American Studies Final Exam Review World War II Terms to Know
advertisement
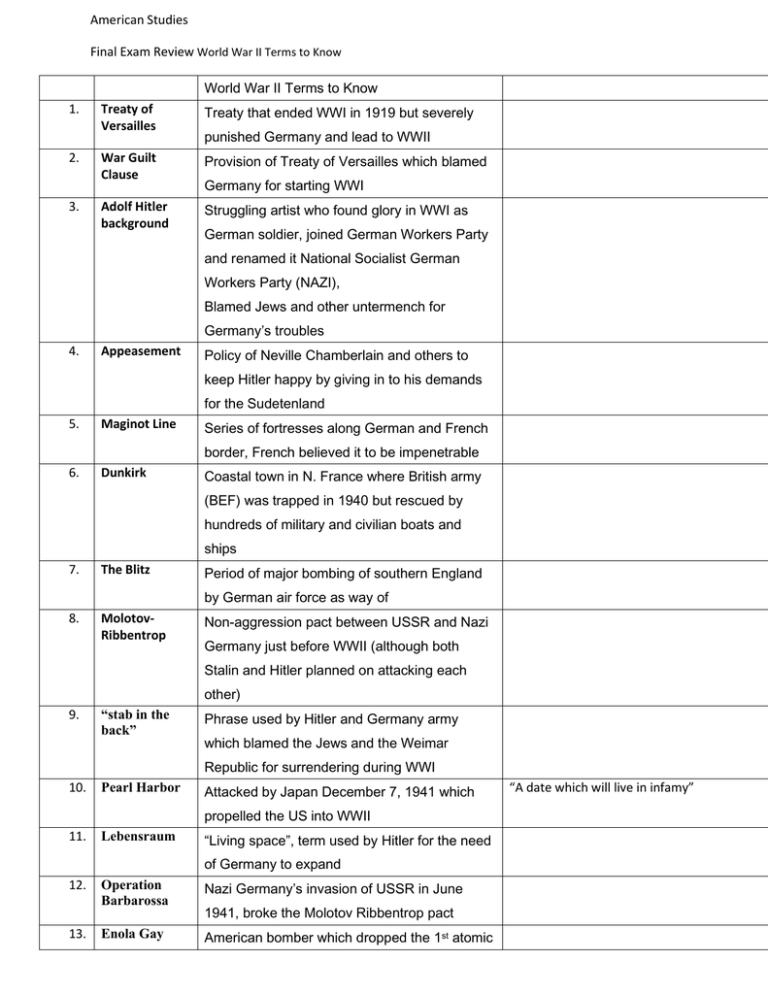
American Studies Final Exam Review World War II Terms to Know World War II Terms to Know 1. 2. 3. Treaty of Versailles Treaty that ended WWI in 1919 but severely War Guilt Clause Provision of Treaty of Versailles which blamed Adolf Hitler background Struggling artist who found glory in WWI as punished Germany and lead to WWII Germany for starting WWI German soldier, joined German Workers Party and renamed it National Socialist German Workers Party (NAZI), Blamed Jews and other untermench for Germany’s troubles 4. Appeasement Policy of Neville Chamberlain and others to keep Hitler happy by giving in to his demands for the Sudetenland 5. Maginot Line Series of fortresses along German and French border, French believed it to be impenetrable 6. Dunkirk Coastal town in N. France where British army (BEF) was trapped in 1940 but rescued by hundreds of military and civilian boats and ships 7. The Blitz Period of major bombing of southern England by German air force as way of 8. MolotovRibbentrop Non-aggression pact between USSR and Nazi Germany just before WWII (although both Stalin and Hitler planned on attacking each other) 9. “stab in the back” Phrase used by Hitler and Germany army which blamed the Jews and the Weimar Republic for surrendering during WWI 10. Pearl Harbor Attacked by Japan December 7, 1941 which propelled the US into WWII 11. Lebensraum “Living space”, term used by Hitler for the need of Germany to expand 12. 13. Operation Barbarossa Nazi Germany’s invasion of USSR in June Enola Gay American bomber which dropped the 1st atomic 1941, broke the Molotov Ribbentrop pact “A date which will live in infamy” bomb on Hiroshima 14. Doolittle Raid Small raid on Tokyo by American bombers soon after Pearl Harbor which did little physical damage but did Japanese to become more militarily defensive 15. “Collective Guilt” Policy of Allies on Germany at end of WWII which blamed WWII and the Holocaust on German citizens themselves, not just the Nazi government 16. Gold Star Mothers Mothers of American servicemen killed in 17. Rosie the Riveter Symbolic figure of American women who Rationing US policy during WWII to limit the consumption 18. action during WWII performed male-dominated jobs during WWII of resources needed for the war effort 19. Victory Gardens Garden of vegetables found throughout America during WWII planted to supplement the lack of food available due to rationing, viewed as a way the average American could help in war effort 20. Air Raid Warden Enforced the order to turn all lights out in the 21. Office of War Information “sold” the war to the American people via 22. War Bonds sold to Americans as way of raising money for event of enemy bombers propaganda war 23. Executive Order 9066 Ordered all Japanese Americans living along west coast to relate to internment camps during the war 24. “Fifth Column” Term for Japanese Americans during WWII meant to imply that they were a disloyal group 25. 26. 27. “A Jap's a Jap. The only good one is a dead one!” Korematsu v. US case Common expression of WWII illustrating the Total War War in which there are no rules, entire hatred towards Japan Japanese American who sued US gov over Executive Order 9066 economy directed towards victory, civilians are targeted for attack “Lights out up there” 28. Guernica Town in Spain bombed during Spanish Civil War, dress rehearsal for WWII 29. 30. Kamikaze 31. Bataan Death March Japanese Suicide pilots who crashed planes into American ships towards end of war Forced march of US prisoners by Japanese noted for brutality, thousands of Americans died on their war to prison camp in Philippines 32. Manhattan Project Government project made up of thousands of scientists, physicists, to create an atomic weapon, led of Robert Oppenheimer, based in Los Alamos, NM 33. Hiroshima & Nagasaki Japanese cities bombed with atomic weapons in Aug. 1945 under Truman’s order, lead to end of WWII 34. Cold War 35. The Big Three Roosevelt, Churchill, Stalin (Allies during WWII) 36. Yalta & Potsdam Agreements Meetings of Allies during WWII to determine War of