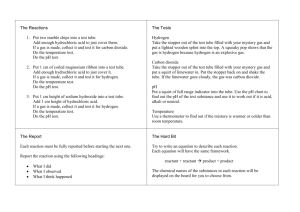
Downlod - nimelssa unimaid
advertisement
Phlebotomy By Mrs. Saliu Phlebotomy Standard Practices Using Vacuum Collection Set Wash Hands (before and after the procedure) and Wear New Gloves Label tube with the client identification number Put tourniquet on client about 3-4” above venipuncture site Have client form a fist so veins are more prominent After palpating the path of the vein, clean the venipuncture site with alcohol using a circular motion. Allow the area to dry Assemble needle and vacuum tube holder Insert the collection tube into the holder until the tube reaches the needle Remove cap from needle Use your thumb to draw skin tight about 12” below the venipuncture site. Hold skin tight Insert the needle, bevel side up, into the vein Push the vacutainer tube completely onto the needle. Blood should begin to flow into the tube. Release the tourniquet Fill the tube until it is full or until vacuum is exhausted. After opening client’s hand, place dry gauze over the venipuncture site Apply mild pressure to the pad and slowly remove the needle Apply bandage or continue applying mild pressure until bleeding has stopped Collect Supplies; New vacuum set (holder, needle and collection tubes), new gloves, alcohol swab, sterile gauge, tourniquet, sharp box and infectious waste container ORDER OF DRAW Blood collection must be drawn in a specific order to avoid cross contamination of anticoagulant. The recommended order is First draw – Blood culture tube (yellow-black stopper) Second draw – Plain tube (red stopper) Third draw – Coagulation tube (light blue stopper) Last draw – Anticoagulated tube Red-grey, or gold stopper – gel separator and clot activator ORDER OF DRAW CONTD Dark green stopper – sodium heparin. Light green stopper – lithium heparin and a gel separator. Lavender stopper – Ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) Pale yellow stopper – acid citrate dextrose Light gray stopper – oxalate fluoride RED TOP ADDITIVE: None MODE OF ACTION: Blood clots, and the serum is separated by centrifugation USES: Chemistries, Immunology and Serology, Blood Bank (Cross match) LIGHT GREEN TOP ADDITIVE: Plasma Separating Tube (PST) with Lithium heparin MODE OF ACTION: Anticoagulates with lithium heparin; Plasma is separated with PST gel at the bottom of the tube USES: Chemistries PURPLE/LAVENDER TOP ADDITIVE: EDTA liquid MODE OF ACTION: Forms calcium salts to remove calcium USES: Hematology (FBC) requires full draw invert 8 times to prevent clotting and platelet clumping GOLD TOP ADDITIVE: None MODE OF ACTION: Serum separator tube (SST) contains a gel at the bottom to separate blood from serum on centrifugation USES: Chemistries, Immunology and YELLOW TOP ADDITIVE: ACD (acid-citrate-dextrose) MODE OF ACTION: Complement inactivation USES: HLA tissue typing, paternity testing, DNA studies LIGHT GRAY TOP ADDITIVES: Sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate MODE OF ACTION: Antiglycolytic agent, preserves glucose up to 5 days USES: Glucose requires full draw (may cause hemolysis if short draw) Venipuncture site selection The larger and fuller median cubital and cephalic veins of the arm are used most frequently; wrist and hand veins are also acceptable. Sites for venipuncture g Site selection contd Avoid these areas when choosing a site Extensive scars from burns and surgery. Hematoma Intravenous therapy/ blood transfusion Vein selection Palpate and trace the path of veins with the index finger. Arteries pulsate, are more elastic than vein and have thick wall. Thrombosed veins lack resilience, feel cord like and roll easily. Performance of venipuncture Approach the patient in a friendly calm manner. Provide for their comfort as much as possible. Briefly explain the procedure to the patient and assure him/her. Gain the patient’s cooperation before going ahead. Performance contd Verify the patient’s condition, e.g. fasting, medication, timing etc. Position the patient, can either sit in a chair, lie down, or sit up in bed. Hyperextend the patient’s arm. Apply tourniquet 3 - 4 inches above the puncture site. Do not place too tightly or leave tourniquet on the arm for more than 1 – 2 minutes. Performance contd The patient should make a fist without pumping the hand. Select the venipuncture site. Prepare the patient' arm using alcohol wipe. Cleanse in a circular fashion, beginning at the site and working outward. Allow to air dry. Grasp the patient’s arm firmly. 15º - 30º angle with the surface of the arm Swiftly insert the needle through the skin into the lumen of the vein with the bevel side facing up. Avoid trauma and excessive probing. contd When the last tube is about filling, remove the tourniquet. Remove the needle from the patient’s arm using a swift backward motion when the tube is filled Press down the gauze once the needle is out of the arm. Apply adequate pressure to avoid formation of a hematoma. contd Dispose of contaminated materials / sharps in appropriate containers. Dispose of needles immediately upon removal from the patient’s vein. Do not bend, break or re cap needles. Mix by inversion and label all tubes at patient’s side. Deliver specimens promptly to the laboratory. LABELING SAMPLES Properly labeled samples is essential so that the results of the test match the patient. Key elements in labeling include Patient’s surname, first name & middle name. Patient’s ID number/Hospital number. Both of the above MUST match with the request form. An example of a properly labeled tube Do not recap. Dispose of all Parts in a Sharp Container / Safety Box. DO NOT reuse holder