City States of Mesopotamia
advertisement

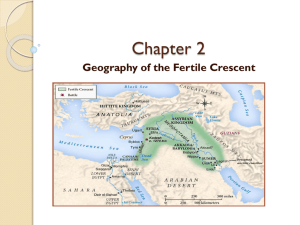
City States of Mesopotamia I. Geography a. “Fertile Crescent” => b. Tigris & Euphrates Rivers i. Flows SE into Persian Gulf ii. Mesopotamia = “_________________________________________” iii. Annual flooding of rivers left __________ => II. Humans’ arrival a. Why settle here? i. River valley had . . . ii. Access to major body of water => iii. Allowed for easy irrigation … b. Challenges to settlers i. Annual flooding was unpredictable ii. No natural __________________ iii. Limited natural resources => c. Solutions i. Irrigation projects ii. Built ____________ around cities iii. ___________ for goods III. City states of Mesopotamia a. City States => i. Culturally _____________________ ii. Politically _____________________ iii. Economically _____________________ iv. Militarily _____________________ b. City states named . . . c. Political power i. Irrigation projects needed . . . ii. Beginning of ________________________ iii. Religious basis of political power 1. City state’s gods own all land 2. King served as ______________________ of gods 3. “Priest-Kings” 4. In times of war, _______________ chosen to lead army iv. After 3000 BC, as war became more common . . . 1. Why fight? => 2. Dynasties = series of … d. Cultural Diffusion i. Idea or product spreading . . . ii. Spread by __________________ iii. What ideas? => IV. Case Study: Sumerian Culture a. Religion i. Polytheistic => 1. About _____________ in all 2. Gods immortal, all powerful 3. Many had . . . ii. Built ziggurats => b. After life => c. Science and technology i. Inventions 1. Wheel => 2. Sail => 3. Plow => 4. Metallurgy a. Pre 3000 BC => b. Post 3000 BC => 5. Sun dried bricks => 6. Cuneiform a. First . . . b. Wedge shaped reed pressed into . . . c. Needed record keeping system => 7. Number system was base __________ => d. Sumerian Life i. Social classes 1. Priest-Kings 2. Wealthy __________________ 3. Farmers, artisans => 4. Slaves ii. Women had many rights, but . . .