ASIA
advertisement

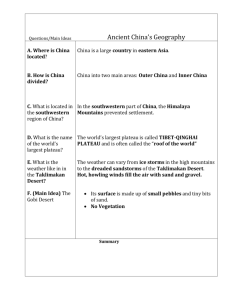
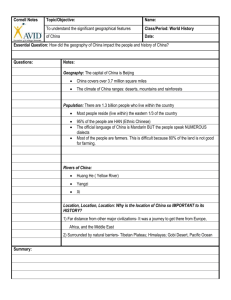
Location (Physical Features & Countries) FSMS Standard SS7G9.a Days 1-3 SS7G9 – The student will locate selected features in Southern and Eastern Asia. a. Locate on a world and regional political-physical map: Ganges River, Huang He (Yellow River), Indus River, Mekong River, Yangtze (Chang Jiang) River, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, Sea of Japan, South China Sea, Yellow Sea, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Himalayan Mountains, and Korean Peninsula Agenda Message: Today we start our study of Southern and Eastern Asia. Before school tutoring is Tuesday starting at 7:30a. Standard: Locate selected features in Southern & Eastern Asia including rivers, mountains, Seas, Deserts, Oceans, Bays and the Korean Peninsula. Essential Question for Wednesday 11/6/13: What are the major geographic features in Southern & Eastern Asia? Warm Up for Wednesday 11/6/13: Name three things that you know about Asia. TODAY WE WILL: 1. Introduce the map of Southern & Eastern Asia E.Q. Answer for Monday November 4th: Ganges River Yellow Sea Indus River Indian Ocean Huang He (Yellow River) Sea of Japan Mekong River Gobi Desert Yangtze River Taklimakan Desert Himalayan Mountains South China Sea Bay of Bengal Tibetan Plateau Korean Peninsula Warm-Up Answer: Bay Sea Ocean Typhoon Monsoon River peninsula Tributary – Any smaller stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. Aquifers – Underground, water-bearing layers of rock, sand, or gravel. Acid rain – A type of polluted rain, produced when pollution from smokestacks combines with water vapor. Ozone layer – A form of oxygen in the atmosphere that helps protect Earth from harmful solar radiation. Global warming – A slow increase in Earth’s average temperature. Greenhouse effect – Process by which Earth’s atmosphere traps heat. Physical Geography Introduction The southern and eastern parts of Asia are home to almost half of the world’s population. The geography of this large area is varied, containing some of the world’s longest rivers, highest mountain ranges and large extensive deserts. http://app.discoveryeducation.com/search?Nt t=southeast+asia&N=4294949099 Land forms http://app.discoveryeducation.com/search?Nt t=southeast+asia&N=18342&N=4294949099 The Indus River Indus River begins in the mountains of Tibet and flows almost 200 miles through the country of Pakistan before emptying into the Arabian Sea. The Indus River valley is one of the richest farming areas in this region. Many different civilizations have lived along this river throughout the centuries. Ganges River The Ganges River is India’s most important river. It begins in the Himalayan Mountains and flows southeast through India and Bangladesh before emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The water of the Ganges carries tons of rich sediment (topsoil, silt and minerals from the mountains) that is gradually spread along its path enriching the farmland and creating a large, fertile delta at the mouth of the river. Ganges River cont. Because so many people live and work along the Ganges, the water in the river is heavily polluted. The country of Bangladesh is located almost completely in the Ganges River delta. Monsoon Season Heavy flooding in this part of the world during the monsoon season (a seasonal prevailing wind, lasting several months, bringing heavy rains) often causes great hardships for those living in this country. Water Pollution The Ganges http://www.compulsivetraveler.tv/videos/408-Ganges-River-Pollution http://www.reuters.com/news/video?videoId=166276235 Indian Ocean Further out to sea is the Indian Ocean, which is the third largest ocean in the world. Mountains & Plateau The Himalayan Mountains form the southern border of China. This high ground spreads to the north to form the Tibetan Plateau. Mountains & Plateau cont. The area is sometimes called “the roof of the world” because of its high altitudes. This wide area of mountains and high plateau blocks any moisture coming from the rivers and seas to the south. The Himalayan Mountains form India’s eastern border with China and Nepal. Mountains & Plateau cont. These high mountains form a barrier between Indian and countries to her north and east. The Himalayan Mountains stretch for almost 200 miles. The highest mountain in the world, Mount Everest, is on the border between Nepal & China. Mt. Everest Himalayas Deserts As the mountains begin to level off in the north, the land becomes desert. Here one finds the Taklimakan Desert and the Gobi Desert. The Taklimakan Desert is over 600 miles in length, one of the longest deserts in the world. Deserts cont. To the west and in the central part of China is the Gobi Desert, which can be one of the “hottest” and also one of the “coldest” places in the world. Much of the Gobi Desert is covered with sand and rocks. Gobi Desert http://app.discoveryeducation.com/search?Nt t=southeast+asia&N=4294949099 China’s River China’s fertile farming areas lay north and east of the Gobi desert region. The Huang He, or Yellow River, begins in the Tibetan Plateau. It flows toward the east and finally empties into the Yellow Sea. China’s Rivers cont. The yellow dust blowing out of the Gobi Desert is picked up by the Huang He and carried along as loess (another name for silt), giving both the river and the sea a yellowish color. The frequent flooding has led some to call the Yellow River “China’s Sorrow.” Huang He or Yellow River Agenda Message: Map Review Quiz Wednesday November 20th, 2013 Standard: Locate on a world and regional politicalphysical map Pakistan, India, China, Japan, Indonesia, North Korea, South Korea, and Vietnam. E.Q. Friday 11/15/13: List the names of the seven countries we are responsible for in S&EA for this unit. Warm Up: Why is India sometime referred to as the subcontinent? TODAY WE WILL: 1. Complete Geography & Political highlights of S&EA including Maps E.Q. Answers for Friday November 8th: Pakistan