Review-Questions-for-mendeliangenetics
advertisement

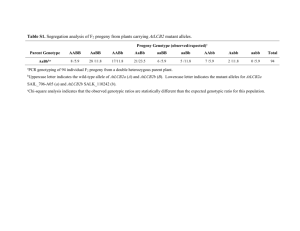
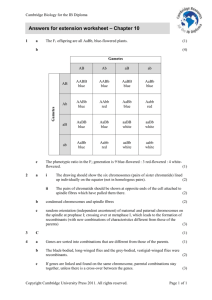
Review Questions for Mendelian Genetics Match the description with the genetics terms. Each question can have more than one answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. The mixture of alleles in an individual A A. genotype The specific form of a gene. C B. phenotype For example, tall, short, white, purple B, C C. allele Where a gene is located on a chromosome F D. gene For example, BB or Tt A E. Chromosome Homozygous dominant A F. Locus heterozygous A hybrid A For example, B or b C For example, flower color D For example, green seeds or yellow seeds B Can contain multiple genes E The specific genetic makeup of an individual A Match the description with the genetics terms. Each question can have more than one answer. 1. Genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype D, E 2. Requires mating with a recessive individual A 3. Has the alleles G and t from an individual A. Test cross that was GgTt B B. Gamete 4. Used to determine the possible offspring from a cross C C. Punnett Square 5. Genotype of an individual with the F D. Heterozygous recessive trait E. Homozygous 6. A way to determine the genotype of an dominant individual with the dominant trait A F. Homozygous 7. Contains two different alleles D recessive 8. For example, hh F 9. hybrid D 7 Steps to doing genetics problems • • • • • Define alleles Parental genotypes Gametes that parents can produce Punnett Square using gametes Fill in Punnett Square to determine offspring genotypes • Write genotype ratios & phenotype ratios of offspring • Answer the question and circle your answer. If parents are Aabb and AaBb, assuming independent assortment and random recombination, what is the chance that they have a child who is aaBb? • Determine the gametes that each parent can produce. Ab ab AB Ab aB ab • Create your Punnett Square. AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb • Answer the question 1/8 or 12.5% chance of having aaBb child If parents are aaBB and AaBb, assuming independent assortment and random recombination, what is the chance that they have a child who is AaBb? Use the product law: • Chance of aa X Aa making Aa: Possible gametes: a A a • Chance of BB X Bb making Bb: Possible gametes: B B b Aa ½ chance aa BB of getting Aa ½ chance of getting Bb • Multiply the two probabilities Bb to get your answer: (1/2)(1/2) = ¼ or 25% of having AaBb child If parents are AaBB and AaBb, assuming independent assortment and random recombination, what is the chance that they have a child who is aaBb? Use the product law: • Chance of Aa X Aa making aa: AA Aa A A a a Aa aa • Chance of BB X Bb making Bb: B B b BB 1/4 chance of getting aa ½ chance of getting Bb • Multiply the two probabilities to Bb get your answer: (1/4)(1/2) = 1/8 or 12.5% chance of having aaBb child If parents are Aabb and AaBb, assuming independent assortment and random recombination, what is the chance that they have a child who is AaBb? Use the product law: • Chance of Aa X Aa making Aa: AA Aa A A a a Aa aa • Chance of BB X Bb making Bb: b B b Bb 1/2 chance of getting Aa ½ chance of getting Bb • Multiply the two probabilities to bb get your answer: (1/2)(1/2) = 1/4 or 25% chance of having AaBb child In peas, yellow color pea is dominant to green. Tall is dominant to short. What percent of the offspring of two individuals heterozygous for both traits is expected to be tall and green? Define alleles: Yellow = A; green = a tall = T; short = t Parental genotypes: Both AaTt Use the product law: • Chance of Aa X Aa making green:AA Aa A a A a Aa • Chance of Tt X Tt making tall: T t T t TT • Multiply the two probabilities to Tt get your answer: aa 1/4 chance of getting aa that is green 3/4 chance Tt of getting tt tall (both TT and Tt) (1/4)(3/4) = 3/16 chance of having tall green pea If parents are AabbDd and AaBbDd, assuming independent assortment and random recombination, what is the chance that they have a child who is aaBbDD? Use the product law: • Chance of Aa X Aa making aa: A a A a • Chance of bb X Bb making Bb: b • • B b AA Aa 1/4 chance Aa aa of getting aa Bb ½ chance of getting Chance of Dd X Dd making DD: bb Bb D d d D DD Dd 1/4 chance of getting Multiply the 3 probabilities to get Dd dd DD your answer: (1/4)(1/2)(1/4) = 1/32 chance of having aaBbDD child If one parent has the genotype AabbDd assuming independent assortment and random recombination, which of the following are possible gametes made by that a. Aa individual? b. c. d. e. f. g. h. AbD ABd Aabbdd D d B abd What is the chance that that parent would produce the gamete AbD? ½ for A, 1 for b, ½ for D, so all together ¼ chance to produce AbD