PBS Final Exam Review 4th Period Answers
advertisement

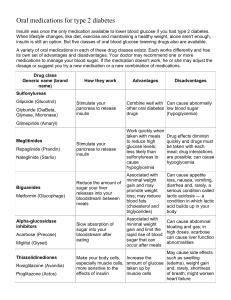
PBS Final Exam Review 4th Period (Any missing activities is your responsibility to study on your own.) Activity 1.1.1 a Mysterious Death Review Guide Information for Anna Garcia Case: It was a hot, 92°F summer morning. The emergency call came in at 9:45 am. A man contacted the police to report that he was worried about his next door neighbor, a woman named Anna Garcia. He informed the police that he had spoken to Anna the previous morning when he saw her walking her dog around 6:30 am. He noted that she was wearing a sweater even though they were currently experiencing a heat wave. He decided to call the police this morning because Anna’s dog had been barking excitedly for the last two hours (which is extremely unusual in this normally quiet suburban neighborhood). He tried to call Anna on the telephone, but no one answered. Next he tried ringing her doorbell, but there was no answer. Both the police and the EMT arrived at the scene at 9:56 am. The front door had to be broken down. Upon entering the house, they found Anna lying face down in the entry hallway. It was a comfortable 73˚F inside the house. The EMT determined that Anna was dead. Processing a Crime Scene and Concept Maps: The five basic tasks to process a crime scene include interview, examine, photograph, sketch, and collect the evidence. To create a concept map for this you need to do the following: 1) open the Inspiration software, 2) click the diagram icon, 3) type in the title, 4) insert an oval with one of the five tasks typed inside it, 5) insert arrows going from the main idea to each task, 6) insert ovals around the task ones to expand on the topic until you have said everything. Questions 1. How many tasks must you do to fully process a crime scene? a. 4 b. 7 c. 10 d. 5 2. Which of the following are parts of the basic five tasks to process a crime scene? Task 1 Photograph Sketch Task 2 Take measurements Task 3 Interview Task 4 a. b. c. d. 1 1,2,4 1,3,4 2,3 3. How did Anna Garcia’s neighbor describe the morning she was found dead? a. Unusual b. Normal c. Quiet d. Peaceful 4. Both Anna Garcia’s behavior was unusual because: a. She was wearing a sweater in the middle of a heat wave b. She let her dog continue be nosy in her usually quiet neighborhood c. She did not answer the phone or answer the door d. All of the above 5. What software do you use to make the concept map? a. Imagination b. Inspiration c. Innovation d. Illumination *MiSSING 1.1.2 GUIDE and Questions 1.1.3 Careers in the Biomedical Sciences 911 OPERATOR ● ● ● ● CPR certified high school degree answering emergency calls and sending response teams undergo an extensive training program of 3 to 6 months The 911 operator relates to Anna’s case because the person who was suspicious of something might have happened dialed 911, and the 911 telephone operator answers EMT ● ● ● ● ● ● ● high school degree and some college courses before training training requires 120 hours minimum, or 6 months CPR certified must pass a state certification test (SCT) must study anatomy,physiology,and advanced life support giving first aid, working in ambulances training occurs in the classroom,ambulances,hospitals,and fire departments When in an emergency or hurt or endangered peoples the 911 operator would send a dispatch team of EMT’s in an ambulance along with the police to help any wounded people. CRIME SCENE INVESTIGATOR ● ● ● ● ● ● ● must hold a basic law degree in criminology must have twenty-twenty vision must be citizen of the country can not have a criminal record that is less than 10 years old (includes DWIs) must hold a bachelors degree in forensic medicine and science daily activities include collecting and examining evidence found in a crime scene work with evidence boards When it was discovered Anna Garcia was dead and the cause was unknown the case was handed over to the CSI agents who would look for evidence and take crime scene pictures to try and help solve the mysterious death of Anna Garcia. Questions 1. A. B. C. D. What are the minimum hours of training required for an EMT? 150 100 120 60 2. A. B. C. D. A Crime Scene Investigator must be all EXCEPT which of the following? a citizen of the country have twenty-twenty vision over the age of 25 cannot have a criminal record that is less than 10 years old 3. A. B. C. D. Why did the 911 operator relate to the case of Anna Garcia? Anna called 911 Someone found her body in a dumpster and called 911 A 911 operator found Anna’s body The concerned neighbor called 911 and the operator answered 4. A. B. C. D. When becoming an EMT you must pass a test called the SCT, what does SCT stand for? State Certification Test Systems & Computer Technology Standard Completion Test System Certification Test 5. A. B. C. D. What two degrees are required to become a Crime Scene Investigator? law degree in criminology and forensic medicine and sciences forensic medicine and sciences and physiology psychology and criminology none of the above Activity 1.1.4 “The Evidence” Review Guide Blood, DNA, Fingerprints, and shoeprints