U.S. History
advertisement

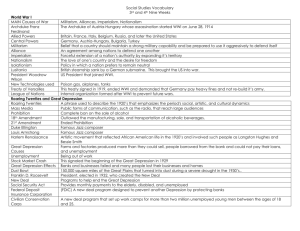
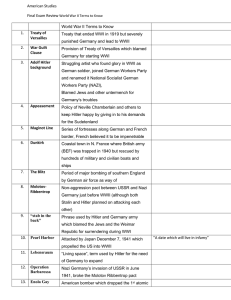
U.S. History Final Exam Review 1920’s to Present 1920’s 1. Population patterns: A. Great Migration – African Americans move from South to Northern Industrial centers (cities) B. More people live in cities and surrounding areas than rural countryside C. Suburbanization (#1): middle class America 1) Automobile (#5) a. Ford’s assembly line production b. growth in petroleum / oil industry c. development of service stations / strip malls d. residential neighborhoods 1920’s 2. Social & Cultural Trends: A. Immigration: increase due to growing American Industries 1) National Origins Act of 1924 (#6)– Nativists (#2) a. Southern / Easter Europeans (Catholic) & Japanese B. Harlem Renaissance (#4): African American inner-city cultural movement 1) Langston Hughes – Jazz poetry 2) Louis Armstrong – Jazz music (#8) African American musical traditions 3) Marcus Garvey (#11) – U.N.I.A. / migration to Africa C. Scopes Trial (#3): evolutionary Science 1920’s 3. Politics: Republican Presidents A. President Warren Harding (1921-1923) 1) Republican Party – put their faith in big business (#10) 2) Teapot Dome Scandal (#9) - gov’t officials illegally leased land to oil companies for illegal “kickbacks” B. President Coolidge (1923-1928) 1920’s 4. Economy: A. Booming economy (#7) 1) Aggressive advertising 2) Consumerism 3) steady increase in industrial profits B. Characteristics of Consumerism (#13) 1) living on credit (beyond their means) 2) spending less due to limited income 3) more then 50% of population were working poor ($1,500 a year) Great Depression A. Causes: 1) unequal distribution of wealth and income 2) oligopolies “administered prices” 3) weakness of key industries: agriculture, mining, textiles 4) lack of government regulation Great Depression B. Black Tuesday: Stock crash of 1929 (#12) due to over speculation / buying on margin 1) start of the Great Depression C. Bank Failures (#14) 1) panicked rush on banks – withdrawal $ 2) banks lacked revenue – lost $ in market crash 3) no federal insurance to protect accounts Great Depression 1. President Herbert Hoover (#16) (1929-1932) A. limited response: 1) volunteerism: private action not federal 2) self-reliance & charity for relief – not gov’t bailout 3) Gov’t should direct relief measures – but avoid increasing size of government a. RFC: Reconstruction Finance Corporation B. Result – deepening of recession / Hoovervilles / Bonus Army Great Depression 2. Social consequences: A. Minority groups (#15) African & Hispanic Americans 1) higher unemployment 2) racial violence 3) deportation 4) denied government relief programs B. Women – reduced employment / abandonment C. Marriage – rapid decline / reduced divorce rate Great Depression 3. President FDR (1933-1945) A. First Hundred Days: 1) New Deal program – FDIC, Emerg. Banking Act, SEC, FERA: CWA, PWA, CCC, AAA, NRA 2) Budget deficit spending = increased federal bureaucracy B. 2nd New Deal: 1935 1) Wagner Act = Union’s collective bargaining 2) Emergency Relief Appropriations Act: WPA, NYA Path to War 1. Majority of American’s supported isolationism: A. Neutrality Act of 1939 (#17) – allowed arms sales to belligerent nations on a “cash & carry” basis. 1) favored British & French who controlled the Atlantic Ocean B. Lend-Lease Program of 1941(#18) – allowed Great Britain to borrow military equipment from the United States C. Atlantic Charter of 1941(#19)– provided a political framework for the possibility of American involvement in the war WWII 1. Pearl Harbor – Dec. 7, 1941 A. Two Theatre War: 1) Pacific – “Island Hopping Campaign” 2) European – N. Africa / Italy / D-Day: France B. Unconditional Surrender / Europe 1st C. Turning tide of the war: 1) Europe – Battle of Britain, El Alamien, Sicily Stalingrad, D-Day 2) Pacific – Coral Sea, Mid Way, Leyte Gulf WWII 2. Home front A. War Production: 1) U.S. production = 40% of world materials 2) Ended the Great Depression 3) full employment = equalization of population B. Mobilization of workforce 1) Bracero Program(#20)– recruitment of Mexican workers for 6 to 12 month contracts 2) Women workers(#22) a. “Rosie the Riveter” – poster propaganda b. vital role in shipyards and aircraft industries c. High employment WWII C. Executive Order 9066(#24) – interment of Japanese Americans 3. Manhattan Project(#23) 1) developed the atomic bomb 4. Using the Bomb 1) President Truman’s decision to use the bomb(#21) a. projected casualties in a U.S. invasion of Japan Post WWII 1. G.I. Bill (#51): guaranteed loans for veterans to buy a house, and tuition for college A. Levittown (#52): provided affordable housing in American suburbs 2. Baby Boom (1945-1950) – period of significant increase in babies being born 3. Fair Deal (#53): Truman’s economic package A. extension of FDR’s New Deal Post WWII 4. Social & Economic Trends of the 1950’s and 60’s A. President Dwight D. Eisenhower (1952-1960) 1) IKE – popularity as WWII General a. positive image with both liberals and conservatives B. Consumerism: growth