Cold War 1945-1960

Postwar America 1945-1960
Chapters 24 and 25
Potsdam Conference
Divided Germany into 4 zones controlled by US, USSR, GB, and
France
Eliminated the Nazi Party
Rebuild German Industry
Moved Germans in other territories back to Germany
Potsdam Problems
Stalin refuses to allow elections in new Eastern European nations
Stalin also wants complete control of half of Germany
Churchill loses re-election while at the conference
It is at Potsdam that the other Allied leaders are informed of the Atomic
Test
Japan
US occupied Japan from 1945 to 1952
Emperor Hirohito remained with NO power,
Premier Hideki Tojo was sentenced to death by a Military Tribunal
Gen MacArthur was given the responsibility to write a new constitution
1947 Constitution: A democratic system was set up, freedom of religion and the right of women to vote were included
Japanese military was dismantled to ensure an end to the militarism
Most Japanese accepted the constitution
Nuremberg Trials
War Trials were setup in one of Hitler’s most supportive cities, Nuremberg
12 Nazi leaders were sentenced to death
Others avoided prosecution by leaving
Germany before the surrender and going to safe havens in South and Central America
At the trials survivors gave vivid accounts of the atrocities brought on by the Nazi’s
Most of the men who took the stand claimed they were simply “following orders”
United Nations
Drawn from the League of Nations it to was designed to prevent wars and foster peace
General Assembly: all members
Security Council: 5 permanent members (US, Britain, Russia, China, and France) and 10 rotating members
Security Council can veto a General
Assembly motion
Founding of Israel p. 836
1.
What is Zionism? Why is it a problem?
2.
What happened when Britain withdrew from Palestine in 1948?
3.
What countries attacked the new Israeli state?
4.
Why were they able to fight them off?
5.
Who is Ralph Bunche?
6.
How did the final 1949 agreement resolve the conflict?
7.
Is this the end of the problems in
Palestine?
Quiz: Section 1 T/F
1.
At Potsdam, Germany was divided into 3 zones between USSR, USA and Great
Britain.
2.
The Emperor and the Premier were both executed after WW2.
3.
Eisenhower is sent to help write a new
Japanese Constitution.
4.
At the Nuremberg Trials more than 100
Nazi leaders were killed.
5.
The United Nations Security Council has 5 permanent members.
COLD WAR Begins
Chapter 25 Section 1
Cold War: Political standoff between
Democracy and Communism
Begins due to American mistrust of Soviet motives in Eastern Europe
The USSR intended to occupy nations in
Eastern Europe in order to install
Communist governments to help ensure their safety from Germany and the Western
Powers (USA, Great Britain)
Cold War: Page 852
1.
Satellite State:
2.
Containment:
3.
What countries did the USSR control by the end of WW2?
4.
What did Churchill claim the USSR had done to Europe?
Cold War
1.
Satellite States: Countries under Soviet control, most had “puppet” communist governments
2.
Containment: US and British policy of stopping the Soviet Communist spread
3.
What countries did the USSR control by the end of WW2? (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, parts of Poland and Romania)
4.
What did Churchill claim the USSR had done to Europe? (He said an “Iron
Curtain has descended across the continent”)
Atomic Age
1.
What are the Baruch Plan? (BP was an international organization that would impose penalties on countries violating nuclear restrictions)
2.
Atomic Energy Act? (AEA created a commission that oversaw nuclear research and promoted the use of peacetime atomic energy)
Crisis in Berlin
Page 851
1.
What was the cause of the Berlin
Airlift?
2.
What is NATO and what was the
Soviet response to it?
Crisis in Berlin
Page 851
1.
What was the cause of the Berlin
Airlift? (Soviets had blocked access to
Berlin in an effort to keep the Western
Powers out. US and Britain airlifted food and supplies to people of Berlin.
The blockade failed.)
2.
What is NATO and what was the Soviet response to it? (North Atlantic Treaty
Organization: promised to defend one another from attack. Soviets respond with the Warsaw Pact.)
Greece
1946-Civil War erupts between Communist and British backed Greek monarchs
1947-Britain stops aiding Greece
1947-Russia takes land from Greece to control the Mediterranean and Black Seas
1947-Truman Doctrine: The US will aid
ANY country who wishes to fight communism (Korea, Vietnam, etc.)
1948-US gives $400 million to aid Turkey and Greece
Marshall Plan (E.R.P.)
George C. Marshall, Truman’s Sec of State
European Recovery Program: Thought that if the US helped countries in Europe financially they could fight off communism
Truman requested $17 billion for European aid in 1948
After the Soviets overthrew the Czech government the aid for Marshall Plan was granted
Marshall won the Nobel Peace prize for his efforts, he later served as Sec of Defense for
Truman to deal with wars against communist countries
Quiz Section 2 T/F
1.
Satellite nations were countries in
Eastern Europe with Soviet friendly
Communist governments.
2.
During the Berlin Airlift the US and
Britain brought food and supplies to West
Berlin breaking the Soviet blockade.
3.
The US never joins NATO.
4.
The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any country being threatened by Communism.
5.
The Marshall Plan, although supported by
Truman, is never enacted into law.
Communism In China p. 854
1.
Who was the leader of the Chinese
Nationalist forces?
2.
Who led the Chinese Communists?
3.