helps Forensic Investigators determine suspects. Every person has some differences that the Forensic see and use to find out who committed the crime. In this section, we studied and analyzed evidence in different stations such as fingerprints, identifying an unknown substance, examined the shoeprints and hair, and ran blood tests. Part II: Identifying Unknown substance Forensic Chemists use two types of test, Presumptive and Confirmatory. Presumptive (calorimetric tests) indicate which type of substance is shown, but can’t specifically identify it. Confirmatory tests (gas chromatography)/mass spectrometry are tests that can identify the substance. Station 1/ Blood: There are 4 blood types; a blood type A, B, AB, and O. Each person has one of these types. Differences between the blood types are from the presence/absence of antigens (protein molecules). Antigens are located on the surface of red blood cells and anti-bodies in the plasma (liquid blood portion). Note: People can have the same blood type. Station 2 /Hair: Hair at microscopic level can provide info. on the owner’s race, gender, and possible age. The structure of the hair consists of Keratin, the Cuticle, Medulla, and cortex. The Keratin is a protein that is also in nails and skin. The Cuticle is the outer layer of hair that consists of flattened/ scale-like cells that overlap each other. Medulla is the inner layer that is continuous/discontinuous fragmentary, or even absent. The Intermediate Layer is the home to pigment containing granules (affects hair color). Station 3/ Fingerprints: Fingerprints are the tiny raised spiral and concentric patterns called ridges found on the tip of each finger. Fingerprints consist of different patterns and styles. Arches- slope upward and then downward, there are two kinds tented and plain. Plain- slope slightly up, cascades back down on one side of finger Tented- similar to plain, but the ridges of the center merge upward in appearance of a tent. Loops- Begins on one side of finger, curves upward/around, and exits other side Radial- slope toward thumb Ulnar- slope toward little finger Whorl- forms circular/spiral patterns Minutiae- tiny fingerprint details, there are 12 minutiae Station 4/ Shoeprints: Soles of shoeprints may contain different patterns/ shapes, but may have the same brand. Still, the differences can be spotted, because of the way it is made. The appearance of the shoe may fade depending on the weight & walk. The size can be determined by a shoe. Study Questions 1) Based on what you know about hair, briefly (in 3 sentences least) yet informally describe each of the hair layers. The Cuticle is the outermost layer of hair that consists of flattened/ scale-like cells that overlap each other. Medulla is the innermost layer that is continuous/discontinuous fragmentary, or even absent. The Intermediate Layer is the home to pigment containing granules (affects hair color). 2) On an early Saturday Morning, Stacy went out for a walk. She stopped and notices there were a pair of muddy shoeprints that were the same shape and style, but one was able to be seen clearly, and the other was a little faded. What factor(s) caused the same details to be seen differently? a. b. c. d. Weight and walk Speed and Stance Balance and Position Strength and Walk 3) Based on what you’ve learned from fingerprints, which of the following is a Tented Arched Fingerprint. A. B. C. D. 4) Identify the location of the medulla in the following picture. Part 4 Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 a. b. c. d. Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 5) Valerie ran a test to examine the substance she picked up from the library, the test did not specifically identify the substance, but shown what type it is. What kind of test did she run? a. b. c. d. Confirmatory Presumptive Verification Assumption Activity 1.1.5 Review Experimental Design Glaister’ Equation Identify the Problem Predict a solution Design Experiment to test hypothesis Do experiment Analyze data and observations State Conclusion *98.4 - Rectal Temperature/1.5= estimated hours since death Ambient Temperature The outside temperature surrounding an object *Many factors influence the rate of heat loss including clothing, victim size, and environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. The body core temperature can be measured rectally or with a hypodermic probe of the liver or brain, because of their large mass and density Rigor Mortis Lividity Algor Mortis Stiffening of muscles after death cooling of blood after death cooling of body after death Questions: 1. A student wants to find out if coffee has an effect on a person’s behavior. Design an experiment using the proper “Experimental Design.” (Ans. Problem: the effect of coffee on a person’s behavior, Hypothesis: If a person drinks 1 cup of coffee, then he will be hyper, Experiment: Two teenage boys (one who will drink the coffee, and one who will not), observations will be taken 30 minutes after consumption) (Note: this will be all that is required, because we cannot physically run the experiment) 2. It is found that the approximate hours of death was 4 hours ago. Find the rectal temperature. Work: 98.4 X________/1.5=4 A) B) C) D) 3. 