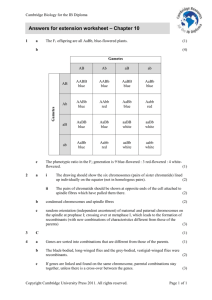
AABB
advertisement
Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Chapter 7 Skin Color Terms Used in Modern Genetics Heredity- characteristics passing from Genes parents to offspring through genes Each gene has a specific locus on a chromosome Heterozygous (Aa or Bb) Homomzygous (AA or BB) Gregor Mendel Genetics An allele is dominant if its effect masks the effect of a recessive allele paired with it Mendel’s Law of Segregation Only one of the 2 alleles gets put into each gamete Segregation of Alleles at a Gene homozygous homozygous dominant parent recessive parent Locus (chromosomes duplicated before meiosis) meiosis I meiosis II (gametes) (gametes) fertilization produces heterozygous offspring Fig. 11-5, p. 172 genotype phenotype Construction of a Punnett Square Punnett square Dihybrid Cross 2 loci AABB x aabb F2 phenotype ratio is 9:3:3:1 Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment Mendel’s law of independent assortment One trait does not influence the inheritance of the other Exception: linked genes parent plant homozygous parent plant for purple homozygous flowers for white flowers and long and short stems stems aabb AABB AB x ab Fig. 11-9a, p. 175 AaBb AaBb AaBb What gametes will they form? F1 generation Fig. 11-9b, p. 175 AB Ab aB ab AB AABB AABb AaBB AaBb Ab AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb aB AaBB AaBb aaBB aaBb ab AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb D Out of 16 possible genetic outcomes of this dihybrid cross, 9 will result in plants that are purple-flowered and tall; 3, purple-flowered and short; 3, white-flowered and tall; and 1, white-flowered and short. The ratio of phenotypes of this dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. Fig. 11-9c, p. 175 Codominance Two nonidentical alleles of a gene are both fully expressed in heterozygotes, so neither is dominant or recessive Multiple allele systems Incomplete Dominance One allele is not fully dominant over its partner Epistasis Epistasis Two or more gene products influence a trait Typically, one gene product suppresses the effect of another Epistasis in Coat Colors Pleiotropy Pleiotropy One gene product influences two or more traits Example: Marfan syndrome Or sry Sex-linked traits Genes and the Environment Expression of some genes is affected by environmental factors such as temperature, altitude, or chemical exposure