November 11, 2013
advertisement

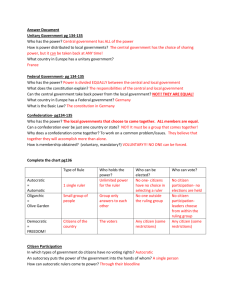
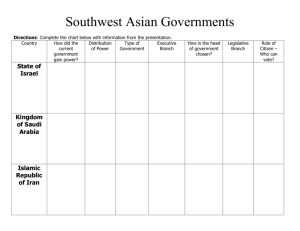
Warm Up- November 11, 2013 (Select one ) 1. In which form of government are the citizens most likely to directly participate? A. theocracy B. oligarchy C. democracy D. monarchy 2. In which form of government is power controlled by a select few individuals, rather than the citizens? A B C D Autocracy Oligarchy Monarchy Democracy Standards SS7CG5 The student will explain the structures of the national governments of Southwest Asia (Middle East). a. Compare the parliamentary democracy of the State of Israel, the monarchy of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and the theocracy of the Islamic Republic of Iran, distinguishing the form of leadership and the role of the citizen in terms of voting rights and personal freedoms. Essential Question How are the governments of the Middle East structured? Music Mix You will be given 3 minutes to write down as many facts or ideas about: citizen participation and distribution of power. When the music starts, the students will mingle until the music stops. When the music stops you will partner with the person closest to you and share their thoughts. When the music starts back up, the students will mingle one more time. When the music stops, you will partner with the person closest to you. This should be a different person than the last time. COUNTRY TYPE OF GOVERNMENT STATE OF ISRAEL PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRACY FORM OF LEADERSHIP PRIME MINISTER (head of state) How does the prime minister become the leader? Prime Minister is selected (chosen) by the legislative branch, which in Israel is the Knesset (kind of like our Congress in the U.S.) Citizens vote for members of the Knesset, but cannot vote for the Prime Minister. This is a big difference compared to a presidential democracy. KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN VOTING RIGHTS PERSONAL FREEDOMS PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRATIC Universal (men and women) voting age 18 years and up Law provides for right to vote, freedom of speech (except if it risks national security), freedom of religion, right to privacy, right to fair trial etc. However, many instances exist of prejudice against its Arab citizens. COUNTRY TYPE OF GOVERNMENT STATE OF ISRAEL PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRACY FORM OF LEADERSHIP PRIME MINISTER (head of state) How does the prime minister become the leader? Prime Minister is selected (chosen) by the legislative branch, which in Israel is the Knesset (kind of like our Congress in the U.S.) Citizens vote for members of the Knesset, but cannot vote for the Prime Minister. This is a big difference compared to a presidential democracy. KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN MONARCHY Example of a Unitary distribution of power MONARCH (King) How does the monarch (king) become the leader? A monarch (king) is the hereditary ruler, usually the first born son of the king (birthright), no election. In Muslim monarchies a female cannot become queen like in other countries. The king and his relatives are known as royal families and usually control the wealth of a country. VOTING RIGHTS PERSONAL FREEDOMS PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRATIC Universal (men and women) voting age 18 years and up Law provides for right to vote, freedom of speech (except if it risks national security), freedom of religion, right to privacy, right to fair trial etc. However, many instances exist of prejudice against its Arab citizens. AUTOCRATIC Only men 21 and over can vote when the government allows. Human rights in Saudi Arabia are based on Sharia. Many political freedoms do not exist. Capital punishment given without due process. Religious and political minorities as well as women do not have many rights. STATE OF ISRAEL PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRACY PRIME MINISTER (head of state) How does the prime minister become the leader? Prime Minister is selected (chosen) by the legislative branch, which in Israel is the Knesset (kind of like our Congress in the U.S.) Citizens vote for members of the Knesset, but cannot vote for the Prime Minister. This is a big difference compared to a presidential democracy. KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA MONARCHY Example of a Unitary distribution of power MONARCH (King) ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN THEOCRACY PRESIDENT (political leader) How does the president become the political leader? A president is elected by the citizens by a popular vote and becomes leader of the executive branch that enforces the laws of a country. AYATOLLAH (religious leader) How did the ayatollah become the religious leader? They are appointed (selected) by religious leaders (Assembly of Experts) in the country and serve this role for life. Their influence on the elected president is very powerful. This is why Iran is a theocracy and the laws of the Quran are followed. How does the monarch (king) become the leader? A monarch (king) is the hereditary ruler, usually the first born son of the king (birthright), no election. In Muslim monarchies a female cannot become queen like in other countries. The king and his relatives are known as royal families and usually control the wealth of a country. PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRATIC Universal (men and women) voting age 18 years and up Law provides for right to vote, freedom of speech (except if it risks national security), freedom of religion, right to privacy, right to fair trial etc. However, many instances exist of prejudice against its Arab citizens. AUTOCRATIC Only men 21 and over can vote when the government allows. Human rights in Saudi Arabia are based on Sharia. Many political freedoms do not exist. Capital punishment given without due process. Religious and political minorities as well as women do not have many rights. PRESIDENTIAL DEMOCRATIC THEOCRACY Universal voting age 16 and up The new government continues to close down newspapers, silence opposing voices and ban or censor books and websites. The peaceful demonstrations and protests of the previous era are no longer tolerated. Closing Reflective Statements I learned… I wonder… I appreciate… I now truly understand… (Please be prepared to share your response) Homework You should work on your Government Study Guide tonight it is due Wednesday! We also will have our unit test Wednesday!
![Why American government does not work very well [2 views]: corrupt,](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015633764_1-7ce0214c78c757020f95d8959ab10647-300x300.png)