1.5 X 4=6 98.4-6= 92.4 84 55 27 92.4 A man is presumed to be dead, because his blood reads 91.8 degrees, his body 93.4 degrees, and his body is erected. The last piece of information regarding his body stiffness discusses… A)Lividity B) Rigor mortis C) Algor MOrtis D) Elgort Mortis 4. Look at the information Ambient Temperature Temperature Change 50 degrees 12.3 Room Temperature 3.18 0 degrees 26.3 What does this information say about the cooling of the body’s temperature? A) As ambient temperatures decrease, the body’s temperature increases B)As ambient temperatures decrease, the body’s temperature remains neutral C)The body and ambient temperatures have a direct relationship with each other D)Ambient temperatures have no effect on the body’s temperature 5) A dead body was found with stiff legs, cool blood, and a body temperature that dropped 5 degrees. The last piece of information regarding body temperature describes… a) Lividity b) Algor Mortis c) Rigor Mortis D) Elgor Mortis Missing 1.1.6 Activity 1.2.1 What is DNA? DNA is the genetic material of cells. It is a polymer, a large molecule made of repeating units, or monomers, called nucleotides. It consists of three components: o A nitrogenous base o A sugar, called deoxyribose o A phosphate group Phosphate is on the outside Nitrogenous bases on the inside DNA is a double helix, made up of two strands The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions There are 10 base pairs per turn of the double helix DNA is a densely packed structure The amount of adenine was always the same as thymine, and the amount of guanine was always the same as cytosine. This is known as Chargaff’s rules. A and G belong to a class of compounds called purines C and T belong to a class of compounds called pyrimidines The nucleotides bond, and the bond between paired nucleotides are called hydrogen bonds Correctly paired nucleotides will easily stay linked because their bonds are very stable Below is a picture of phosphates, deoxyribose, and the 4 nitrogenous bases. Note: The names of the four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Here is a picture of DNA: QUESTIONS 1: What is DNA made up of? A: Phosphate group, sugar, nitrogenous base B: sugar, guanine, and cytosine C: Nitrogenous Base, and thymine D: phosphate group, sugar, adenine 2: What does adenine pair with? A: Guanine B: Cytosine C: thymine 3: How many base pairs are there per turn of the double helix? A: 5 B: 2 C: 10 D: 100 4: What is the bond between two nucleotides called? A: Hydrogen bond B: nucleotide bond C: bond D: nucleotide hydrogen bond 5: What makes up the purines, and what makes up the pyrimidines? A: Purines: A&C Pyrimidines: T&G B: Purines: A&G Pyrimidines: T&C C: Purines: A&T Pyrimidines: C&G D: Purines: T&C Pyrimidines: A&G Missing 1.2.2 Missing 1.2.3 1.3.1 AUTOPSY Information/diagrams The organ systems in humans are Integumentary System External covering protects deeper tissue helps regulate body temperature. Skin, hair, nails Skeletal System Protects and supports organs, structure, stores minerals Bones joints Muscular System Moves Body and substances, maintains posture, produces heat Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle Nervous System Responds to internal and external changes, processes information Spinal cord, brain, sensory receptors, nerves Cardiovascular system Pumps blood around body, transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and waste. Heart, blood vessels Respiratory System Assists with gas exchange with the external environment; keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Lungs, nasal cavity, trachea, bronchus Lymphatic and Immune System Filters fluid in the body; mounts the attack against foreign substances in the body. Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow Digestive System Breaks down food into molecules; absorbs nutrients; rids the body of waste. Oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver Urinary System Eliminates waste from the body; regulates water balance of the blood. Kidney, bladder, ureter, urethra Endocrine System Secretes hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism by body cells. Adrenal gland, pituitary gland, ovary, testis Five manners of death- Natural, accident, homicide, suicide, and undermined Medical Examiner Coroner Officially hired by definition is a physician Elected to the job Appointed to the job Typically in rural areas Forensic pathologist ID body, collect personal belongings, sign death certificate. Autopsy dissection order 1. X-ray the body (through the body bag) 2. Use a body block to protrude the chest and crack chest in a ‘Y’ shape (left shoulder, right shoulder, meet at ribs split until pubic bone. (the body block will make it much more easy to cut) 3. Peel back skin with a scalpel, to reveal ribcage 4. Detach the: larynx, various arteries, esophagus, and ligaments in the ribcage. 5. Then detach the spinal cord, bladder and rectum. 