What agreement did the Communists and Nationalists make during WW2?
4.
In what way did the US aid the
Nationalists?
5.
What was the eventual outcome?
Korean War
1945-Korea is divided into 2 zones. North is Communist, South is occupied by US.
Division is at the 38 th parallel
1948-N. Korea (Kim Il Sung) S. Korea
(Sygmun Rhee) set up government
1949-US and USSR leave Korea as tensions increase
1950-North Korea invades South
1950-Truman responds by sending troops to help the South led by MacArthur
Korean War continued
Sept. 1950-South Korean and US forces are pushed to tip of Korea near
Pusan
Late Sept 1950-MacArthur counterattacks at Inchon, and recaptures Seoul(capital of South
Korea)
Nov 1950-China enters war on North
Korean side and stalemate ensues along the 38 th parallel
Korean War continued
1951-MacArthur publicly states that he would like to “bomb” China, Truman refuses
1951-MacArthur publicly criticizes Truman and goes to Congress for help
1951-Truman fires MacArthur (replaced by
Gen. Ridgeway) MacArthur returns to heroes welcome
1952 –Eisenhower becomes President
Korean War continued
1953-Eisenhower begins massive bombing campaign
July 27 th , 1953-Armistice is signed keeping the 38 th parallel as a boundary
54,000 US Soldiers die
Considered a victory because the spread of communism is stopped
Election of 1952
Truman’s popularity had hit a low thanks to
Korea, chooses not to seek re-election
Republicans saw a chance to break the 20 year Democratic White House
Republicans: Eisenhower (Nixon)
Democrats: Stevenson (Sparkman)
Eisenhower’s patriotic appeal made him a favorite, “I like Ike” was his slogan
Wins by large margin, 442-89
CIA/US Intervention
Page 863-865
Outline the CIA involvement in these 4 instances
Iran
Guatemala
Suez Canal
Hungary
CIA
Iran (1951) Leader is replaced by CIA because he nationalized British owned oil. Shah(dictator)is placed in power and Iranians become Anti-American.
Guatemala (1954) Democratically elected President is assassinated by CIA for being a “communist sympathizer”. He had redistributed land to the poor.
Suez Canal (1955) West and Russia almost come to war when Egypt nationalizes a dam that the US promised to finance but did not. France, Britain and Israel occupy one end of the canal near the Mediterranean Sea and
Russia threatens to use force if they don’t leave.
Hungary (1956) Hungarian Revolution, 40,000
Hungarians flee to US…Revolution fails and USSR maintains control of Hungary after bloody conflict
U2 Incident
1.
What did US officials first say the U-2 plane was doing over USSR?
2.
Who was the pilot?
3.
How did Eisenhower and Khrushchev respond to the incident?
U-2 Incident
1.
What did US officials first say the U-2 plane was doing over USSR? (Spying on military bases in the USSR)
2.
Who was the pilot? (Gary Powers)
3.
How did Eisenhower and Khrushchev respond to the incident? (Eisenhower refused to apologize and relations with
USSR deteriorated, Powers was found guilty of espionage and served 1 year and
9 months in Soviet jail)
Quiz Section 3 T/F
1.
Chaing Kai Shek led the Communist
Revolution in China.
2.
MacArthur wanted Truman to use an
Atomic bomb in China.
3.
Eisenhower easily won the election of
1952.
4.
At the end of the Korean War the 38 th parallel was set as a boundary, same as before the war.
5.
The CIA used force to depose of other countries leaders during the 1950’s.
Define and Identify
Page 868-875
NSC
HUAC
Hollywood 10
McCarthyism (Page 874)
Define and Identify
McCarthyism: Senator Joe McCarthy creates Anti-Communist hysteria in America urging the government to search for and arrest communist sympathizers
(McCarthyism)
HUAC: Investigated suspected communists, mostly in Hollywood
Hollywood 10: California directors and film writers who chose to go to jail rather than speak to the HUAC, they were blacklisted in Hollywood thereafter
Court Cases
Alger Hiss vs. Whitaker Chambers
Ethel and Julius Rosenberg
Ethel and Julius Rosenberg
Convicted of selling atomic energy secrets to Russia
Proof is shaky, both are found guilty and executed (electric chair)
Hiss v Chambers
Whittaker Chambers, former communist, accuses Alger Hiss (state dept worker) of being a communist
Hiss denies charges, sues Chambers
Chambers produced “Pumpkin
Papers” to prove Hiss lied to HUAC
Hiss is accused of perjury, 5 years in jail
Page 861
1.
How powerful is the hydrogen bomb?
2.
In what ways did the US government try to ease the fears of US citizens?
3.
Do you believe that these government suggestions would have helped in case of nuclear war?
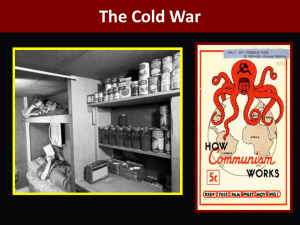
Cold War Fears
In 1949 the USSR tested its first atomic bomb
By 1951 the US had developed a new type of bomb, the H-Bomb or
Hydrogen Bomb (it was equivalent to 10,000,000 tons of TNT compared to the Trinity test at Alamogordo that measured 20,000 tons)
Duck and Cover (1951)
Space Race (define)
Sputnik
NASA