V: 0
advertisement

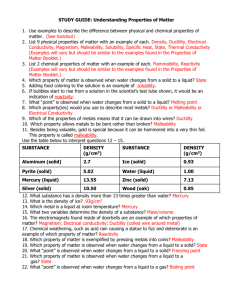
DO NOW V: 0 Monday Answer the following question on a post-it note. SHOW YOUR WORK!! What is the identity of a substance that has a mass of 72 grams and a volume of 9 cm3? Today’s Agenda Material Density (g/cm3) Aluminum 2.7 Brass 8 Copper 8.9 Steel 7.6 -Cornell Notes -Density Practice -Archimedes Dilemma Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. TEKS 8.5 (D) Recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts 8.5 (E) Investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed 8.5 (F) Recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. 6.6 (A) Compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability 6.6 (B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance; and 6.6 (C) Test the physical properties of minerals, including hardness, color, luster, and streak. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does the structure of matter affect its identity and properties? - How do we describe and classify matter? - What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction? - What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? - What are the signs that a chemical changes has occurred? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will calculate the density of unknown and known substances. VOCABULARY Mass Volume Density Physical Property Chemical Property Metal Nonmetal Metalloid Luster Malleability Conductivity Magnetism Chemical Formula Subscript Coefficient Chemical Reaction Chemical Formula Chemical Equation Reactant Product Yield Balanced HOMEWORK & AGENDA Grade Level -Density Worksheet Pre-AP -Density Worksheet Today’s Agenda -Cornell Notes -Density Practice -Archimedes Dilemma Density Presentation V: 0 Take Cornell Notes from the Density PresentatioN. Density Practice Complete the Calculating Density worksheet. V: 0 Archimedes Dilemma Archimedes Dilemma V: 0 DO NOW V: 0 Tuesday Answer the question on the Do Now handout. Today’s Agenda -Physical Properties of Matter -Physical Properties Stations Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. TEKS 8.5 (D) Recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts 8.5 (E) Investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed 8.5 (F) Recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. 6.6 (A) Compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability 6.6 (B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance; and 6.6 (C) Test the physical properties of minerals, including hardness, color, luster, and streak. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does the structure of matter affect its identity and properties? - How do we describe and classify matter? - What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction? - What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? - What are the signs that a chemical changes has occurred? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will compare the physical properties of metals and nonmetals. VOCABULARY Mass Volume Density Physical Property Chemical Property Metal Nonmetal Metalloid Luster Malleability Conductivity Magnetism Chemical Formula Subscript Coefficient Chemical Reaction Chemical Formula Chemical Equation Reactant Product Yield Balanced HOMEWORK & AGENDA Grade Level -Density Worksheet Pre-AP -Density Worksheet Today’s Agenda -Physical Properties of Matter -Physical Properties Stations Physical Properties V: 0 Complete the Properties of Matter Vocabulary handout as much as you can. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 The amount of matter in a given amount of space. Physical Properties ____Density_______ V: 0 The amount of matter in a given amount of space. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Amount of matter in a substance. Physical Properties _____Mass________ V: 0 Amount of matter in a substance. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Unit of measurement for mass Physical Properties _____Grams_______ V: 0 Unit of measurement for mass Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Units of measurement for volume Physical Properties __mL or cm3____ V: 0 Units of measurement for volume Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Malleable, shiny, good conductor of heat and electricity, located on the left side of the Periodic Table. Physical Properties ___Metals_________ V: 0 Malleable, shiny, good conductor of heat and electricity, located on the left side of the Periodic Table. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Brittle, poor conductor, dull luster, located on the right side of the zigzag line on the Periodic Table. Physical Properties __Nonmetals_______ V: 0 Brittle, poor conductor, dull luster, located on the right side of the zigzag line on the Periodic Table. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Has properties similar to metals and nonmetals, located along the zigzag line on the Periodic Table. Physical Properties __Metalloids_______ V: 0 Has properties similar to metals and nonmetals, located along the zigzag line on the Periodic Table. Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Ability of an object to reflect light Physical Properties ____luster_________ V: 0 Ability of an object to reflect light Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Ability to transmit heat and/or electricity Physical Properties __conductivity____ V: 0 Ability to transmit heat and/or electricity Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Able to be hammered into sheets Physical Properties __malleable________ V: 0 Able to be hammered into sheets Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 Units of measurement for density Physical Properties _g/cm3 or g/mL___ V: 0 Units of measurement for density Physical Properties _________________ V: 0 The amount of space an object takes up. Physical Properties __volume_________ V: 0 The amount of space an object takes up. Physical Properties Stations V: 2 TASK: Compare the physical properties of metals and nonmetals. INSTRUCTIONS: - Create the table below on the next blank page of your INB. Element Name Aluminum Sulfur Copper Iron Carbon Magnetic? Luster Conduct Electricity? Malleable or brittle? Group # Metal or Nonmetal Physical Properties Stations V: 2 TASK: Compare the physical properties of metals and nonmetals. INSTRUCTIONS: Gets a tray of materials. - Use the materials to test the substances using the following physical properties: Luster, Magnetism, Malleability, Conductivity - The teacher will come to each group with the device to test conductivity. - Complete the table as you test the substances. Put tray away. Exit Ticket Exit Ticket V: 0 DO NOW Wed/Thrs Today’s Agenda V: 0 Answer the question below under your Physical Properties Lab Data Table. 1. Where are metals found on the Periodic Table? 2. List 3 properties of metals. -Chemical Properties/Changes Stations Lab -Physical and Chemical Changes Reading -Frayer Model Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. TEKS 8.5 (D) Recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts 8.5 (E) Investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed 8.5 (F) Recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. 6.6 (A) Compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability 6.6 (B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance; and 6.6 (C) Test the physical properties of minerals, including hardness, color, luster, and streak. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does the structure of matter affect its identity and properties? - How do we describe and classify matter? - What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction? - What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? - What are the signs that a chemical changes has occurred? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed and will compare physical and chemical changes. VOCABULARY Mass Volume Density Physical Property Chemical Property Metal Nonmetal Metalloid Luster Malleability Conductivity Magnetism Chemical Formula Subscript Coefficient Chemical Reaction Chemical Formula Chemical Equation Reactant Product Yield Balanced HOMEWORK & AGENDA Grade Level -Density Worksheet Pre-AP -Density Worksheet Today’s Agenda -Chemical Properties/Changes Stations Lab -Physical and Chemical Changes Reading -Frayer Model Chemical Properties/Changes Lab V: 2 TASK: Observe chemical reactions. INSTRUCTIONS: - Create the table below on the next blank page of your INB. Station Observations 1 2 3 4 Summary of Station Chemical Properties/Changes Lab TASK: Observe chemical reactions. INSTRUCTIONS: - As a table group, complete each station. - Record your observations in your data table. - Answer the lab questions. V: 2 Frayer Model V: 1 1. Complete a Frayer Model for Physical Change and Chemical Change. 2. Below the chemical change frayer model, write 7 different signs that a chemical change has occurred: • Change of color • Temperature change • Precipitate forms • Bubbles • Gas • Light or sound is produced Exit Ticket RM 4 – Properties of Matter White Board Practice V: 1 DO NOW V: 0 Friday Complete the Chemical vs. Physical Changes handout. Today’s Agenda -Chemical Reactions/Equations Reading -Cornell Notes -RM 50 and 51 Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. TEKS 8.5 (D) Recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts 8.5 (E) Investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed 8.5 (F) Recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. 6.6 (A) Compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability 6.6 (B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance; and 6.6 (C) Test the physical properties of minerals, including hardness, color, luster, and streak. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does the structure of matter affect its identity and properties? - How do we describe and classify matter? - What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction? - What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? - What are the signs that a chemical changes has occurred? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed and will compare physical and chemical changes. VOCABULARY Mass Volume Density Physical Property Chemical Property Metal Nonmetal Metalloid Luster Malleability Conductivity Magnetism Chemical Formula Subscript Coefficient Chemical Reaction Chemical Formula Chemical Equation Reactant Product Yield Balanced HOMEWORK & AGENDA Grade Level -Density Worksheet Pre-AP -Density Worksheet Today’s Agenda -Chemical Reactions/Equations Reading -Cornell Notes -RM 50 and 51 Chemical Reactions/Equations Reading: Chemical Reactions/Equations Cornell Notes: - Subscript - Coefficient - Reactants - Products - Yield - Law of Conservation of Mass V: 3 RM 50 & 51 Read RM 50. Complete RM 51. V: 1