6. Dissect those in detail. A.k.a. weigh, take tissue and vessel samples 7. Open and examine and weigh stomach, and stomach contents 8. Remove the body block, and place behind the neck. 9. Remove the brain by, cut with a scalpel from ear to ear, then across the forehead. Pull back skin. 10. Use the electric saw, remove the cap, with the Dura still attached. 11. Expose the brain, remove the brain. 12. Examine individual unexamined organs 13. Dress for funeral home 1.3.1 Potential final questions 1. What body system would first distinguish that it is hot outside? Then help regulate body temperature after distinguishing this? A. Lymphatic and Immune System B. Nervous System C. Integumentary System D. Endocrine System 2. Which bone do you want to stop cutting at while cracking the chest? A. Left Shoulder B. Right Shoulder C. Sternum D. Public bone 3. The pituitary gland is a gland located in the brain that secretes hormones that signal puberty to begin. This gland is a part of which body system? A. Endocrine System B. Nervous System C. Skeletal System D. Urinary System 4. After using the electric saw and when starting to remove the cap be sure that the _______ is still attached. A. Brain B. Dura C. Scalp D. Hair 5. What is the body block’s most important purpose? A. To make organs easier to view B. To protrude the chest, making it easier to cut C. To raise the body to a more comfortable angle for the medical examiner/ coroner D. To push the organs upward 1.3.2 Confidentiality What is HIPAA Privacy Rule? Health HIPAA privacy Rule regulates how medical professional and other people use and disclose certain individually identifiable health information. Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Maintaining Confidentiality: Information that is protected: Individual’s name, address, birth date, social security number, etc. Individual’s past, present, or future physical or mental health or condition The health care services provided to the individual The past, present, or future payment for health care services provided to the individual Professionals are not to speak about patients. Only to other professionals that are also working with the patient Patient records should not be left in public areas unattended where anyone could easily look at them Professional may NOT leave messages regarding the patient’s health to anyone other than the patient without the patient’s consent Professionals may only disclose health information to a family member if the patient is present during the disclosure When Can Health Information Be Shared? Providing information needed for payment of benefits or health coverage Disclosing information to specific agencies as required by public health laws for the purpose of: Controlling infectious disease Preventing injury Preventing child abuse, neglect, or domestic violence Preventing any serious threat to public health or safety Complying with workmen’s compensation laws Assisting coroners or medical examiners to identify a deceased person Telling someone that is your legal representative if you are under the age of 18 Questions 1. In which scenario is it ok to share health information to someone besides the patient? a. A teacher telling her co-worker about one of her students health b. A doctor discussing loudly with another doctor about a patient’s health at the super market c. A doctor reporting back to the mom of a patient under the age of 18 d. A doctor leaving a message about a patient’s lab result to the patient’s kid 2. What identifiable health information must be kept confidential? a. The individual’s name b. The individual’s mental health c. The individual’s birthdate d. All of the above 3. When would it be appropriate for health information to be disclosed? a. When providing information needed for payment of benefits or health coverage b. When the husband demands to know he wife’s lab results c. When a doctor meets the patient’s friend for lunch and the friend asks d. When the patient doesn’t pick up the phone but his wife does 4. In which scenario is disclosing information illegal? a. When providing information for legal proceedings b. When assisting coroners or medical examiners to identify a deceased person c. When complying with workmen’s compensation laws d. When talking about a patient to another doctor in a public area 5. In what ways can professional help maintain confidentiality? a. Professionals cannot tell any information to the parents of a 12 year old b. Professionals can leave records in a public space unattended c. Professionals may disclose information to a family member only when the patient is present during the time d. Professionals can leave a message about a patient’s health to anyone as long as they are family Activity 1.3.3 Was It a Crime. Cause of death:The cause of death is the disease or injury that produces the physiological disruption inside the body resulting in death, for example, a gunshot wound to the chest Manner of death: explains how the cause of death arose. There are four main manners of death: Homicide: The taking of one human life by another human being by means of premeditated murder (purposely planned). Accident: non -intended or involuntarily. Natural:Quite simply when