View Content - DAIDS Learning Portal
advertisement

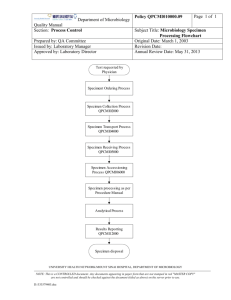
Laboratory Quality Management Version 6.0 August 2012 This project has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the Division of AIDS (DAIDS), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, under contract No. HHSN272201200009C, entitled NIAID HIV and Other Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Support Services (CRSS). Objectives 2 Define the key elements of Quality Management (QM) Describe the benefits of a Quality Management Plan (QMP) Describe the key elements of Quality Control (QC) Define the statistical tools used in standard QC calculations Explain the importance of monitoring key quality indicators Explain the importance of external assessments and internal audits Define the elements of a Quality Improvement process Pre-Assessment Question #1 Which of the following are key elements of Quality Management? A. Quality Assurance B. Quality Control C. Regulatory Affairs D. A and B E. B and C F. All of the above 3 Pre-Assessment Question #2 Which of the following are benefits of establishing and maintaining a Quality Management Plan? A. Improve clinical trial outcomes B. Increase productivity and efficiency C. Reduce risk of medical errors D. All of the above 4 Pre-Assessment Question #3 Which of the following are elements of Quality Control? A. Policies B. Performance/Documentation C. Reviews D. All of the above 5 Pre-Assessment Question #4 This statistic measures the central tendency of a set of data: A. Mean B. Standard Deviation C. Range D. None of the above 6 Pre-Assessment Question #5 The following are examples of post-analytic quality indicators: A. Customer satisfaction B. Specimen preparation C. Reporting abnormal/critical test results D. Turnaround time E. A and C 7 Pre-Assessment Question #6 To implement an effective Proficiency Testing (PT)/ External Quality Assurance (EQA) program, laboratory staff must: A. Demonstrate evidence of review of the PT/EQA report B. Implement necessary Corrective Action/Preventive Action (CAPA) C. Rotate PT/EQA samples among all testing personnel D. All of the above 8 Pre-Assessment Question #7 The elements of the Quality Improvement process are: A. Prepare, Decide, Study, Act B. Plan, Do, Study, Act C. Plan, Do, Study, Communicate 9 Glossary 10 Quality: The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs Quality Management: The overall system that includes all activities involved in Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) including the assignment of roles and responsibilities, the reporting of results, and the resolution of issues identified during the review Glossary (cont’d) 11 Quality Assurance: A periodic, systematic, objective, and comprehensive examination of the total work effort to determine the level of compliance with accepted Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards Quality Control: The real time, on-going (“day-to-day”) observation and documentation of a site’s work processes to ensure that accepted procedures are being followed Quality Improvement: Part of quality management focused on increasing the ability to fulfill quality requirements Division of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (DAIDS) Policies Risk Assessment Documented Key Points All Aspects of Services 12 Include EQA and Quality Control Quality Management Plan (QMP) Communicates Information About The mission The scope of and goals of laboratory the laboratory activities Assigning responsibilities Establishing laboratory’s commitment to quality Providing framework for the laboratory documentation Promotes Standardization and Consistency 13 Benefits of a QMP Streamline laboratory processes Enhance employee potential Meet accreditation requirements Reduce risk of medical errors Improve study participant care Increase productivity and efficiency Reduce costs Improve clinical trial outcomes 14 Laboratories Without QMP Experience 15 • Lack of standardization • Unsatisfied customers • Unsafe environment (for study participants and staff) • Fiscal irresponsibility Top Issues Found During Audits 1. Assay validation 2. Approval and attestation signatures on standard operating procedures (SOPs) 3. Parallel testing 4. Supervisor review of QC, EQA, maintenance records 5. Temperature monitoring on weekends and holidays 6. Personnel training/competency 7. Pipette calibration 8. Improper storage of reagents, QC, and calibrators 9. EQA corrective action 10. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) not present in the laboratory 16 Quality Control (QC) QC “…procedures for monitoring the work processes, detecting problems, and making corrections prior to delivery of products or services. Statistical process control, or statistical quality control, is the major procedure for monitoring the analytical performance of laboratory methods. ” 17 Elements of Quality Control Policies Performance/Documentation Review Corrective action 18 QC Nomenclature Mean: The average of a data set _ X = ∑xi/n 19 QC Nomenclature (cont'd) Trend + 2SD +1SD Mean -1 SD -2 SD 20 QC Nomenclature (cont'd) Shift + 2SD +1SD Mean -1 SD -2 SD 21 QC Nomenclature (cont'd) Standard Deviation (SD): A measure of the dispersion or variation in a distribution _ ∑ (Xi – X)2 (n-1) . SD = 22 QC Nomenclature (cont'd) Coefficient of Variation (CV): A measure of the dispersion or variation in a distribution 23 QC Tools – Westgard Rules +3 sd +2 sd +1 sd Mean -1 sd -2 sd -3 sd 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Date 24 Quality Control Multi-Rule Flowsheet 25 What do you see? 26 Quality Indicators Which Key Quality Indicators do you monitor within your laboratory? Which Key Quality Indicators should you monitor within your laboratory? 