Civilization & Mesopotamia
advertisement

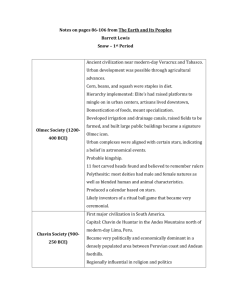
1. Advanced Cities ◦ Large group living together ◦ Trading center 2. Specialized Workers ◦ Develop skills in a specific kind of work (trader or priest) ◦ Why? Abundant food Complex Institutions 3. ◦ Long-lasting pattern of organization in a community ◦ Examples: Religion Government Economy 4. Record Keeping ◦ System of writing ◦ Taxes, laws, religious rituals ◦ Scribes – professional keepers 5. Advanced Technology ◦ Anything that makes life easier Complex Institutions: formal governments (laws and officials), priests w/ religious power Specialized Workers: soldiers, merchants, teachers, priests, etc. Advanced cities: Uruk – 50,000 Lagash – 10,000 -50,000 Sumer Record Keeping: Cuneiform writing system Advanced Technology: 3000 BCE wheel, plow, sailboat; bronze weapons and armor Tigris Rivers & Euphrates Annual flooding ◦ Silt – rich layer of soil deposited by a river (good for growing crops) ◦ Alluvial Plain – flat landform created by deposit of silt from rivers coming from highlands Unpredictable flooding & little rain irrigation ditches No natural barriers for protection built city walls Limited natural resources traded grain & cloth for stone & wood City-state: city & surrounding area functioning as a country does today Priests head government 3,000 BCE Kings head government 2,500 BCE ◦ Create Dynasties - series of rulers under one family Ziggurat – walled temple Akkadian – Sargon of Akkad (2350 - 2150 BCE) defeated city-states of Sumer 1st empire: brings together several independent peoples, nations, or states Babylonian – Babylon (2000 - 539 BCE) Hammurabi’s Code ◦ Hammurabi (Babylonian King) ◦ 1792-1750 BCE ◦ Unified code of laws ◦ Oldest known legal system ◦ Stressed justice & punishment based on social class Polytheism: belief in Human-like, but immortal & powerful Humans were servants two or more gods (kings representatives of gods) Built ziggurats & offered sacrifices to please gods Sumerian Social Hierarchy Kings, Priests, Landholders Merchants Farmers Slaves Arithmetic, Geometry ◦ Helped in building projects Architecture Cuneiform ◦ Arches, columns, ramps, pyramid shape ◦ Writing system ◦ Pictograph – symbols stand for words