of domestic economy due to consumers buying commodities on credit 1) Counterculture(#56) – 1960’s youth expressed their alienation from American society (drugs) Cold War 1. Yalta Conference, 1945(#25) A. “Big Three” – U.S., G.B., Soviet Union 1) met to discuss post war Europe, Germany, Soviet occupied Eastern Europe 2. Truman Doctrine(#26) A. U.S. military and economic support of countries threatened by Communism 1) Greece & Turkey B. Containment (#27): to block Soviet attempts to spread communism by creating alliances & support of weaker nations Cold War 3. Marshall Plan(#28): U.S. plan for European economic recovery after WWII 4. NATO(#29): North Atlantic Treaty Organization A. Military alliance between the U.S., Canada, and 10 Western European nations B. Warsaw Pact(#29): Soviet response to NATO 1) alliance between USSR and 8 Eastern European nations Cold War 5. Escalation of U.S. fear of Communism in the late 1940’s and 50’s A. China became Communist B. Soviets get the bomb 6. 1960’s A. Brinkmanship (#30)– U.S. and Soviet willingness to go to the edge of war to keep peace B. Sputnik(#31) – USSR launched 1st satellite C. Bay of Pigs(#32) – failed U.S. supported invasion of Cuba in 1961 D. Cuban Missile Crisis(#32) – U.S. & USSR came the close to full scale nuclear war Hot War 1. Korea (1950-1952) A. North Korean invasion of South Korea 1) UN – Gen. MacArthur 2) Chinese involvement 3) 39th Parallel 2. Vietnam A. Domino Theory(#33) – idea that countries bordering communist countries were in danger of becoming communist Vietnam War 1. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution(#34), 1965 A. Congress granted President Johnson broad military powers in Vietnam 1) Operation Rolling Thunder (#35)- first U.S. sustained bombing of North Vietnam 2) by end of 1965 – 180,000 U.S. troops in Vietnam 3) Vietcong fighting for their survival 4) increasingly negative view of the war (T.V.) 5) strain on U.S. economy Vietnam War 2. Tet Offensive (#36), 1968 A. Vietnamese New Year 1) Vietcong / N. Vietnamese attacks of U.S. bases and South Vietnam cities 2) intended to trigger uprising in South – resulted in defeat for the North 3) Increased American opposition to the war a. Johnson doesn’t run for reelection in 68’ Vietnam War 3. Vietnamization(#37) – President Nixon’s plan to withdrawal troops from Vietnam 4. Nixon: secret war in Cambodia a. anti-war protest: 4 students killed at Kent State (#49) Civil Rights 1. Brown v. Board of Education A. Supreme Court decision of 1954 – segregation in public schools / facilities was unconstitutional 2. Little Rock Arkansas (#38), 1957 A. Little Rock Nine – 9 African American students who were enrolled in a white school to integrate 1) federal troops used to ensure their safety Civil Rights 3. Civil Rights Movement A. Montgomery Bus Boycott: Martin Luther King, Jr. 1) used carpools B. Freedom Riders (#45): integrated buses challenged segregation of interstate bus terminals C. Greensboro (#48): black college students hold sit-ins at lunch counters D. Freedom Summer (#42): registered black voters E. March on Washington of 1963 (#46): 1) transformed civil rights into a national cause 2) biracial crowd of nearly 250,000 people 3) Martin Luther King, Jr. – I Have a Dream Speech Civil Rights 4. Kennedy’s assassination – Nov. 23, 1963 A. Warren Commission (#55): official investigation of the assassination that left many loose ends 5. President Johnson (1963-1968) A. Civil Rights Act of 1964 (#43): 1) prohibited segregation in public facilities Civil Rights 6. Watts Riots of 1965 (#47): A. looting and burning of Los Angeles in response to the arrest of a black man 1) built up tension due to poor condition of cities and racism B. Black Panthers (#39): Bobby Seal & Huey Newton C. Black Power 1) celebrated African-American heritage 2) Stokely Carmichael & Malcolm X 3) controlling local black communities through political activism Civil Rights 7. Spread of Civil Rights: A. Cesar Chavez (#40)– organized the United Farm Workers B. American Indian Movement (#41) 1) established to increase economic opportunity, stop police mistreatment, insert their distinctiveness w/in American society 2) organization refused to ally itself with other Indian groups Modern Women’s Movement 1. Betty Friedan: Feminine Mystique (#54) – A. book that provided a voice for women who felt dissatisfied with limits of their domestic lives 2. Roe v. Wade,1973 (#50) – Supreme Court ruled that state laws could not forbid abortions in the first 3 months of pregnancy 1970’s 1. Summer of 1969 – Neil Armstrong 1st man to walk on the moon 2. Economic problems of the 1970s: A. OPEC – oil embargo by Arab nations B. Energy Crisis: increased gas prices, rising energy costs, high inflation C. Stagflation (#57): inflation + high unemployment + flat economic growth Nixon 1. President Nixon (1969 – 1973) A. Watergate Scandal (#58): 1) special prosecutors independent of the White House 2) Nixon’s urge for power 3) President’s administration had broken the law 4) Separation of Powers reigned in the President 5) President’s tapes revealed cover up