amino acids
advertisement

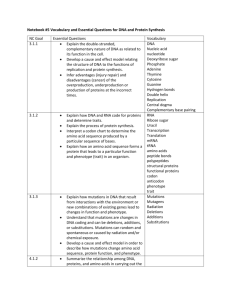
Ms. Rossi 2012 Discovery of DNA DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. What did Rosalind Franklin do? Click here to find out. What about James Watson and Francis Crick? Click here to read about them. Click through the series of slides! How does it all fit together? Chromosomes, which are made up of DNA molecules, are found within the nucleus of the cell. A gene is a section of DNA that contains the code for building proteins. Proteins are made of amino acids; the amino acids are determined by codon’s or groups of three bases. Ultimately, the protein produced determines the traits! Use this info to fill in your paper for number 4! Subunits of DNA - Nucleotides Nucleotides are the subunits that create the double helix structure of DNA. What are the parts of a nucleotide? Draw and label this on your paper. The base can be any of the following: adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine. Practice rebuilding DNA here. What is a codon? A codon is a group of ______ bases? How many codon’s are in this gene sequence? AAT TGC ACC GCT CAT How many amino acids would this produce? GTA Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are made of amino acids (building blocks of proteins). The genetic code is read three bases at a time (codon) and each codon determines which amino acid is added to the protein. Use the attached amino acid chart to determine the correct amino acid. Remember – in RNA, we will use a U (uracil) instead of a T (thymine). RNA AUG CUA GAC GUG UUC UAG Write the correct amino acid on your paper. How and when is DNA copied? Watch this to see how and when DNA is copied. Answer the question on your study guide in your own words. Genetic Mutations What is a genetic mutation? Find out here: Mutations Describe the three types on you paper. Are all mutations negative? What are some other outcomes of mutations? What can cause mutations – name three environmental things that can cause mutations? Information here. Advances in DNA and Genetics What is the Human Genome Project and when was it completed? Find out here. To learn more about cloning, check out this website. Find out what cloning is and when the first animal was cloned. Genetically Modified Organisms Today, scientists can change the DNA of organisms to produce plants or animals with desirable characteristics. Find out about some Genetically Modified Organisms. Why would scientists want to change how fast (or slow) organisms like salmon or grass grow. Do you think this should be done? DISCUSS WITH YOUR NEIGHBOR. Learn More…and games! How big, how small? Its hard to comprehend how small some cell structures and chemical compounds are. Click here to zoom in and investigate. Online quiz – how much do you know? More practice – here – challenge! Cloning or not? Play the game here. What is DNA?– an animated explanation.