India Vietnam South Korea North Korea Japan China Warm-Up Answers: Because India is such a large landmass that is part of the Asian continent, but is in many ways geographically separate from it. SS7G9 – The student will locate selected features in Southern and Eastern Asia. a. Locate on a world and regional political-physical map: Ganges River, Huang He (Yellow River), Indus River, Mekong River, Yangtze (Chang Jiang) River, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, Sea of Japan, South China Sea, Yellow Sea, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Himalayan Mountains, and Korean Peninsula Mekong River Flowing through China, Myanmar (formerly known as Burma), Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, & Vietnam, the Mekong River affects the lives of over 60 million people, many of whom are the poorest in the world. One of the regions most important crops, rice is grown extensively in the Mekong River Basin. Mekong River http://app.discoveryeducation.com/search?Nt t=south+east+asia Mekong River Oceans, Bays, & Seas Indian Ocean The third largest of the world’s five oceans is the Indian Ocean. It’s Relative Location is between Africa to the west, Asia to the north, Australia to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south. Indian Ocean Bay of Bengal The Bay of Bengal is an arm of the Indian Ocean with India to the west and Myanmar to its east. The Ganges River flows into the bay. Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is an arm of the Pacific Ocean that lies between the Asian continent and Japan. Bay of Bengal South China Sea The South China Sea lies between Vietnam and the Philippines. Weather in the region is marked by violent monsoons and typhoons. Yellow Sea This arm of the Pacific Ocean lies between China and Korea. It gets its name from the Yellow River which flows into the sea. Korean Peninsula The Korean Peninsula juts out of the northeastern China in between the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Since 1948, this peninsula has been divided into two countries: Communist North and Democratic South Korea. Korean Peninsula cont. The Korean Peninsula is a mountainous peninsula. It is attached to China and is bordered by the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Over half of the peninsula is made up of mountains. Even though so much of the country is rocky and mountainous, there is still plenty of rich farmland. Agenda Message: Map Review Quiz Wednesday November 20th, Standard: Locate selected features in Southern & Eastern Asia including rivers, mountains, Seas, Deserts, Oceans, Bays and the Korean Peninsula. E.Q. Tuesday, 11/18/12: What are the major geographic landforms in Southern & Eastern Asia? Warm Up: What percentage of the world’s population is found in India & China combined? TODAY WE WILL 1. Continue review on map of Southern & Eastern Asia Ganges River, Huang He (Yellow River), Indus River, Mekong River, Yangtze (Chang Jiang) River, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, Sea of Japan, South China Sea, Yellow Sea, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Himalayan Mountains, and Korean Peninsula Southern & Eastern Asia Landforms 1. Himalayan Mountains (Nepal, Tibet, Pakistan, Bhutan, and southern China) 2. Subcontinent (India) A large landmass that is part of a continent, but is geographically separate from it. 3. Tibetan Plateau (southern China) The highest plateau on earth. Nicknamed, “the roof of the world”. 4. Korean Peninsula (North and South Korea) 5. Archipelagos (Indonesian Islands) A group of islands. Indonesia has the 4th largest population in the world and is made up of over 17,000 islands. Relative Location Southern and Eastern Asia is located between Pakistan on the west to Japan and the Philippine Islands on the east. To the north is Russia and the southern border is the Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, Indonesia, Malaysia and the South China Sea. China’s Population Distribution Only the areas to the east and south are humid and even tropical. Therefore, most of China’s 1.4 billion people live in these areas of the country (east & southeast) that have the milder climates. This area is also where one finds the great river valleys and most of China’s fertile farmland. Absolute Location Between 50o North Latitude & 10o South Latitude Between 60o East Longitude & 155o East Longitude Agenda Message:. Standard: Locate on a world and regional political-physical map Pakistan, India, China, Japan, Indonesia, North Korea, South Korea, and Vietnam. E.Q. Friday 11/8/13: India considers the Ganges River to be sacred. What is their main religion? Warm Up: Name the seven countries in Southern and Eastern Asia that will be our focus for this unit. TODAY WE WILL: 1. Geography & Political highlights of S&EA Agenda Message:. Standard: Locate on a world and regional political-physical map the leading countries of Southern & Eastern Asia. E.Q. Monday 11/11/13: Which river in S&EA is known as “China’s Sorrow”? Why? Warm Up: Using relative location describe where one can locate the Tibetan Plateau. TODAY WE WILL: 1. Label the seven leading countries on the map of Southern & Eastern Asia Agenda Message: Standard: Locate on a world and regional politicalphysical map Pakistan, India, China, Japan, Indonesia, North Korea, South Korea, and Vietnam. E.Q. Tuesday 11/12/13: Which is the longest river in China? Warm Up: What percent of the world’s population lives in India & China combined? TODAY WE WILL: 1. Finish Geography & Political maps of S&EA. Agenda Message: Quick Quiz Friday. Quiz will be fill-in the blanks & maps. Choice Board Project is due in 22 days. Standard: Impact of location, climate, & natural resources on population distribution in S&EA. E.Q. Wednesday: 11/13/13: Where do most people live in China? Warm Up: Two thirds of China is basically uninhabited, due to what geographic features? Today We Will: 1. The impact of climate & location on population distribution in S&EA (India, China, Japan, & Korean Peninsula).