Circulatory System - Mr. Lambdin's Biology
advertisement

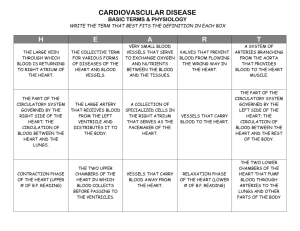
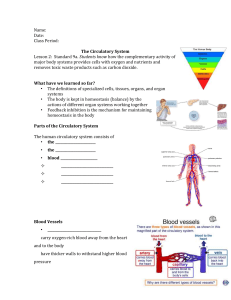
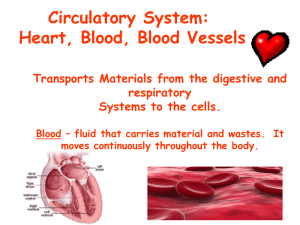
Circulatory System Chapter 37 Function • Transportation system • Brings oxygen, food, and chemical messages to cells What type of organisms have Circulatory Systems? • Large organisms – cells don’t come into contact with the environment (need circulatory system) • Small organisms – oxygen, nutrients, and waste can diffuse directly through the cell membrane and out of the organism Closed vs. Open Circulatory Systems • Closed = circulating fluid (blood) is contained within blood vessels (most vertebrates) • Open = circulating fluid enters and leaves vessels (insects) Organs of the Circulatory System • Heart • Blood Vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) • Blood The Heart • Receives and pumps blood • size of a clenched fist • Pericardium = protective tissue around heart • Myocardium = heart muscle • contracts ~72 times/minute • ~70 mL of blood each contraction 4 Chambers of the Heart • Right Atrium: receives oxygen poor blood from the body • Right Ventricle: pumps oxygen poor blood from the heart to the lungs • Left Atrium: receives oxygen rich blood from the lungs • Left Ventricle: pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of the body Circulation Through the Body • Pulmonary Circulation – right side – pumps blood from the heart to the lungs • Systemic Circulation – left side – pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body Circulation Through the Heart 1. Blood gets oxygen in lungs 2. Oxygen-rich blood enters Left Atrium 3. Oxygen-rich blood pumped to Left Ventricle 4. Oxygen-rich blood pumped to rest of body 5. Oxygen-poor blood returns to Right Atrium 6. Oxygen-poor blood pumped to Right Ventricle 7. Oxygen-poor blood pumped back to Lungs Heart Valves • Flaps of tissue between chambers • Keep blood from going backwards • increases pumping efficiency • 4 valves in the heart Heartbeat • Pacemaker cells in right atrium trigger heart to contract • Contraction flows like a wave through heart • Atria Contract = Pumps blood to Ventricles • Ventricles Contract = Pumps blood out of Heart • Increases during exercise Atherosclerosis • Cholesterol and fats build up in arteries • Forms a plaque that prevents blood passage • Plaque in heart = Heart Attack (most common) • Plaque in brain = Stroke • Plaque in arms or legs = Gangrene • Process sped up by high cholesterol, smoking, high blood pressure, stress Aortic Aneurysm • The main artery leading out of the heart weakens • Balloons and explodes if not treated • 15,000 Americans die/year from aneurysms • Can be fixed with surgery • Cause = smoking, high blood pressure, infection, other??? Congenital Heart Disease • Structural birth defect of the heart • 30,000 babies born with it in USA each year • Many Types – Abnormal passages in the heart or between blood vessels – Problems with the heart valves – Problems with development of the heart itself. • A blood vessel leading to the brain is blocked by a clot or ruptured • No oxygen to brain = part of the brain dies • Result = loss of movement, speech, memory, vision, etc… • 700,000 Americans/year have a stroke • #3 Killer in America Stroke Blood Vessels and Blood Chapter 37-1 and 37-2 Arteries • Largest blood vessel • Contain muscle tissue for contracting • Almost all carry oxygen-rich blood • Carry blood away from heart to other tissues • (ex.) Aorta, Carotid Artery Veins • thinner walls • lined with muscle for contracting • large veins have valves to keep blood moving towards the heart • pumps mostly oxygen-poor blood to the heart • (ex.) Pulmonary Vein, Vena Cava Capillaries • Smallest • Walls are one-cell thick • Nutrients and waste pass through easily • Important for gas exchange Blood Pressure • The force of blood on artery walls • Caused by the heart pumping blood • Sphygmomanometer = measures blood pressure and gives 2 numbers (120/80) – 1st Number = Systolic Pressure = force felt by arteries when ventricles contract – 2nd Number = Diastolic Pressure = force felt by arteries when ventricles relax Blood Functions • Collects oxygen, nutrients, and wastes • Regulates body temperature • Fights infections • Repairs damaged blood vessels Blood Plasma • 55% of your blood volume • straw-colored liquid • 90% water, 10% gases, salts, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, waste, proteins • what blood cells float in Red Blood Cells • • • • • Erythrocytes most numerous cells in the blood 1mL of blood = 5 mill RBC’s transport oxygen Hemoglobin = iron-protein that binds to oxygen (give blood red color) • Last ~120 days and then are destroyed in the liver and spleen • Shaped like a disk White Blood Cells • Leukocytes • produced in the bone marrow of large bones • they guard against infection, fight parasites, and attack bacteria (part of the immune system) • # is increased during an infection Platelets • Help to clot blood • produced in bone marrow • stick to broken blood vessels and form a barrier until other cells can permanently repair the vessel High Blood Pressure (hypertension) • Too much pressure on arteries/heart works harder • Hardening of the blood vessels, bloodshot eyes, stroke, kidney failure, death • Causes: genetic and environmental (overweight, aging, smoking, diet) • 1 in 4 people Anemia • Not enough red blood cells • Body can distribute enough oxygen • Tired, weak, pale, rapid heart beat, heart failure Leukemia • Cancer of the bone marrow and blood • uncontrolled accumulation of functionless cells • not enough red and white blood cells made • easy bruising or bleeding, paleness, fatigue, recurrent minor infections, poor healing cell count) Hemophilia • • • • Absence of proteins that clot blood unable to stop bleeding from cuts internal bleeding and deep bruising could lead to death if untreated Varicose Veins • Twisted and enlarged veins • muscle around vein weakens from too much pressure • always on your feet • occurs mostly in older women • mostly a cosmetic problem Respiratory System Chapter 33 Function • Brings oxygen to the body and rids the body of carbon dioxide • Nose and Mouth: where air comes in and leaves, filter • Epiglottis: protects food from going down the trachea • Larynx: vocal cords/voice box • Diaphragm: dome-shaped muscle under chest cavity Major Organs • Trachea: passage to lungs/windpipe (tree trunk) • Bronchi: 2 branches from trachea to lungs (main limbs of tree) • Bronchioles: very small air passages (branches and twigs) • Alveoli: air sacs in grapelike clusters, where gas exchange occurs (leaves) Gas Exchange • Occurs in the capillaries on the alveoli • Carbon dioxide waste goes in and oxygen goes out • Process of diffusion Breathing • Inhale (breathe in): diaphragm contracts, size of chest cavity increases and fills with air • Exhaling (breathe out): diaphragm relaxes, chest cavity size decreases and pushes air out • Controlled by brain stem Smoking • Foreign particles are allowed to enter lungs • Increased mucus production (smokers cough) • Less air flow to alveoli (tire easily) • Tar builds up in lungs, goes to blood stream = cancer Emphysema • Loss of elasticity in alveoli • Makes breathing difficult (less gas exchange) • 85% of cases caused by smoking • Quit smoking or death Lung Cancer • Lung cells dividing at an uncontrollable rate • Spreads quickly through out body • Causes more deaths than any other cancer • Over 200,000 deaths in the USA • 87% of deaths were smoking related