Presentation slides - Oregon Sexual Assault Task Force
advertisement

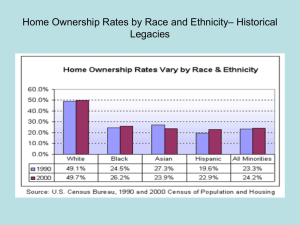
The Barriers Men of Color Face in the Movement to End Gender Violence and Strategies to Support Them May 20, 2011 Presenters Monica Collins & Alejandro Covarrubias ROAD MAP Introductions Ground Rules Barriers & Strategies Examples & Impact Questions Monica Collins • Assistant Director for Prevention and Education Programs & Victim Advocate in the Women and Gender Advocacy Center at Colorado State University • Current graduate research is in the field of Sociology and is titled The Symbolic and Structural Similarities between Antebellum Slave Markets and Modern Day NCAA Football Recruiting. • Teaches courses at CSU on race/ethnicity in popular media, gender socialization and violence prevention. Alejandro Covarrubias • Program Specialist, Center for Multicultural Excellence at the University of Denver • Developed and facilitated Men’s program on masculinity development and sexual assault prevent at 3 different college campuses • Presented on Men of Color in anti-violence/gender violence movements Introductions Where are people from? East Coast Midwest Northwest Mountain Region South Southwest What field are people in? Corporate Higher Education Non-Profit Other Field How much experience do you have working with Men of Color in anti-violence work and/or discussing this topic? No Experience Limited Experience Some Experience Extensive Experience Community Guidelines • There are no “experts”… including us! • We will speak from our personal experiences and ask that you do the same. • We all might experience moments of feeling triggered, defensive or uncomfortable, especially as we are talking about unconscious racism in the movement. Try to remain open to the process. • Let’s all pay attention to moments when we feel defensiveness, discomfort and/or validation. Those feelings are clues! 6 BARRIERS & STRATEGIES 1. Singular definition of masculinity 2. Limited space to process trauma 3. Racism within institutions and society 4. Leadership within the anti-violence movement 5. Loss of community 6. Historical Context 1 BARRIER Singular definition of masculinity “Masculinity” is synonymous with White Masculinity Men of Color experience a racialized masculinity: Driven by Media Images Black and Latino men are often seen as hyper-aggressive and hyper-violent Asian men often seen as asexual, passive, and feminized 1 BARRIER Singular definition of masculinity Impact: Black and Latino men are stereotyped as more masculine and thus more violent Asian men face added homophobic harassment and/or feel the need to use hyper-masculine posturing as a response to racial harassment Example: Media response to Common’s invitation to perform at the White House STRATEGIES Move from masculinity to masculinities Honor that there are many forms of masculinity for all men An individual’s masculinity is formed by intersections of other social identities like race, class, disability, sexuality, religion and nationality Do not let White culture define the experiences of Men of Color What is “Machismo”? Present multiple versions of masculinity Resources should include information for/about men with various intersecting identities: Queer Men of Color, Men with disabilities, Working-Class Men of Color 2 BARRIER Men lack spaces to talk about trauma Men tend not to talk about the trauma that has been inflicted on them or about the trauma they have inflicted on others. This is generally true for all men, regardless of race Our framework for “trauma” is typically physical or sexual abuse… we typically don’t count harassment, bullying or teasing Men of Color especially need this space as their racial identity often intersects with gendered experiences of violence and trauma 2 BARRIER Men lack spaces to talk about trauma Impact: Men of Color are processing trauma around gender and racism Silencing of racist trauma Men of Color don’t get to explore their own issues Example: Men of Color might not feel safe talking about violence within communities of color while in a majority White space (gender caucus) STRATEGIES Create spaces for Men of Color to talk about victimization and victimizing Need to broaden the definition of “trauma” so that experiences around race, ability, class, etc. matter Name the racialized violence men of color experience or are perceived to experience Scar Story Activity Have men tell story of physical scar Open space for emotional scars Who has scarred them? Who have they scarred? (What does it feel like to know that you have scarred someone?) 