PPT_Observe_&_monitor_people_refined
advertisement

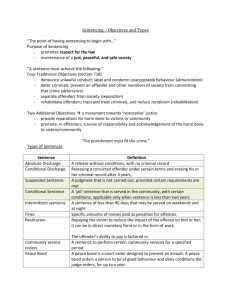
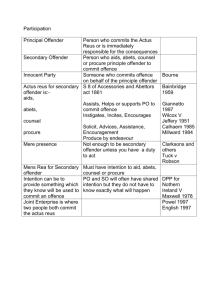
OBSERVE AND MONITOR PEOPLE D1.HSS.CL4.05 Slide 1 Observe and monitor people This Unit comprises five Elements: 1 Prepare for observation and monitoring 2 Implement observation and monitoring activities 3 Determine apprehension of offenders 4 Arrest offenders 5 Fulfil administrative responsibilities Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from employer/supervisor Slide 3 Prepare for observation and monitoring Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify areas and people who require observation & monitoring Read logs and records or previous events Prepare equipment Plan the observation and monitoring Notify relevant other staff or support services Slide 4 Identify areas and people to monitor Reasons to observe and monitor: Predict problems and issues Gather intelligence Provide a sense of safety and security (Continued) Slide 5 Identify areas and people to monitor Discharge ‘duty of care’ obligations Meet expectations Honour obligations Slide 6 Identify areas and people to monitor Areas which may need to be monitored: Internal and external areas Known trouble-spots High-traffic areas As identified by ‘assignment instructions’ Slide 7 Identify areas and people to monitor People who may need to be monitored: VIPs and their entourage Members of the public who fit an identified profile Persons displaying certain attributes Slide 8 Read logs and reports You may need to share information and communicate with: Owner Managers and supervisors Other security staff Operational and support staff Nominated staff at other venues Police Complainants Victims Slide 9 Read logs and reports Communication and information-sharing options: Attending meetings and briefings Using the telephone Sending emails Sharing hard-copy materials Slide 10 Read logs and reports Before you start work: Read relevant comms books, logs, records and reports from previous shift/s Take notes of important information contained Integrate ‘new’ information into your personal bank of existing venue knowledge Slide 11 Prepare equipment Items/equipment to check before starting work: Notebook – check: Working pen/pencil Spare pages or spare notebook (Continued) Slide 12 Prepare equipment Binoculars – check: Clean lenses Mechanisms operating as required/expected Fit for use Case provided (Continued) Slide 13 Prepare equipment Camera and audio recording devices – check: You know how to use it Lenses are clean Batteries charged Space on memory card – or spare card Case is provided (Continued) Slide 14 Prepare equipment Electronic surveillance equipment (CCTV) – check: Cameras fully functional Recording equipment working properly Tests conducted to verify status (Continued) Slide 15 Prepare equipment Electronic surveillance equipment (detection equipment/systems) – check: Operational status Self-diagnosis tests have been conducted If there are alarms/alerts to be investigated (Continued) Slide 16 Prepare equipment Torches/flashlights – check: Location/availability How to operate – light/s; SOS function Batteries/how long they will last (Continued) Slide 17 Prepare equipment First aid kits – check: Location/availability Kits are fully-stocked Also check name of First Aid provider on duty for your shift. (Continued) Slide 18 Prepare equipment Barriers and signage – check: Location and availability Items are ready to use Sufficient in number (Continued) Slide 19 Prepare equipment Comms equipment is required by Security staff: So management can communicate with staff To enable communication in event of emergency To allow staff to talk with each other So venue can communicate with patrons/guests To communicate with emergency services Slide 20 Prepare equipment Commonly used Comms equipment: Hand-held radios Comms set with headset Landline phones Cell phones Pagers PA systems Megaphones Slide 21 Prepare equipment Checks on Comms equipment: Freshly fully-charged batteries Sending and receiving capacity Channel check Headset and earpiece check Volume setting Slide 22 Prepare equipment Vehicles may also be used and therefore need to be checked – check: Operational status and safety Fuel ‘Vehicle Use’ form has been completed ‘Required items’ are in the vehicle Slide 23 Prepare equipment Examples of PPE: Body armor Protective shields Masks Safety boots (Continued) Slide 24 Prepare equipment Head protection Safety glasses Knee pads Clip-on neck ties (Continued) Slide 25 Prepare equipment Duty/utility belt – which can carry: Holders for pager, flashlight and asp Pouch for handcuffs, medical & camera Holster for Comms and pistol Holders for keys, camera, knife and extra clips of ammunition OC spray carrier Slide 26 Plan observation and monitoring Work must be planned – this is important to: Make sure all allocated tasks are factored into the working day/shift ID and obtain