciei Candidiasis • Opportunistic inf. • Predisposing: age extremes, D.M, low immunity, ill fitted denture, obesity, antibiotics, pregnancy, and malignancy. • Oral thrush: whitish patches, its removal reveal erythematous base • Angular stomatitis: whitish patches, soreness • Intertrigo: (inguinal, axilla, under the breasts) erythematous patches, satellite papules and pustules • Erosio interdigitale: eroded patch affects the webs Investigations • Swab or scrapping for microscope exam yeasts • Culture Treatment ● Correction of underlying pred. factor ● Topical azoles ● Nystatin or amphotericin ● Fluconazole, itraconazole Pityriasis versicolor • Affects young adults, hot humid climate • Pityrosporum orbiculare, Keratinophilic and lipophilic. • Brownish or hypopigmented round patches, with fine scales • Upper trunk, upper arms, neck. • Tend to recur. Investigations • Usually it is a clinical diagnosis • Scrapping. • Wood’s light ----- lemon yellow Treatment • Topical: azoles: *ketoconazole shampoo * other azole creams selenium sulphide shampoo ● Systemic : fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole