CHEMISTRY
advertisement

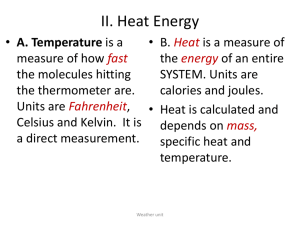
CHEMISTRY Nov 16, 2009 Warm Up • Name the different phase changes of a matter – For example: Solid Liquid (Melting) Agenda • Unit 4 Phase Changes Notes and Heat Transfer • Collect Progress Report • Homework – Phase Change Worksheet – Last Day for Make up Work : Wednesday – Research Project: Due Thursday/Friday Phase Changes • Explain how the addition and removal of energy can cause a phase change • To learn about interactions among water molecules. • To understand and use heat of fusion and heat of vaporization. • Interpret a heating/cooling curve for water Phase Changes • Refer to diagram – Six possible transitions between phases Phase Changes that Require Energy • What happens to molecules in a solid as it melts? • Melting – The amount of energy (heat of fusion) required to melt one mole of a solid depends on the strength of the forces keeping the particles together (Intermolecular force). Phase changes that require energy • When liquid water is heated, some molecules escape from the liquid and enter the gas phase. Phase changes that require energy • If a substance is usually a liquid at room temperature (as water is), the gas phase is called a vapor. • Vaporization is the process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor. • As temperature increases, water molecules gain kinetic energy – At Boiling point, molecules throughout the liquid have the energy to enter the gas or vapor phase. Phase changes that require energy • The process by which a solid changes directly into a gas without first becoming a liquid is called Sublimation. – Solid air fresheners and dry ice are examples of solids that sublime. Phase changes that release energy • Some phase changes release energy into their surroundings. • For example, when a vapor loses energy, it may change into a liquid. • Condensation is the process by which a gas or vapor becomes a liquid. It is the reverse of vaporization. Phase changes that release energy • Water vapor undergoes condensation when its molecules lose energy, their velocity decreases. • The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a crystalline solid. • When a substance changes from a gas or vapor directly into a solid without first becoming a liquid, the process is called deposition. – Deposition is the reverse of sublimation. Frost is an example of water deposition. Phase Change Diagram • Potential energy (Ep) – Stored energy • Energy of position • Chemical energy (gas or food) • Electrical energy (batteries) • Kinetic energy (Ek) – Motion • Mechanical energy • Radiant (Ed) – Heat/Light/Sound Summary: Phase changes (Refer to handout: Label phases, Label energy change, draw atomic diagram at each phase Temperature Heating Curve Energy or Time ) Practice Substance Freezing point (oC) Boiling Point (oC) Water 0.0 100.0 Gallium 23.0 89.0 Iron 723.0 2780.0 • At room temperature (27 oC), Iron is a solid, mixture, liquid or gas? • At 800 oC, Iron is a solid, mixture, liquid or gas? • During the process of heating water from 27 to 85 oC : – Did the potential energy change? Kinetic energy? – Is it an endothermic or exothermic reaction? Homework • Phase Change Worksheet Methods of Heat Transfer • http://www.wisconline.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=SC E304 Methods of Heat Transfer • Conduction: – Transfer of heat between substances that are in direct contact with each other • Occurs mainly in solid • Better conductor More rapid heat transfer – Examples of good and poor conductors? • Convection: – Up and down movement (circulation) of gases and liquids caused by heat transfer • Does not occur in solid (molecules not free to move around) • Examples of convection? • Radiation: – Electromagnetic waves traveling through space • Does not require a medium to transfer heat – Waves transfer heat to the object • Examples of radiation heat transfer? Practice Heat Transfer • Boiling water over a campfire • Melting a tub of ice cream on the kitchen counter • Electric Stove versus Gas Stove – Which stove will boil water faster? Why? • Why is the second floor usually warmer than the first floor? Why? Warm Up • Energy Conversions – Flash Light • A 20 g sample of water is put into a calorimeter and heated until its temperature increases from 60 to 80oC. If the specific heat of water is 4.184J/g.oC, calculate the heat absorbed by the water. Conversions • Converting between oC & oF – ºC = 5/9(ºF – 32) – ºF = 9/5 (ºC) + 32 • Converting between oC & K – ºC = K – 273 – K = ºC + 273 • Practice Problems – Convert 37 ºC to K – Convert 100 oF to ºC – Convert 50 oF to K Conversions • The breakfast shown in the photograph contains 230 nutritional Calories. • How much energy in joules will this healthy breakfast supply? Conversion factor 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1 cal = 4.19 Joules Calorimetry Practice Problems • What amount of heat would be given off by 3.0 x 103 g of water in order to lower its temperature from 95oC to 12oC? Practice Problem • If 5603 joules of heat is added to 5.6 g of water at a temperature of 15oC, what will the final temperature be? • What amount of heat would be given off by 7.0 x 103 g of water in order to lower its temperature by 5oC? Practice Problem • What is the specific heat of lead that has a mass of 30 g and undergoes a 250oC change while absorbing 229.5 calories? • Copper has a specific heat of 0.387 J/g.oC. What is the mass of a piece of copper that undergoes a 25oC temperature change when it absorbs 755 J of energy? Conversions • Converting between oC & oF – ºC = 5/9(ºF – 32) – ºF = 9/5 (ºC) + 32 • Converting between oC & K – ºC = K – 273 – K = ºC + 273 • Practice Problems – Convert 37 ºC to K – Convert 100 oF to ºC – Convert 50 oF to K Conversions • The breakfast shown in the photograph contains 230 nutritional Calories. • How much energy in joules will this healthy breakfast supply? Conversion factor 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1 cal = 4.19 Joules Practice Problems • Refer to handout – Specific heat problems CHEMISTRY September 29, 2010 Warm Up • Study for Quiz – 5 minutes Agenda • Quiz • Homework – Research Project Presentation • Due Thursday/Friday – Extra Credit: Dress Up Quiz 20. Draw what happens to kinetic energy in water as you cool it from 90oC to 10oC (Use circles to represent molecules! Use “whoosies” to represent speed of molecules) 21. What does it mean when an energy resource is said to be “renewable”? Provide 2 examples 22. What are “fossil fuels”? Which nonrenewable energy resources are “fossil fuels”?