ideology between US and USSR after WWII with post war Europe would look like, agreed to divide Germany 37. Containment Idea of George Kennan and adopted by Truman, policy involved avoiding direct confrontation with Soviet Union but not allowing communism to spread Truman Doctrine Truman's official policy of containment and aid 39. Marshall Plan Gave 17 billion to war torn nations in order to 40. “Iron Curtain” 38. to stop communism from spreading stop communism from spreading “An iron curtain has descended upon ‘eastern Europe” -Churchill’s speech about the prison-like state of Soviet dominated Europe 41. Berlin Airlift Truman's response to the Soviet blockade of Berlin where food, water, supplies were flown into Berlin when Stalin blockaded the city in 1947 42. NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization. Alliance of Domino Theory- Theory that if communism wa allowed to spread into one country adjacent countries would also fall to communism US and W. European nations against Soviet aggression 43. Warsaw Pact Soviet lead alliance against NATO 44. Red China Communist China under Mao Tse Tung 45. Korean War War in which communist North Korea invaded South but were stopped by US and UN forces, ended in truce in 1953 46. 47. th 38 Parallel Rosenbergs Line of latitude which divides N. and S. Korea American communists executed for spying for the Soviets, led to Red Scare of 1950s 48. Fallout Shelters 49. U2 Incident Underground shelters meant to protect Americans in event of nuclear war US spyplane shot down of Soviet territory, pilot Gary Powers and spy equipment found by Russians, made Cold War colder 50. Sputnik 1st man-made satellite successfully launched into space in Oct 1957, began Space Race 51. Bay of Pigs Military fiasco during Kennedy's administration where Cuban commandos were capture by Castro, made JFK look weak 52. Cuban Missile Crisis Closest US and USSR came to nuclear war, Soviet constructed missile bases dismantled after JFK blockaded Cuba until missiles removed 53. HUAC House Committee on Un-American Activities, investigated suspected communist, especially in Hollywood 54. McCarthyism Period of intense fear of communism in US, witch-hunt to find communist lead by political opportunist Joseph McCarthy 55. Alger Hiss Adviser to FDR who was accused of spying for Russia, cross-examination by Nixon revealed that he was lying, pumpkin papers found at his farm 56. Hollywood Ten Prominent Hollywood directors, writers, producers who refused to cooperate with HUAC during Era of McCarthy, accused of placing procommunist subliminal messages in “Are you now or have you ever been a membe of the communist party” films, books 57. GI Bill of Rights Government program to help returning WWII soldiers pay for college and housing, fueled US economy with well-educated workforce 58. Consumerism Characteristic of the 50s where Americans sought material goods to “keep up with the Jones” 59. Conformity Characteristic of 50s America where Americans avoided individuality and conflict and embraced tradition, trusted authority 60. National Highway Act of 1956 Eisenhower era law which built thousands of 61. Levittown Planned community in Pa and Long Island, NY miles of roads & fueled car industry built for newly married returning WWII soldiers 62. “Little Boxes” Song by Pete Seeger which criticized conformist America and lack of indivuality 63. Baby Boom 64. Dr. Benjamin Spock Dr. who encouraged Americans to nurture their Election of 1948 Truman won although predicted to lose to 66. Dixiecrats Southern democrats who didn't want civil rights 67. Truman, Dewey, Thurmond, Wallace Eisenhower’s candidacy Candidates of 1949 election Checkers Speech Nixon’s TV speech in which he denied Term that illustrates the rapid rise in the birthrate during the 50s. 65. children. Republican Thomas Dewey legislation and left Truman for Thurmon in 1948 68. 