jesus christ-2-chapter 3 - matthew
advertisement

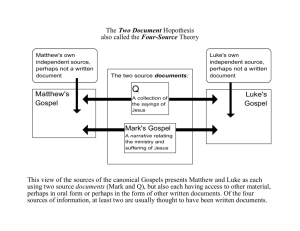
The Gospel of Matthew • • • • The first book listed in the New Testament canon Well-ordered and contained detailed teaching lessons Link between the Old Testament and the New Testament Vital role in Christian instruction and worship Lord’s Prayer • Contains 80% of Mark’s gospel Omits passages (from Mark) that paint Jesus or the apostles in an unfavorable light • Author: Jewish-Christian scribe • Originally written in Greek • Date: 80’s AD (after the destruction of the Temple in Jerusalem) • Audience: Jewish-Christian community Knowledge of Jewish customs Use of Hebrew terms like Gehenna, Beelzebul, Kingdom of Heaven Use of the number “7” Compares Jesus to Moses Over 130 passages in Matthew have Old Testament roots “This happened so that what had been spoken through the prophet might be fulfilled” (Mt 21:4) “Do not think that I have to abolish the law or the prophets. I have come not to abolish but to fulfill” (Mt 5:17) Uses Q, Mark, and M as sources Matthew’s audience struggled with how Judaism would continue now that the Temple was destroyed According to Matthew, true Judaism involved a Church gathered around the Teacher Jesus Themes in Matthew’s Gospel • Judgment Second coming of Christ; We should always be ready for the Lord’s return • Jesus is Emmanuel “God with us” • Discipleship Requires humility, rejection, even suffering • Church Only gospel where the word for church (ekklesia) appears Local or universal community of believers • Right Instruction An instruction manual for new converts and faithful disciples Teaches righteousness, prayer, conversion Comparing the Gospels of Matthew and Mark • Matthew’s gospel begins with a genealogy of Jesus, tracing his ancestors to both David and Abraham • Son of David Jesus as Israel’s Promised Savior • Four women mentioned in genealogy: Tamar, Rahab, Ruth, Bathsheba (foreigners) – Gospel will eventually be preached to all people • Infancy Narrative: Joseph’s dream about Jesus’ birth Jesus’ birth in Bethlehem Homage of the Magi Plotting of the evil King Herod Warning given to Joseph in a dream Flight to Egypt Massacre of the infants Return of the Holy Family from Egypt after the death of Herod Settling of the Holy Family in Nazareth • Matthew shows Jesus as Emmanuel • Mark’s gospel ends abruptly with no resurrection appearances; Matthew’s gospel with 2 resurrection appearances • Conclusion of Matthew’s gospel: met with the Eleven in Galilee and instructed them to preach to all the nations • Matthew’s gospel organized into 5 narratives with discourses (speeches) by Jesus Discourse One: The Sermon on the Mount Matthew 5-7 • First and most important of the five discourses • Summary of the New Law (love, grace, freedom) • Moses delivered the Old Law on Mount Sinai; Jesus delivers the New Law on a mountain • Involves conversion of the heart and putting discipleship into practice • Beatitudes: offer blessings on unlikely people like the poor in spirit, mourners, the meek, and peacemakers • Christians are the “salt of the earth” and the “light of the world.” (5:13-16) Faithful disciples will change the flavor of the world Christians should dispel darkness, show the way, and help eliminate fear of the unknown Good works will act as a beacon of light that lead other people to God • Christians observe a new standard of law (Mt 5:17-48) Jesus and His teachings fulfill the Old Covenant Mere external observation of the Law is not enough Interior conversion is necessary • Christians have a right attitude (Mt 6:1-34) A need for a clean heart and pure intention The Lord’s Prayer as the model prayer for Christians Golden Rule: “Do to others whatever you have them do to you.” We must put Jesus’ words into practice Discourse Two: Sharing the Faith with Others Matthew 10 • Jesus directs the apostles to preach the gospel in a spirit of poverty and not burden themselves with accumulating money or carrying excess baggage • “Behold I am sending you like sheep in the midst of wolves; so be shrewd as serpents and simple as doves. (Mt 10:16) • “Whoever finds his life will lose it, and whoever loses his life for my sake will find it?” (Mt 10:39) • “Whoever receives you receives me, and whoever receives me receives the one who sent me.” (Mt 10:40) Discourse Three: Parables About the Kingdom Matthew 13 • Parable: a short story drawn from ordinary life that makes a comparison with a religious message To confuse outsiders and to present truths about the kingdom to insiders (disciples) in ways that show how God works Unbelievers do not “get” the parables because they lack the eyes and ears of faith Disciples are blessed with the vision that comes with faith in Jesus Allegory: a story in which people, things, events have symbolic meanings that represent something else Discourse Four: Jesus Founds and Instructs the Church Matthew 18 • Matthew’s gospel as “the gospel of the Church” • “You are Peter, and upon this rock, I will build my church. . . I will give you the keys to the kingdom of heaven.” (Mt 16:18-19) • Christ’s power to forgive sin and to teach authoritatively • Pope as successor to Peter • Greatness lies in serving, not in being served • No limits on forgiveness (7 times 70 as a symbol for infinity) Discourse Five: The Final Judgment Matthew 24-25 • Eschatological (end time) • Involves the end of the Temple, the end of the world, and the divine judgment on the Last Day • Daniel 7-8 with apocalyptic (revelation) language Ongoing war between good and evil God is in charge during times of trial Disciples should remain faithful Disciples should always be prepared for God’s return • “Whatever you did for one of these least brothers of mine, you did for me.” (Mt 25:40) Jesus Challenges Judaism • Matthew 23 critical of Judaism Jesus criticizes the scribes and Pharisees for their arrogance Jesus exclaims seven woes against the scribes and Pharisees Woe: in the Old Testament; shows sorrow or grief; used to shock people to examine their behavior and change it Strong language reflects religious turmoil within Judaism in the 80’s Matthew trying to convince Jews that Jesus fulfills the promises made to Israel Not Anti-Semitic language