the body ceases to function of its own accord or if there are mitigating medical factors such as terminal illness, heart disease or the like, which would bring about death , aging. Suicide: The deliberate taking of one's own life due to extreme emotional distress often brought about by severe depression. A pathologist is a physician who examines tissues, checks the accuracy of lab tests, and interprets the results in order to facilitate the patient’s diagnosis and treatment. To find the correct cause and manner of death, a pathologist is included to examine the patient’s body. Toxicologists determine how harmful chemicals can be counteracted in case of a spill, improper use or deliberate poisoning. They help in investigation to find out if a certain body has any drug or chemicals in it. Medical examiners have several different duties since some of their work takes place at crime scenes, and the other half takes place in the facility or laboratory. At crime scenes, they examine and document injuries, collect the remains of the body and transport it. In a crime lab they perform autopsies while in courts they testify for the defense or prosecution. Morgue assistant assists pathologists in preparing bodies and organ specimens for examination, while also maintaining the morgue room, supplies and equipment. Medical examiners and coroners there is a slight difference between a medical examiner and a coroner. A medical examiner is a licensed professional physician while coroner is just a selected person who is not professional. A medical examiner the one who identifies the manner of death. QUESTIONS 1. What is the meaning of the manner of death? a) An injury b) Explains how the cause of death arose c) A disruption inside the body d) A homicide 2. What kind of physician is specialized in the diagnosis and management of human disease by laboratory methods? a) Toxicologist b) Pharmacist c) Biochemist d) Pathologist 3). How would a toxicologist assist in a crime scene? a) They help in investigation if a body has a certain drug or chemical in it b) Examine and document injuries c) Interprets the results of a lab d) Assists in preparing dead bodies 4). Which of the following is an example of a manner of death? a) Gunshot b) Puke c) Suicide d) Flu 5. Who determined the manner of death after the autopsy has been performed. a) Toxicologist b) Medical examiner c) Coroner d) Biochemist Activity Review Guide 2.1.1 Diagnosing Diabetes Diabetes is a metabolic disease in which the body’s inability to produce any or enough insulin causes elevated levels of glucose in the blood. Glucose Tolerance Testing (GTT)- monitors the amount of sugar in the liquid portion of blood called plasma, a set time period and gives doctors information as to how the body utilizes sugar. It is used to only indicate whether or not a person has diabetes, but it cannot be used to determine whether a person has Type 1 or Type 2. When a person is doing the Glucose Tolerance Testing the patient is given a large amount of sugar after they have not eaten for a certain amount of time. Then the person is running the test examines how the patient’s body responds to the sugar by watching the glucose levels in the blood. If the glucose levels stay high most of the time than the person is mostly has diabetes. Insulin Level Testing- To determine whether a patient has Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, you need to test the level of insulin in the patient’s blood. To figure out if a person is diabetic they would have a prolonged rise in blood glucose levels. A lack of insulin in the blood at each period would indicate that she is a Type 1 diabetic, thus the person is not producing insulin and their glucose levels would remain elevated over the time period. Now if the insulin test reveals a normal level of insulin in the blood in response to increased levels of glucose, but they have a prolonged rise in blood glucose levels would indicate they have Type 2 Diabetes. Now if the person has a brief rise in glucose levels, but stays within the range of normal the person would be seen as not diabetic, but could be considered pre-diabetic. Type 1 Diabetes • The body makes little or no insulin • Treatment: Injections of insulin, Sometimes medicine by mouth, Dietary plan, physically active, regular checkup of blood sugar levels, Controlling blood pressure, and Monitoring cholesterol levels. • Find out about has a child or teenager • Cause: Beta cells in pancreas are being attacked by body's own cells and therefore cannot produce insulin to take sugar out of the blood stream. Insulin is not produced Type 2 Diabetes • Affects middle-aged and older people • The body produces insulin, but the body does not permit this hormone to effectively do its job • Treatment: Using diabetes medicines, sometimes insulin injections, Healthy food choices, Exercise, SelfMonitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG), controlling blood pressure, and monitoring cholesterol levels. • Preventable and can be delayed with a healthy diet and exercise • Warning signs: blurred vision, excessive itching, and skin infections, sores that heal slowly, dry, itchy skin, pins and needles or numbness in feet. • Cause: Diet related insulin release is so large and frequent that receptor cells have become less sensitive to the insulin. This insulin resistance results in less sugar being removed from the blood Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes • Glucose builds up in blood • Must be physically active • Control blood pressure levels • Control cholesterol levels • Must make healthy food choices • Warning signs: very thirsty, urinating frequently, rapid weight loss, feeling very hungry, feeling extreme weakness and fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and irritability • Complications: Diabetic coma or ketoacidosis (from high blood sugar), High blood pressure, Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), Nephropathy, Blindness, Heart attack, Kidney disease, Stroke, Neuropathy, and Amputation. • Diagnosis you can use but not all are recommended: A1C test, also called the hemoglobin A1c, HbA1c, or glycohemoglobin test, Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, and Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) Questions Time of Blood Collection (minutes after drinking glucose solution) Glucose Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Anna Garcia Glucose Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Patient A Glucose Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Patient B 0 (Baseline Level) 150 150 150 30 175 175 200 60 225 175 225 90 225 175 225 120 200 150 200 1. Using the chart given above tell who as diabetes and who doesn’t. A. Anna: Does not have Diabetes; Patient A: Does have Diabetes; Patient B: Does have Diabetes B. Anna: Does have Diabetes; Patient A: Does have Diabetes; Patient B: Does have Diabetes C. Anna: Does have Diabetes; Patient A: Does not have Diabetes; Patient B: Does have Diabetes D. Anna: Does not have Diabetes; Patient A: Does not have Diabetes; Patient B: Does not have Diabetes 2. The risk factors for type 1 diabetes include _____. A. Blurred vision B. Being overweight C. Skin Infections D. Excessive itching 3. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed through _____. A. Weight loss B. Lifestyle interventions C. Exercise D. All of the options listed are correct. 4. After a meal, blood glucose levels increase and stimulate the secretion of which hormone? A. Insulin B. Pancreatisome C. Glycogen D. Glucagon Time of Blood Collection (minutes after drinking insulin solution) Insulin Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Anna Garcia Insulin Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Patient A Insulin Level in the Blood (milligrams/deciliter) Patient B 0 (Baseline Level) 50 100 100 30 50 150 250 60 50 400 400 90 50 400 400 120 50 250 250 5. Using the chart above and the chart from the first question, tell whether they have Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes? A. B. C. D. Anna: Type 1 Diabetes; Patient A: Not Diabetic; Patient B: Type 2 Diabetes Anna: Not Diabetic; Patient A: Type 1 Diabetes; Patient B: Type 1 Diabetes Anna: Type 2 Diabetes; Patient A: Type 2 Diabetes; Patient B: Not Diabetic Anna: Type 1 Diabetes; Patient A: Not Diabetic; Patient B: Type 1 Diabetes Missing 2.1.2 2.1.3 Feedback Loop Review Guide The human body maintains homeostasis, a steady state, by monitoring changes in the internal and external environment and feeding this information back to the body so that it can make necessary change. The control of body temperature, heart rate, and the concentration of sugar in the blood are all regulated by these feedback mechanisms or feedback loops. There are actually two types of feedback mechanisms: negative feedback and positive feedback. In this instance, the terms positive and negative do not infer good or bad. Instead, the terms refer to the effect the input of information (feedback) has on the output (action) of the system. Positive feedback causes a reinforcement of the original action, so the input causes the reaction to increase . Negative feedback causes the system to stop doing the original action and to either take no action or to perform an opposite action. While our nervous system communicates using electrical signals, the body’s endocrine system uses chemical signals, called hormones, to regulate body functioning. Hormones are proteins involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and regulate many of the body’s functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction. Hormones are secreted by tissues in the body referred to as glands. Each hormone has a specific list of target tissues, and in many cases these include other endocrine glands. Hormones are a vital component of the body’s feedback system. Insulin is one of the key hormones that helps maintain a healthy blood sugar level. ‘ Questions 1.What does homeostasis do for our body? a steady state, by monitoring changes in the internal and external environment and feeding this information back to the body so that it can make necessary change 2.How does negitive feedback react to an issue? it completly stops it without trying to fix it 3. How does positive feedback react to an issue? it gets reinforcements and atttemps to fix the problem. 4. What is one of insulins many purposes? Its one of the key hormones that maintain healthy blood sugar level. 5. What else are hormones referred to? Chemical signals Activity 2.2.1 Food Testing Review Guide ● The main nutrients in our food are classified as carbohydrates (sugars and starches), lipids (fats and oils), and proteins. ● Carbohydrates are a great source of energy. ● Proteins help build tissue, fight diseases, and faciliate chemical reaction. ● Lipids include cell membrane and hormone production. ● Benedict’s solution is an indicator that can be used to test for simple sugars, such as glucose. Benedict’s solution is light blue in color. However, when it is heated in the presence of simple sugars, it turns from blue to green or yellow/orange or even red.The final color depends on the amount and type of sugar. Benedict’s solution need to be heated to work properly. ● Lugol’s Iodine can be used as an indicator for starch, a complex carbohydrate. Lugol’s Iodine is yellow or light brown in color; in the presence of starch, it turns dark purple or even black. ● Biuret solution is a protein indicator. Biuret solution is a light blue color; in the presence of protein, the color changes to purple. The shade or darkness of the color depends on the type and concentration of the protein, and can range from a very light purple to a deep purple. ● Fats and lipids leave a translucent mark on brown paper. Translucent means light can pass through, although distinct images may not be seen through it. Most foods can be applied directly to brown paper to test for lipids; dry foods can be tested once they are made into an alcohol extract. This is done by grinding the food, placing it in alcohol, and applying samples of the liquid extract to the paper. Activity 2.2.1 Food Testing Questions 1. When testing food items, a certain food in the benedict’s solution turned a yellow/orange color. What nutrient was present in that food that made it and the solution change in color? A. B. C. D. Lipids Protein Carbohydrates Fats and Oils 2. Which of the following food items change dark purple when Lugol’s Iodine and that food was mixed together? A. B. C. D. Apple Juice Whole Milk Blueberries Whole Wheat Toast 3. Glucose Starch Protein Lipids Apple Juice Yes No No Yes Whole Milk Yes No Yes No Anna’s Stomach Yes Yes No Yes Which Solution work for all the food items in the above chart? A. B. C. D. Benedict’s Solution Lugol’s Iodine Biuret Solution Brown Paper 4. __________ solution is a protein indicator. _________ solution is a light blue color; in the presence of protein, the color changes into purple. The shade or darkness of the color depends on the type and concentration of the protein, and can range from a very light purple to a deep purple. Which of the following fits the blanks? A. B. C. D. Benedict’s solution Lugol’s Iodine Biuret solution Brown Paper 5. Carbohydrates include which of the following. A. B. C. D. Fats and Oils Sugars and Starches Fats and Starches sugars and Oils Missing 2.2.2 Activity 2.2.3: The Biochemistry of Food Biochemistry- the study of chemical process in living organism Elements of the human body Four major elements make up 96% of the body: Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Symbol for elements First letter is capital Ex: carbon- C Second letter if included is lowercase Ex: iron- Fe Atoms Elements are made of subatomic particles Atoms are the smallest whole particles of an element Atoms have 3 major subatomic particles: o Protons- positive charge, located in nucleus, number of protons = atomic number o Electron- negative charge, orbits around nucleus, electrons = number of protons o Neutron- no charge, located in nucleus Valence electron want a full shell to complete the octet rule Type of Bonds Chemical Bonds Formed due to the force of attraction between the atoms Ionic Bonds Formed by the attraction of opposite charges Covalent Bonds Share electrons H H O Oxygen and Hydrogen atoms can bond with anything they fit with A molecule is stable only if it has no available pegs or slots; proteins are an exception Molecules are formed when two or more molecules are joined together Chemical Reaction: Occurs when atoms, molecules, or ions interact Ex: X+Y XY Reactants reacts to form Product 1. When does a chemical reaction occur? A. When atoms interact B. When molecules interact C. When ions interact D. All of the above 2. Which subatomic particle is equal to the atomic number? A. Neutrons B. Protons C. Electron D. Atoms X+Y XY 3. What is the picture shown above called? A. Octet rule B. Bonds C. Chemical reaction D. Chromosomes 4. Where are the neutrons located at? A. In the nucleus B. In the orbits C. In the protons D. In the electrons 5. What is the charge of the electrons? A. Positive B. Negative C. No charge D. None of the above Activity Review Guide 2.2.4 Energy from Food Every bit of food you eat gives you some amount of energy. The amount of energy and the amount of time it lasts will differ in the large variety of foods. Your body breaks down the food bit by