resources available/to be used Place tasks in logical order/sequence (Continued) Slide 27 Plan observation and monitoring Obtain relevant intelligence Clarify requirements of jobs/tasks Determine/allocate time for each job Take responsibility for personal safety Slide 28 Plan observation and monitoring Planning activities: Determining relevant locations and sites for work Calculating security staff number required for work to be done safely and effectively Identifying resources required (Continued) Slide 29 Plan observation and monitoring Selecting observation points/locations Identifying targets for observation and monitoring Human Physical Functions/events Slide 30 Plan observation and monitoring Tasks/duties you may be required to undertake: Conducting routine venue security Monitoring and observing crowds Undertaking screening activities (Continued) Slide 31 Plan observation and monitoring Checking patron ID Controlling access to: Venue Designated areas Monitoring egress of people from the venue Slide 32 Plan observation and monitoring You may also receive ‘assignment instructions’ for specific tasks as determined by management: May be in written or verbal form They are in addition to normal duties May/will require: Changes to standard day-to-day activities Integration of normal work with special assignments Other staff to undertake your normal duties while you focus on the assignment Slide 33 Plan observation and monitoring Written assignment instructions usually provided for tasks such as: Special surveillance Investigations Escort duties (Continued) Slide 34 Plan observation and monitoring In response to advice/requests from authorities Where internal risk assessment has identified a problem/threat Large events/high-traffic situations Slide 35 Plan observation and monitoring Details provided in ‘assignment instructions’: Specific requirements for the assignment Objective/s Access arrangements Timing (Continued) Slide 36 Plan observation and monitoring Specified work tasks to be completed as part of the job Integration of other work with ‘assignment’ requirements Resources available/to be used Management structure (reporting, control & command authority) for the assignment Documentation Slide 37 Plan observation and monitoring Your work will also require you to respond to situations which you have not planned/prepared for – such as: Investigating alarms Assisting other staff Escorting people (Continued) Slide 38 Plan observation and monitoring Detaining offenders Providing ‘first response’ to emergencies Acting ‘as directed by management’ Liaising/working with police Fulfilling necessary internal administrative requirements Slide 39 Notify others You need to keep others informed of your activities and location so: Others are updated about what is happening Personal safety is optimised Others can use your intelligence/input Others can give you relevant intel/information Slide 40 Notify others Communication/notification may need to occur: On arrival at work When starting work When taking a break and when returning from a break When you are ‘involved’ At scheduled times Slide 41 Notify others You may need to notify/communicate with: Management Owner Head of Security Other internal security staff Police Emergency services Private/external security providers Slide 42 Notify others Notification/communication can occur in several ways: Radio Telephone Pager Computer-based Direct, face-to-face Slide 43 Summary – Element 1 When preparing for observation and monitoring: Determine areas and/or people to be observed/monitored Identify, check and prepare surveillance and detection items, equipment and technology required Obtain necessary PPE Obtain and check required communication devices Identify and clarify required work for the shift (Continued) Slide 44 Summary – Element 1 Analyse and clarify requirements for assignment instructions Read necessary logs, reports and registers before starting work to update personal knowledge Plan the upcoming shift – what will be done, where and when Identify other staff required to support/assist Advise relevant others regarding start of work/departure for duty Slide 45 Implement observation and monitoring activities Performance Criteria for this Element are: Check identification cards Ensure authorised access to restricted areas Monitor entry into the premises Identify unattended items Identify banned/prohibited persons Observe people who are behaving suspiciously Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people Slide 46 Check ID cards Reasons to check ID: Verify person presenting ID is the rightful owner of the card Check age of person Prove permission to enter restricted areas Deter illegal activities (Continued) Slide 47 Check ID cards Track movement of people in the venue Ensure compliance with legal requirements Serve as basis for verifying answers given by customers to questions you ask them Slide 48 Check ID cards