27 Most Frequently Monitored 28 External Quality Assurance Performance Internal Quality Control Laboratory Operations Pre-Analytic Tasks 29 Analytic Tasks Post-Analytic Tasks Examples of Key Quality Indicators Correct test(s) ordered/ cancellations Phlebotomy customer satisfaction 30 Specimen/study participant ID Specimen collection/ redraw Pre-Analytic Tasks Accessioning of specimen Specimen preparation Transport of specimen/ lost specimen/ missed pick-ups Examples of Key Quality Indicators (cont'd) Report content Correct results Analyzer performance 31 Preparation of specimen Analytic Tasks EQA results Turnaround time (TAT) Quality control Specimen integrity Missed diagnosis/ correlation to clinical picture Examples of Key Quality Indicators (cont'd) Customer satisfaction for testing services Release of results Transmission of results/ creation of report Post- Analytic Tasks Interpretation of results 32 Reporting abnormal/critical results Reporting errors (e.g., transcription) Assessments Assessments – External and Internal • Assessment of quality is the means to determine the effectiveness of the Quality Management System • Procedures, forms, and records − Developing indicators to measure aspects of the quality − Collecting and analyzing data for quality indicators 33 Internal Audits Internal Audits • An evaluative process for determining the compliance and/or effectiveness of a process or system • A quality audit is a positive and constructive process intended to identify the activities apt to create problems 34 Resolving External Quality Assurance Issues 35 What is the laboratory’s role? How do you investigate/ document? How do you evaluate results not graded by the provider? External Quality Assurance Activity You have just received a report from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) related to your laboratory’s performance of the last general chemistry proficiency test panel. You have received unacceptable scores on two of the five samples. 36 What do you investigate to determine the cause of the unacceptable results? External Quality Assurance Activity (cont'd) You determine that the laboratory tech who performed the testing for the five samples inadvertently aliquoted two of the samples into misidentified secondary containers for testing purposes. 37 What would you do next? Occurrence Management Occurrence Management • Capture and analyze information from nonconforming events to identify systematic problems and gain management’s commitment to removing the cause. Linked to risk management because it provides information on systematic problems that could pose legal or financial risk issues. • Procedures, forms, and records – Identify need for root cause analysis or other process improvement 38 Quality Improvement (QI) The determination of causes or sources of problems identified by QC and QA; for example, root cause analysis 39 Corrective/Preventative Actions Implementation of solutions resulting in the reduction or elimination of an identified problem 40 Process Improvement Process Improvement • Opportunity for improvement does not always come from problems. Many sources of information identify needed improvements. • Procedures, forms, and records – Satisfaction surveys – Occurrence management reports – Complaints 41 Quality Improvement 42 What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) Cycle PLAN DO Communicate ACT STUDY 43 Benchmarking Tools What are they? 44 What are the benefits? How can we use them? Customer Service Customer Service • Who are your customers? What are their needs? What have we done to meet or exceed those needs? Are we seeking feedback? • Procedures, forms, and records – Instructions for receiving complaints – Analyzing survey results 45 Satisfaction Surveys • Why should we be concerned? • Who should we survey? • How do we build questions? 46 Components of a QM Plan Can you produce data that supports the active use of your Quality Management Plan? 47 Quality Management Case Study Using the audit checklist as your guide, review your handout documents. As the new Quality Management Coordinator, you will make notes of the following: 48 Changes to be made to the forms Improvements to be made with documentation Any additional items you would put into place to allow a systematic approach to Quality Management Post-Assessment Question #1 Which of the following are key elements of Quality Management? A. Quality Assurance B. Quality Control C. Regulatory Affairs D. A and B E. B and C F. All of the above 49 Post-Assessment Question #2 Which of the following are benefits of establishing and maintaining a Quality Management Plan? A. Improve clinical trial outcomes B. Increase productivity and efficiency C. Reduce risk of medical errors D. All of the above 50 Post-Assessment Question #3 Which of the following are elements of Quality Control? A. Policies B. Performance/Documentation C. Reviews D. All of the above 51 Post-Assessment Question #4 This statistic measures the central tendency of a set of data: A. Mean B. Standard Deviation C. Range D. None of the above 52 Post-Assessment Question #5 The following are examples of post-analytic quality indicators: A. Customer satisfaction B. Specimen preparation C. Reporting abnormal/critical test results D. Turnaround time E. A and C 53 Post-Assessment Question #6 To implement an effective PT/EQA program, laboratory staff must: A. Demonstrate evidence of review of the PT/EQA report B. Implement necessary CAPA C. Rotate PT/EQA samples amongst all testing personnel D. All of the above 54 Post-Assessment Question #7 The elements of the Quality Improvement process are: A. Prepare, Decide, Study, Act B. Plan, Do, Study, Act C. Plan, Do, Study, Communicate 55 Wrap Up 56