Krebs cycle & ETSrev Patty
advertisement

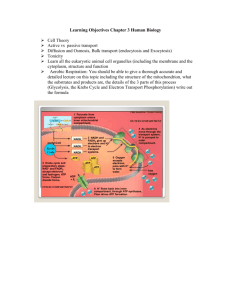
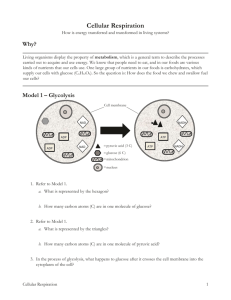
Aerobic respiration: the Krebs cycle & electron transport system What happens in the mitochondria does not stay in the mitochondria Aerobic Respiration • Occurs in the mitochondria. • Composed of two processes: – Citric acid cycle (Krebs). – Electron Transport System (ETS) Mitochonodria located in a muscle cell Krebs cycle: aka Citric acid cycle • Occurs in the matrix. • Uses pyruvic acid as a raw material • uses Oxygen • Produces: 2 ATP, NADH & FADH2 • Waste product is carbon dioxide. Pair share: why is it called a cycle? Electron Transport System • Occurs in the cristae • Produces 34 ATP • Uses NADH & FADH2 in order to store Hydrogen. • Uses Oxygen • Waste product is water. Pair share: what is being pumped out of the matrix? ATP Production Summary • Glycolysis. – 4 ATP produced - 2 ATP used = 2ATP Gained • Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs) – 2 ATP Produced. • Electron Transport System – 34 ATP Produced • Total ATP Produced from each glucose molecule = 38 ATP Efficiency Comparison Anaerobic respiration ------ 2% Aerobic respiration --------- 66% More energy from the same food! = More bang for your buck! Whole foods = anaerobic the dollar store = aerobic Reactants and Products Process Reactants Products • Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvic acid & NADH • Citric Acid Cycle Pyruvic acid (Acetyl CoA) NADH & FADH2 Carbon dioxide NADH & FADH2 Water • ETS Start with glucose in glycolysis, add O2 during Krebs cycle & CO2 is produced, during ETS water is produced. White board Review 1. Where does the Krebs cycle take place and how much ATP is produced? 2. In ETS where are the electrons being transported? 3. Why do you think there are not any multicellular prokaryotes?