There are several types of cards which can be used as ID cards: Government-issued ID cards Venue-issued ID cards Authority/agency ID cards Slide 49 Check ID cards You may be required to check: Staff ID cards Visitor ID cards Supplier ID cards Patron ID cards Police ID cards/badges Slide 50 Check ID cards Process for checking ID cards: Demonstrate appropriate interpersonal skills Inspect the card Compare the photograph against the person presenting the card Ask their date of birth Conduct ‘other’ checks at the same time Scan/record the card Slide 51 Ensure authorised access Reasons to ensure only authorised access is allowed to restricted areas: Stop public from entering back-of-house areas Check tickets Allow delivery drivers access only into approved areas Check authority of visitors Identify and remove unauthorised persons Grant access to suitable authorised staff/persons Optimise venue, staff and patron security Meet legal compliance obligations Slide 52 Ensure authorised access Techniques to control access to restricted areas: Swiping ID cards Using physical barriers Visual recognition Inspecting/checking ID cards Using bio-metric technology Entering security codes Using sensors & alarms Slide 53 Monitor entry to premises Activities involved in monitoring entry: Standing near entry points/doors Observing people as they enter Talking to people as they walk in Checking ID Counting people Recording details Slide 54 Monitor entry to premises Access should be denied to: Unwanted persons: Those who have been barred/black banned Those who are subject to ‘exclusion orders’ Known trouble-makers Vagrants Self-excluded persons (Continued) Slide 55 Monitor entry to premises Under-age persons Intoxicated persons Anyone with a weapon Persons prohibited by legislation Persons ‘in excess’ of maximum patron numbers People trying to gain access after ‘lock out’ time Slide 56 Monitor entry to premises Do not prevent entry to people based only on: Age Gender Race Language spoken Disability Slide 57 Monitor entry to premises Steps in denying access: Be form Be polite Refrain from physical aggression Explain the reason Apologise Tell them they can come back later/tomorrow – if this is in fact true Try to give them a stake in the decision – what can you do for them? What useful suggestions can you make? Slide 58 Identify unattended items Need to promptly identify unattended items: To return a forgotten items to its owner Reduce chance of theft Allow emergency responses to be implemented if item is deemed ‘suspicious’ Slide 59 Identify unattended items Ways to identify unattended items: Being constantly alert to the possibility Actively searching for them Being advised by another person Responding to an alarm ‘Suspicious package’: There is no definition of what is a ‘suspicious package’ Err on the side of caution – best to be safe than sorry Slide 60 Identify unattended items To deal with an unattended item: Do not touch it Inform supervisor Notify authorities Make public announcement seeking owner Ask people nearby if the item belongs to them Leave package where it was found Cordon off the area Evacuate people Turn off anything likely to trigger an explosion Slide 61 Identify banned/prohibited persons Ways to identify banned or prohibited persons: Reading internal communications Talking to other staff Asking for the person’s ID As a result of communications from authorities Through alerts from technology Slide 62 Identify banned/prohibited persons If banned/prohibited person seeks to make a booking: Take details of the reservation Refuse the booking Be alert to possibility booking may be made later under different name and take appropriate action /advise person making the reservation they will be ‘refused’ on arrival Slide 63 Identify banned/prohibited persons To deny access to a banned/prohibited person: Advise other staff immediately Refuse entry Explain reason/s Apologise Stand your ground Ask them to leave Request they do not return Slide 64 Observe suspicious persons Reasons to identify and observe suspicious persons – to: Comply with assignment instructions Deter offenders Safeguard venue, patrons and staff Identify offenders Maintain ‘safe and secure’ image of the venue Slide 65 Observe suspicious persons ‘Suspicious’ person/behaviour: Difficult to define Can be ‘anyone – any age, any race, male or female Often determined by the context May be patron or staff member Slide 66 Observe suspicious persons Examples of suspicious behaviour: People who glance around furtively Someone who spends a lot of time browsing but not buying Someone wearing bulky clothes Anyone lingering around known ‘high risk’ stock Loiterers People found in restricted areas with no permission to be there Nervous drivers Slide 67 Observe suspicious persons Anyone who cannot provide proof-of-age Unknown workers/service providers Customers who appear anxious when you approach/talk to them People who give