File - introduction to language
advertisement

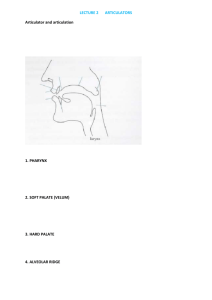
CHAPTER 3 (Yule, 2010, pp. 25-39) THE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE Speech organs 1 PHONETICS speech sounds / phonemes (distinctive sounds) (44 phonemes in English) 1. Articulatory Phonetics (production) 2. Auditory Phonetics (perception) 3. Acoustic Phonetics (sound waves) In this course: Articulatory Phonetics (introductory) 2 Respiratory System & Speech air in breathing is basic ingredient of speech air is modified to create different sounds sounds are produced when we breath out modification by vocal organs 3 VOCAL ORGANS organs of the body involved in the production of speech Some examples: Tongue Palate Vocal cords Lungs Other functions: breathing / eating 4 Vocal Organs Vocal tract Larynx Sub-glottal system 5 SUB-GLOTTAL SYSTEM a) Lungs b) Trachea /trəˈkiː.ə/ / (windpipe) 6 LARYNX /ˈlær.ɪŋks/ (voice box) (on top of the trachea) 1) Vocal Cords/Folds (two elastic bands of muscle in the throat) 2) Glottis (the gap between the vocal cords) 7 Glottal States Vocal Folds/Cords Wall of the Larynx Open vocal cords (air passes through freely) e.g. /s/ 8 Approximated vocal cords (vibration: open and close rapidly and repeatedly– around 100 times per second in men, 200 times in women and children for a given sound / up to 800 times per second) e.g. /z/ Test: put your fingers on your throat/ears and say /s/ and /z/, alternating them. 9 VOCAL TRACT 1) Pharynx /ˈfær.ɪŋks/ (the passage above the vocal cords) 2) Oral cavity (space in the mouth) 3) Nasal cavity (space behind the nose) 10 ARTICULATORS (parts of the oral cavity) 11 Upper articulators (upper surface of the oral cavity) 1) Palate (the roof of the mouth) (separates oral and nasal cavities) 2) Upper teeth 3) Upper lip 12 Lower articulators (lower surface) (they are moved toward the upper surface which is not mobile) 1) Tongue 2) Lower teeth 3) Lower lip 13 THE PALATE alveolar ridge hard palate soft palate 14 Alveolar Ridge (behind the upper front teeth) hard rough fixed 15 Hard Palate (highest part of the palate) (between the alveolar ridge and the soft palate) hard even fixed 16 Soft Palate (velum) (at the back of the mouth) soft movable Uvula the end point of the soft palate 17 States Of The Velum (Soft Palate) Lowered position: gap between soft palate and pharynx; air goes into the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. (e.g. /m/) 18 Raised position: contact with the back wall of pharynx; nasal cavity is closed; air goes into the mouth only. (e.g. /b/ ) 19 THE TONGUE 20 Back Lies under the soft palate/raised to touch the soft palate and to any point beneath that 21 Front Lies under the hard palate/raised to touch the hard palate and to any point beneath that 22 Blade (between the tip and the front) lies under the alveolar ridge very mobile (can touch the lips, teeth, alveolar ridge and the hard palate) 23 Tip (the most forward part) lies under the alveolar ridge very mobile 24 Sides Raised (curved upwards/pressed firmly against the sides of the palate/air goes through the centre) e.g. /s/ Lowered (centre is raised/air goes trough the sides) e.g. /l/ 25 THE LIPS Positions of the lips (extreme positions are rare in English) Closed/Apart /p/ /t/ /m/ /g/ Rounding/Spreading /w/ /v/ Protrusion (pushed forward/almost none in English) 26 THE TEETH /f/ /v/ (upper teeth) / ð // θ/ (upper and lower teeth) 27 THANK YOU! 28