bit and captures the energy released from the food to be used to power your body functions Macromolecules come together and for monomers that then form polymers. The body gets energy from breaking hydrogen bonds. A monomer has very few hydrogen bonds but a polymer has many The body ultimately uses macromolecules to get energy. The preferred macromolecule to use as an energy source is a carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are further broken down into their component sugar molecules through the process of hydrolysis. Sugars, such as glucose, are then absorbed into the bloodstream from the small intestine. The glucose molecules travel to the body’s cells where a series of chemical reactions, known as cellular respiration, ultimately make adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Calories are a way to measure how much energy you are getting from the food you’re eating. a calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water 1° C. The number of calories in a piece of food is determined by measuring the increase in temperature of a known volume of water when a portion of the food is burned. The average person eats 2000 calories a day. 1. how many calories are in a Cheerio if the water weighs 76.5 and the cheerio increases the temperature of the water to 23.29 from 23.01 A. 214.2 B. 72.58 C. 45.84 2. what is the preferred macromolecule to be used as an energy source A. B. C. D. Protein Nucleic acid… Lipids Carbohydrates 3. What does ATP stand for adenosine tri-phosphate? 4. Is this model a monomer or a polymer? A. monomer B. Polymer 5. How many Calories does the average person eat? A. B. C. D. 1500 2000 1750 2250 2.3.1 Life with Diabetes Diabetes: A person who has diabetes suffers by having a metabolic disease in which the body’s inability to produce any or enough insulin which causes elevated levels of glucose in the blood. Recommendations for a diabetic: You should eat healthy and exercise to maintain a healthy weight and treating and doing things for your body that can only turn out positive. Type 1 Diabetes vs. Type 2 Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Symptoms usually start in childhood or young adulthood. People often seek medical help, because they are seriously ill from sudden symptoms of high blood sugar. The person may not have symptoms before diagnosis. Usually the disease is discovered in adulthood, but an increasing number of children are being diagnosed with the disease. Does not produce Insulin Produces insulin, but the body does not permit this hormone to effectively do its job It cannot be prevented. It can be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating sensibly, and exercising regularly. Role of blood sugar monitoring and adjusting: Sugar monitoring helps people with diabetes manage the disease and avoid problems that are associated with it. It can help them make decisions about food, physical activity, and medications. A common way to check glucose level involves pricking a fingertip with an automatic lancing device to obtain a blood sample and then using a glucose meter to measure the blood samples glucose level. People with type 1 diabetes have to take insulin as a part of their treatment plan. Careers that are assistances to a diabetic: Nutritionist or dietician – experts in food and nutrition that advise diabetics on what to eat in order to have a healthy lifestyle Endocrinologist – trained physicians who diagnose diseases related to glands Primary care physician- provides both the first contact for a person with an undiagnosed health concern as well as continuing care of varied medical conditions Certified diabetic educator (CDE)- provides knowledge and experience in diabetic management Ophthalmologist- medical and surgical eye problems Clinical researcher- supervises, monitors, and supports the administration and progress of a clinical trial on behalf of a sponsor Podiatrist- study of diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot or ankle Psychologist or Psychiatrist- study cognitive, emotional, and social processes by observing how people relate to another and their environment 1. What is one difference between type 1 and type 2 Diabetes? A. People with type 1 diabetes produce insulin while type 2 does not. B. Type 2 diabetes cannot be prevented while type 1 can. C. Type 2 produces insulin, but the body does not permit this hormones to effectively do its job, while type 1 does not produce insulin at all. D. No difference. 2. What career could not be an assistance to a person with diabetes? A. Primary Care physician B. Nutritionist or dietitian C. Psychologist D. Farmer 3. What is a common way to check glucose level? A. Calling the doctor B. Pricking your finger with an automatic lancing device C. Looking it up online D. None of the above 4. What would be a recommendation for a good lifestyle of a diabetic? A. Eating the right foods and maintaining a healthy weight B. Eating junk food every day C. Not exercising D. Starving yourself 5. Which Type of Diabetes usually is present during early childhood or a young age? A. Type 3 B. Type 1 C. Type 2 D. None of the above