undue attention to others and or areas where there is cash Slide 68 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people Important background information: Golden rule: Act promptly – ‘nip it in the bud’ Realise everything you do (or do not do) is on public show – this means everything you do/do not do sends a message You cannot act on ‘hearsay evidence’ you must have first-hand evidence Slide 69 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people Keys in responding to unlawful acts: Know what constitutes an illegal act Notify CCC immediately of what you have discovered/identified Obtain assistance Intervene – as required Provide ‘first responder’ action – fight fire, give first aid Record evidence – preserve the scene Slide 70 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people Keys in responding to unacceptable behaviour: Know with certainty what the ‘house rules’ are Move closer & observe Notify CCC Talk to those involved and ask them to modify their behaviour/language Ask them to leave Escort people away/out of the venue Mingle with others and reassure them/apologise Maintain contact with CCC Slide 71 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people Activities involved in monitoring and observing suspicious persons: Covertly watch them Record activities Obtain assistance from others Ask for CCTV tracking and recording Slide 72 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people When immediately responding to a suspicious person situation: Notify others Approach the person Make eye contact Speak directly to them Ask them questions Detain them Direct them what to do Thank them for cooperation Apologise – if appropriate Slide 73 Respond to unlawful or suspicious incidents and people When immediately responding to a suspicious incident situation : Notify CCC Observe Investigate Slide 74 Summary – Element 2 When implementing observation and monitoring activities: Check ID cards as and when required of internal and external personnel Maintain civility and customer service to the best extent when checking IDs and undertaking other observation and monitoring activities Control access to, and patrol and monitor restricted areas Monitor and respond to alarms (Continued) Slide 75 Summary – Element 2 Monitor patrons as they enter the premises and certain areas within the venue to check age, behaviour, dress, language and intoxication Refuse entry to people as necessary Ensure all legal obligations are complied with by the venue and persons who are on the premises Be alert to the presence of unattended items and suspicious packages in the venue and respond promptly to these situations Identify and remove banned or prohibited persons (Continued) Slide 76 Summary – Element 2 Observe, monitor and respond suspicious persons and incidents Be sure to address problems quickly so troublesome situations can be 'nipped in the bud’ Never rely totally on hearsay evidence Respond appropriately to unlawful and suspicious events Respond appropriately to unacceptable behaviour and suspicious persons Realise everything you do and say in a public space is ‘on show’ to others in the area Slide 77 Determine apprehension of offenders Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Prepare for apprehension Slide 78 Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Citizen’s arrest: “A citizen's arrest is when you, as someone who is not a duly sworn police officer, detains a person because you know the other person is committing or has just committed an offence such as a theft, assault or criminal damage.” Detaining a person = a citizen’s arrest Can apply only to specific types of offences (refer Work Project 4.1) Slide 79 Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Points to consider when deciding whether or not to make a citizen’s arrest: Type of behaviour evaluated against legislation Having ‘reasonable grounds’ Personal safety Safety of others Timeliness of the arrest What force may be required? (Continued) Slide 80 Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Verify you have venue permission to make an arrest Check back-up is available Make sure you know the local laws regarding citizen’s arrests Make sure you know exactly who the offender is Be 100% sure of your facts – if in doubt, never make an arrest (Continued) Slide 81 Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Advise CCC of your intentions Wait for police if you believe the offender is likely to stay on the premises – and maintain ‘eyes on’ Try to have a male present when apprehending a male – and a female present when apprehending a female Be as quiet as possible when making the arrest Slide 82 Identify if lawful arrest should be effected Problems potentially associated with making an arrest: Legal action for wrongful arrest or detention: Criminal action Civil action Resistance from the offender Failure to cooperate Slide 83 Prepare for apprehension Planning