3 BARRIER Racism within Institutions and Society Men of Color are disproportionately depicted and reported as perpetrators of sexual assault and gender violence Socialization as a White woman Example: Racism within Victim Advocacy Men of Color are also convicted at a higher rate The media portrays Men of Color (specifically Black and Latino men) as hyper-violent 3 BARRIER Racism within Institutions and Society Impact: Despite the very low percentage of “false” reports, Men of Color are socialized to fear being falsely accused of crimes, specifically when involved with White women Society views and treats men of color with greater suspicion and accountability Men of Color (or organizations/communities comprised of Men of Color) face additional scrutiny and accountability 3 BARRIER Racism within Institutions and Society Example: Chris Brown vs. Charlie Sheen Example: Recent Today Show episode Example: Man of Color at CSU Women’s Conference STRATEGIES Consider intersecting identities when discussing issues of accountability Remain committed to honoring and exploring the complexities of identity within this issue. Speak out against media outlets and challenge anti-violence leaders who fail to recognize how “outrage” is often racialized Offer multiple options for survivors that include and move beyond the criminal justice system Community Accountability and Transformative Justice (TJ) movements We cannot allow men of color to excuse misogynistic behaviors with their racial identity 4 BARRIER Leadership within anti-violence movements The perception is that nationwide leaders and men’s organizations are predominantly White (Men can Stop Rape, 1 in 4, etc) When Men of Color are looked to as leaders, it is typically for a targeted population, community or issue. 4 BARRIER Leadership within anti-violence movements Impact: Lack of nationwide leadership for Men of Color Men of Color get pigeonholed into addressing certain issues Men of Color are stereotyped as not engaged or lacking interest because they do not show up like White leaders Examples: Differences around Leadership (CSU Men’s Project) White men moved from action to self discovery Men of color moved from self-discovery to action and community development STRATEGIES Re-examine leadership within the movement Re-examine expectations of what “leadership” and “engagement” look like Honor that men of color are also facing racism while engaging in anti-violence work Credibility of a white presenter vs. a presenter of color Most Men of Color leadership development happens around sports, we need to move away from this Look to Men of Color for leadership within the anti-violence movement in general 5 BARRIER Loss of Community Men of Color risk losing their community & becoming isolated when acting as bystanders within their racial/ethnic communities Especially true for Men of Color in predominately White institutions, colleges, etc. Impact: Men of Color face additional complexities when discussing “bystander intervention” strategies Due to the lack of visible men of color in the movement, men of color risk feeling misunderstood and alienated in the movement AND within their own communities STRATEGIES Provide opportunities for Men of Color to engage in and create community Support opportunities for Men of Color to engage in communities of pro-feminist Men of Color Actively seek out Men of Color leadership conferences and collaborate with them Create space at Gender-Violence Prevention conferences for Men of Color to meet each other Actively invite Men of Color to Gender-Violence Prevention conferences Acknowledge that most bystander models tend to be based on White/“Western” values 6 BARRIER Historical Context Historical impact of social justice movements Sexism within racial justice movement Racism within feminist movement Most sexual assault/gender violence centers are staffed by White women Socialized racism from White women and socialized sexism from Men of Color leads to mutual mistrust 6 BARRIER Historical Context Impact: Complexities of intersecting identities in relationships between Men of Color and White women When doing “gender work”, the assumption is often that “gender” should be the primary lens Women of Color lack safe spaces because of sexism and racism STRATEGIES Engage in accountability dialogues White folks dialogue together to name and acknowledge the racism they (and the history of the movement) bring to the table when working with People of Color Men of Color dialogue together to name and acknowledge the sexism and dominance they bring to the table when working with all women Recognize the impact that racism and sexism have on Women of Color Become more personally aware of our own advantaged/dominant and marginalized/subordinated identities Ask ourselves and our organizations how these identities have an impact on the way we do the work ? Questions? Comments ? ! Contact Information Alejandro Covarrubias Monica Collins afcovarrubias@gmail.com monicahcollins@yahoo.com