69. Had never voted in election and had no strong political beliefs accepting “gifts” except for a little cute dog named Checkers 70. “We Like Ike” Slogan of 1952 for Dwight Eisenhower 71. Eisenhower’s Farewell Address Warned against the influence of the “military industrial complex” IE. Influence of companies that make weapons & military on our government 72. Kennedy/Nixon Helped JFK win election of 1960 because he Debates looked “presidential” on TV while Nixon looked nervous, sickly, and sweaty Plessy v Ferguson 1896 Supreme Court decision which legalized 74. Jim Crow Laws Segregation laws in the South 75. “Separate but Equal” Brown v Board of Education See above 73. 76. “separate but equal”, legalized Jim Crow Laws Supreme Court case of 1954 that said separate but equal is “inherently unequal”. Reversed Plessy v Ferguson 77. Rosa Parks Refused to give up her seat to a white man in Montgomery, Alabama. Started modern Civil Rights Movement 78. 79. 80. 81. Montgomery Boycott of city buses after Rosa Parks Bus Boycott Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Peaceful leader of the Civil Rights movement, Little Rock Nine 1st students to test Brown v Board of Ed Greensboro SitCollege students who refused to move from in seat until they were served coffee in “I have a dream” “I’ve been to the mountaintop segregated diner 82. SNCC/ Jail Not Bail Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee who got arrested on purpose as a form of protest 83. Freedom Riders SNNC members to traveled in the south in order to protest segregated busing terminals but were brutally attacked 84. Letter from a Birmingham Jail Statement by Dr. King to his critics who had Justice delayed is justice denied. blamed him for the violence in Birmingham during a Civil Rights march in 1963 85. 86. March on Washington Highpoint of Civil Rights Movement where King gave “I have a dream” speech and called for passage of Civil Rights Bill in Aug 1963 87. I have a dream speech King speech in which he speaks of America 88. Civil Rights Act of 1964 Made all segregation based on race illegal in 89. Black Power Militant civil rights movement which regjected where there is no more racism US King’s peaceful protest and embraced Malcolm X’s more eye for an eye approach 90. Malcolm X & Radical black separatist who advocated “eye “judged by the content of their character and not by the color of their skin” 91. 92. Nation of Islam for an eye”, rejected peaceful protest Mountaintop Speech James Earl Ray MLK’s prophetic last speech Assassinated MLK April 4, 1968 in Memphis, Tennessee 93. JFK inaugural address Called on Americans to serve their nation and “Ask not what your country can do for you… warned Soviets that America would stand up to “We will bear any burden, oppose any foe… communism 94. 95. 96. Peace Corps JFK inspired group of Americans who traveled to distant poorer nations to act as ambassadors of good will for US 97. Camelot Term which captures the perceived “regal” nature of JFK 98. Assassination in Dallas November 22, 1963 JFK shot by Lee Havey Oswald, shattered hopes and dreams of many Americans 99. Lee Harvey Oswald 100. Magic Bullet Assassinated JFK in Dallas. 1 bullet which struck JFK and Gov. Connely of Texas, most controversial aspect of Warren Commission’s claim that Oswald acted alone 101. Warren Commission Investigated JFK assassination and found the Oswald had acted alone, many Americans grew to distrust the Commission and the Government itself 102. The Great Society LBJ’s program to eradicated poverty and 103. The Treatment LBJ’s method of convincing political opponents injustice in American to go along with his wishes 104. Michael Harrington’s The Other America Book which said that there was still poverty in 105. Warren Court Not on test 106. Gideon v Wainwright 107. Miranda v Arizona 108. Betty Friedan Not on test America during the 1950s, greatly influenced LBJ to start Great Society program Not on test Wrote Feminine Mystique as a means of showing America that women were not happy with their role as a stay-at-moms. 109. Roe v Wade Supreme Court case of 1973 which legalized 1st trimester abortion. 