to make a citizen’s arrest: Determine if assistance is needed Decide if you should make the arrest or if it is best to wait for police to arrive Plan your actions Ensure safety of others Consider protection of assets to best extent possible Determine how you will hold/restrain the offender Slide 84 Summary – Element 3 When determining apprehension of offenders: Ensure you fully understand the relevant laws of the country Know offences common to your industry/venue Always take consideration of making a citizen’s arrest seriously Realise detaining someone is usually the equivalent of arresting them Be aware of the legal action which can result from a false arrest Ensure you are totally sure of the identity of the offender (Continued) Slide 85 Summary – Element 3 Make sure you have proof Advise others of your intention to make an arrest Obtain back-up Delay the citizen’s arrest if possible until police arrive and let them deal with the situation Be sure your venue authorises you to make a citizen’s arrest Always consider your personal safety and the safety of others Plan what you will do, what you will say and how you will implement the arrest Slide 86 Arrest offenders Performance Criteria for this Element are: Observe legal rights of the offender Apprehend the offender Search the offender Maintain personal safety Detain the offender Slide 87 Observe legal rights of offender Rights of the offender after arrest vary between countries – you can learn what applies by: Speaking with venue solicitor Talking to police Reading legislation Researching on the Internet Asking management Attending specific training Slide 88 Observe legal rights of offender Need to respect legal rights of person who has been arrested: Avoid legal action Optimise chance of offender being prosecuted Inform offender of what is occurring Respect civil liberty and civil rights Demonstrate professionalism Slide 89 Observe legal rights of offender Possible rights of the offender after they have been arrested may include: To be told why they have been arrested Be subject only to use of ‘reasonable force’ To be treated with respect and decency Privacy Right to protection/safety Right not to cooperate with you Right not to speak/answer questions Right not to incriminate themselves Right not to be searched Slide 90 Apprehend the offender Pre-requisites for making a citizen’s arrest: Personal safety is optimised Safety of others is assured You have prepared a plan You are certain an offence has been committed and can identify the offender You believe the citizen’s arrest is the best course of action Slide 91 Apprehend the offender Alternatives to making a citizen’s arrest: Ignore the situation and take no action Look at the offender – let them know they are being watched Talk into your radio while observing the offender Talk directly to the person, ask them to modify behaviour and advise of consequences Ask them to leave the venue Slide 92 Apprehend the offender When making a citizen’s arrest: Approach the person following your plan Identify yourself Tell them you are arresting them Place a hand on them (Continued) Slide 93 Apprehend the offender Explain why they are being arrested Tell them of the evidence/proof you have Ask them to accompany you to certain location Restrain the person – if necessary Comply with all requirements of in-country legislation Slide 94 Search the offender After arrest you may want to search the offender – but: Local laws may not allow this You may be charged by police if you conduct an illegal search The offender may launch civil action against you Slide 95 Search the offender Reasons to search: Look for items which may cause injury Find evidence Identify the offender Slide 96 Search the offender It is usually illegal for you to: Frisk the person Forcibly submit them to a search Open their bags/possessions Slide 97 Search the offender It is legal to: Ask/request the person to turn out their pockets Ask permission to search their bags/belongings The best course of action is to leave the search process to police Slide 98 Maintain personal safety You must always maintain your safety when making an arrest and the safety of others – if you cannot guarantee this: Abandon the arrest Do not initiate the arrest Slide 99 Maintain personal safety When making an arrest it is vital to remember: You are not a police officer You are not paid to risk your life The venue carries insurance to cover most losses/damage Other evidence is likely to exist to enable police to follow-up Slide 100 Maintain personal safety Techniques to maintain safety: Secure/restrain the offender Getting back-up to assist Watching the offender Moving threats/potential weapons out of reach (Continued) Slide 101 Maintain personal safety Continue to use only ‘reasonable force’ (and only do this if necessary) Advise aggression will be met with force Move away from the offender Ask others to move away Advise others of