Quality in the Rural Setting
advertisement

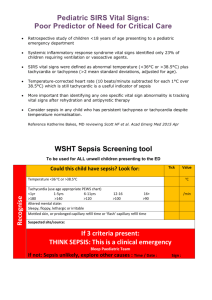
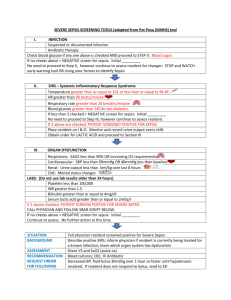
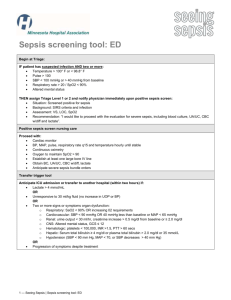
QUALITY IN THE RURAL SETTING COROMANDEL PENINSULA INTRODUCTION Thames hospital and it’s emergency department The quality framework team – what it’s been like 3 audit topics THAMES HOSPITAL Waikato DHB - 4 rural hospitals – Thames, Taumaraunui, Te Kuiti, Tokoroa – the 4Ts Variable skill base, resources and facilities Neale Thornton January 2008 Catchment Thames Hospital • Coromandel Peninsula from Waihi north and Hauraki Plains • Drive Time: 90 minutes to base • Population: 26000 year round Summer population 120900 • Presentations to ED: 15000 pa • Seasonal fluctuations, same infrastructure • Retrieval for severe trauma Neale Thornton February 2007 ED ATTENDANCES ANNUAL VARIATION Facilities/Services-Thames Hospital •48 bed IPU - Medical, Surgical, AT&R •High Acuity Room (3 beds) •Operating Theatres •Emergency Department 15 beds •Midwife-led Birthing Unit •Radiology 08.00-18.00 then on call •Laboratory 07.00-22.00 then on call •Outpatients MEDICAL STAFFING ED mix MO and rural hospitalists – extended role outside ED Physicians and surgeons based Thames Daylight SHOs, rural registrar training Visiting AT&R Many transfers – complexity, speciality, destination, weekends and PH, PATIENT TRANSPORT SERVICE Developed a PTS service enabling a scheduled transfer of patients between Thames and Waikato hospitals. St John’s with skilled transfer nurse Treatment en route Two way Neale Thornton January 2008 Application of the Quality Framework • Quality Framework Team: Clinical Lead (0.3FTE), CNM, 2IC (0.2FTE) • Monthly meetings of team • Feedback of results via M&M, ED business meetings, and heads of departments • Some support by request from IS and CASU. Neale Thornton January 2008 DATA COLLECTION – DON’T REINVENT THE WHEEL! Use what already is available – eg LOS data, time to be seen by decision making clinician DATA COLLECTION What goes in must come out – eg requesting reports by specific discharge codes. DATA COLLECTION Getting into hot water – analysing complaints, incidents and sentinel events Themes DATA COLLECTION Actively gathering feedback from patients and staff DATA COLLECTION Number 8 wire – develop our own audit tools from scratch Eg left before being seen – recoded, data collected daily, patient contacted next day, themes, safety. DATA COLLECTION – TRYING TO SEE THE WOOD FOR THE TREES! Unplanned representation rates within 48 hours of ED attendance 55 pages of raw data for 1 month After 3 hours sifting - 20 patients Several alternative reports available Filtering data to give useful reports. ED LOS - 6 H TARGET – KPI 95% Reasons for breach: July 2014 – 21 breaches Cause of Breach Number Bed access block 7 Department in Overload 0 Awaiting Transfer 3 Awaiting Results (CT) 1 Lack of resource – telemetry, watch 2 Uncertain destination 5 Administration – patient not placed in SSU/computer issue 2 Ongoing care – patient acuity 1 6 HOUR TARGET Transfers CT Departmental overload, summer, inadequate staffing Actions taken January 2015, re audit coming MORTALITY RATES FOR #NECK OF FEMUR July 2013 – June 2014 38 patients presented to Thames with fractured neck of femur. 8/38 subsequently died within 30 days. 30 day mortality = 21% (expected rate = 10%) 11/38 died within 4 months. 4 month mortality = 29% (expected rate = 20%) 12/38 died within one year. One year mortality = 31.5% (expected rate = 30%) WHY IS THIS? Time from injury to surgery – longer for rural patients Multiple delays in patient’s journey Must be in base hospital to be put on surgical list What can be done? Use of NoF clinical pathway Discussion with CD orthopaedics Discussion with St John re priority transfer Dissertation topic TIME TO ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS July 2013 - June 2014 Total: 19 patients; 17 met criteria at triage, 2 had received IV antibiotic prior to ED Average time to first antibiotics: 2 hours 47 minutes Deaths: 2/17 (11.7%) Total no patients received 1st antibiotic dose within 60 min (Sepsis 6 goal) 3/15 - 20% TIME TO ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS After the initial audit, a sepsis treatment pathway was implemented in Thames ED. This pathway is based on the Waikato sepsis pathway and follows international guidelines for sepsis treatment in ED. TIME TO ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Re-audit: Oct 2014 to Feb 2015 (5/12 period) 10 patients presented to Thames ED with “sepsis” diagnosis 9 patients met sepsis criteria Average time to first antibiotics: 108 minutes (1 hour and 48 minutes) Deaths: 1/9 = 11.1% mortality Use of Sepsis Pathway: 2/9 = 22.2% use Total no patients received 1st antibiotic dose within 60 minutes (Sepsis 6 goal) 1/9 = 11.1% BENEFIT OF SEPSIS PATHWAY Average time to antibiotic – 2h 47m prior to pathway -1h 48m after pathway. Antibiotic within 60 min - 20% to 11% Use of sepsis pathway 22.2% TIME TO ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS : ACTION Promotion of use of sepsis pathway and assessment tool Audit nursing documentation - use of assessment tool Place pathway at triage to ensure that paperwork is accessible Re-audit Sept 2015 Better awareness among medical staff. Locums too. FUTURE DIRECTION ISSUES SPECIFIC TO THAMES Sometimes difficult to compare statistics directly- due to transport and available services. No IS service on site so getting specific data can be delayed. Small team, time constraints Small team, ability to bring about change LOST IN THE BUSH – WHEN TO ASK FOR HELP! How to define ED overcrowding measures? Time to analgesia tool? BENEFITS OF QUALITY FRAMEWORK Quality is not geographical – it applies to rural hospitals as much as metropolitan hospitals Unsuspected areas for improvement have been unearthed (Thames is a goldmining town!) It is encouraging to align ourselves with national framework and see how we compare OVERVIEW OF AUDITS UNDERTAKEN Patient journey time stamp ED LOS Waiting time from triage until time seen by decision making clinician ED overcrowding ED demographic measures ED occupancy >100% UPRA ED quality processes M&M Sentinel events Complaint review and response Staff experience evaluations Patient experience Patient experience evaluations measures Left before seeing doctor or decision making clinician OVERVIEW Clinical quality audits Documentation and communication Performance of SSU Education and training profile Departmental education programme Administration profile Mortality rates for #NOF and STEMI Time to thrombolysis Time to adequate analgesia Time to antibiotics in sepsis Procedural sedation Others – DVT, cellulitis, pneumonia, transfers outside scheduled PTS Nursing notes, medical notes, medication Appropriate orientation with feedback Designated quality team