PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. Cellular Respiration

Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
6.11 – 6.13
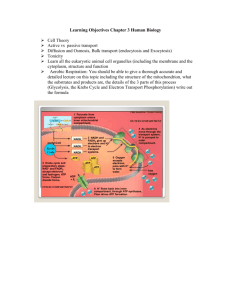
Krebs cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, making many NADH & FADH
2 molecules
• Where does the Acetyl
CoA come from to start the Krebs cycle?
• End of glycolysis, from the pyruvic acid
• Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
• In the mitochondrial matrix
• For every molecule of
Acetyl CoA that enters
Krebs cycle, what are the products?
• 1ATP, 1FADH
2
, 3NADH
• Does glycolysis or Krebs payoff more energy?
• Krebs yields more potential energy even though glycolysis generates more net ATP.
• How is ATP made in
Krebs?
• Substrate-level phosphorylation
• What do the FADH2 and
NADH molecules do?
• They carry the high energy hydrogens from glucose.
• So, how many energy rich molecules has the cell gained from one molecule of glucose processed through glycolysis & Krebs?
• The cell has gained a total of: 4 ATP, 10 NADH,
2 FADH
2
• How does the cell use the energy in NADH &
FADH
2
?
• It has to be converted to
ATP & used immediately.
Chemiosmosis powers most ATP production
• Why is the mitochondrial membrane structure ideal for making ATP?
• The space in the phospholipid membrane of the folds of the cristae allow the proteins of the ETC and
ATP synthase to be embedded.
• *role of NADH & O2*
• How do the protein complexes transport H+ ions through membrane?
• Energy released as electrons pass from protein to protein.
• How does this create a potential energy storage?
• H+ ions accumulate in the inner membrane space
• What effect would the absence of O2 have on the ETC?
• No chemiosmotic production of ATP, nothing to pull electrons, or harness
NADH energy
Certain poisons interrupt critical events in cellular respiration
• How does Rotenone interrupt cell respiration?
• Blocks the electrons from passing from electron carrier molecules, no ATP is made.
• How does cyanide and carbon monoxide work?
• They block passage of electrons to O2, no ATP is made.
• Oligomycin stops what?
• The H+ ions from passing through ATP synthase, no ATP is formed…it is an antibiotic prescribed to combat skin fungal infections.