potential risk Protect assets from danger/damage Slide 102 Detain the offender Once person has been arrested: They must be handed over to police as soon as possible Check to confirm police have been called/notified Contact/call police if this has not already been done Tell offender police have been called and are on the way Slide 103 Detain the offender While detaining an offender: Maintain/observe their rights Protect them against harm/injury Give first aid – if necessary Provide suitable responses to basic human needs Slide 104 Detain the offender Always adhere to internal requirements when a person has been arrested – these may include: Notifying management/designated person Recording details of the arrest on internal documentation Slide 105 Summary – Element 4 When arresting offenders: Be sure you have sufficient reason/proof to make the arrest Be convinced making an arrest is the best course of action Make sure the legal rights of the offender are maintained Protect the safety, well-being and human rights of the offender Notify the police as soon as possible to arrange transfer of custody (Continued) Slide 106 Summary – Element 4 Document the incident according to house policy capturing all relevant details Notify the offender they are under arrest Tell the offender why they have been arrested Only search the offender is permission to do so is given Do not frisk the person Detain the offender in accordance with local laws/requirements Slide 107 Fulfill administrative responsibilities Performance Criteria for this Element are: Complete necessary internal forms and reports Cooperate with the authorities to process the offender Cooperate with management in making recommendations to enhance patron and staff safety Slide 108 Complete forms and reports Requirements when completing documents: Documents and requirements vary between venues Must be completed in a timely manner Forms and reports usually need to be ‘forwarded’ Accuracy is vital Obtain in-house training Look at forms and reports competed by others Keep a copy Seek advice when unsure about what to do Slide 109 Complete forms and reports Forms will be either/or: Paper-based Electronic Slide 110 Complete forms and reports Forms and reports may include: Incident details/report, log or register Damage and loss assessments Patrol logs Insurance claims Witness statements Legally-required documentation Slide 111 Complete forms and reports Reasons to complete forms and reports: Provide source of information Establish legal cause Comply with management requirements Provide basis for evidence Assist investigation Monitor incidents and trends Slide 112 Cooperate with authorities to process offender Helping police may include: Being interviewed and making a statement Providing police with copies of internal forms/reports Sharing/showing evidence you have Picking offender from line-up Providing CCTV footage Verifying statements of offender Answering questions Explaining context of the incident Slide 113 Cooperate with management to enhance safety Ways to help management enhance safety: Engage with risk management activities Participate in staff meetings and briefings Participate in workplace inspections Attend relevant industry seminars, conventions and conferences Contribute ideas and suggestions (Continued) Slide 114 Cooperate with management to enhance safety Be willing to trial initiatives Complete all forms and reports as required Visit other venues to see what they are doing in relation to safety Develop and use an industry network of security people/staff Identify and analyse internal indicators of safety problems/issues Comply with management directives Slide 115 Cooperate with management to enhance safety Follow a two-stage approach for making recommendation: (1) Make verbal suggestion (2) Supplement with written recommendation: If management seems interested If requested Slide 116 Cooperate with management to enhance safety Include the following in written recommendations: Your name and contact details Date Rationale Action plan (Continued) Slide 117 Cooperate with management to enhance safety Recommendations for: Equipment, systems and technology Providers/suppliers Timelines Training required Staff/hours required Transitional arrangements Benefits anticipated Costs Slide 118 Summary – Element 5 When fulfilling administrative responsibilities: Complete all necessary documents following regular shifts & individual incidents Comply with venue requirements and legally imposed obligations Forward completed to documents to nominated person/s View what others have done to get a feel for what is required (Continued) Slide 119 Summary – Element 5 Seek to understand why reports and forms are required and what they are used for Work with authorities/police as required to process offender Support management in their efforts to enhance patron and venue safety Make informed suggestion to improve workplace safety Slide 120