110. Equal Rights Amendment 111. Phyllis Schlafly Not on test 112. Election of 1964 LBJ v Barry Goldwater, Johnson won by 113. Barry Goldwater Republican conservative candidate in the 1964 114. Counter Culture Culture of the baby boomers after 1964, Not on test landslide Daisy Ad election and “father of modern conservatism” rejected values of their parents, forefront of Anti-Vietnam War 115. The Establishment 116. Hippies Culture of WWII generation, Silent Majority Most visible counterculture group Haight-Ashbury 117. Epicenter of counterculture movement in San Francisco 118. Woodstock Music and art festival in NY which featured most popular musicians of counterculture, meant to illustrate counterculture values of peace, love, and music 119. Andy Warhol Counterculture artist who mocked consumerism and celebrity worship of the 1950s 120. Dien Bien Phu 1954 battle in which French were defeated by Ho Chi Minh 121. 122. Viet Cong South Vietnamese communist insurgents who fought the US during war 123. Ho Chi Minh Communist leader of North Vietnam. 124. 125. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Law which allowed LBJ to take “all necessary 126. “search and destroy” Tactic of US soldiers to look for and kill NVA 127. Tet Offensive Major military offensive by VC and NVA measures” to defeat North Vietnam and VC soldiers soldiers in Jan 1968, turning point of War, tarnished rosy claim that US was winning the war 128. Presidential Race of 1968 LBJ dropped out, RFK assassinated, race “I’m Andy Warhol and I just ate a Wopper with chesse” between Humphrey and Nixon 129. Eugene McCarthy Democratic senator who defeated LBJ in NH primary on an antiwar platform. 130. Democratic Convention in Chicago Seen of major protests lead by Chicago 8, 131. George Wallace Alabama gov who said “Segregation today, 132. Chicago 8 See above 133. Richard Nixon & “Law & Order” 134. Free Speech Movement Not on test greatly tarnished image of Democratic party segregation tomorrow….. 1964 peaceful protest movement which called for right of college students to speak out on issues in college campuses 135. SDS & Port Hudson Statement Students for a Democratic Society- Viewed US Gov, Universities as a “Machine” which tried to produce obedient robotic citizens and not free thinking individuals 136. Weather Underground Radical wing of SDS who used terrorism and 137. The Draft, Deferment, Conscientious Objector Required military service by government, 138. Hawks v Doves Dove- Someone who favors peace. violence to end Vietnam War controversial because wealthy often able to get out of military service Hawk- someone who favors war 139. My Lai Massacre Murder of over 300 unarmed civilians at the hands of US soldiers (Charlies Co.) soon after the Tet Offensive, stopped by helicopter pilot Hugh Thompson 140. Silent Majority Nixon’s term for Establishment people, hard working, law abiding Americans 141. Cambodia 'Invaded' under Nixon in order to destroy enemy bases and the Ho Chi Min Trail. Led to the Kent State 142. Kent State Scene of death of 4 college students killed accidentally by nervous national guardsmen during protests after US invasion of Cambodia 143. Maya Lin & Vietnam Memorial 144. Asian American who designed Vietnam memorial “Be clean for Gene” 145. Nixon Doctrine Not on test 146. Vietnamization Nixon's plan to turn the major fighting over to the Vietnamese by training and financing them. 147. Détente Not on final 148. Pentagon Papers Top secret documents released to press by Daniel Ellsberg which revealed that government was lying to pubic 149. The Plumbers Clandestine group who spied and played dirty tricks on Nixon’s “Enemies” 150. The Fall of Saigon City in S. Vietnam that fell in 1975 and marked 151. Realpolitik Not on final 152. SALT Not on final 153. Enemies List List of 200 people considered 'unfriendly' to the official end of the Vietnam War. Nixon. 154. CREEP Committee to ReElect the President, directed the Plumbers to spy on Democratic party 155. Watergate Hotel in Washington where the Democratic National Committee Headquarters was located and where the “Plumbers” were caught spying--scandal lead to Nixon’s resignation 156. Saturday Night Massacre Weekend in 1974 when Nixon ordered the firing of Cox who was investigating his involvement in Watergate 157. The Tapes Recordings of Nixon’s conversations in the Oval Office, revealed that Nixon tried to cover up the Watergate break-in 158. Gerald R. Ford Pardoned Nixon as a way of ending “Our long national nightmare”








