Update: Operational Delivery Networks
advertisement

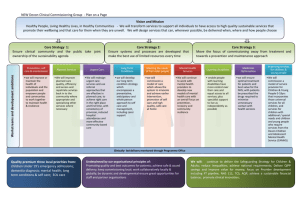
Update: Operational Delivery Networks Denise McLellan Transitional Lead, Networks and Senates, Midlands and East November 2012 Context • NHS CB recognition of the value of networks -The Way Forward: Strategic Clinical Networks July 2012 • A range of networks : – Operational Delivery Networks i.e. neonatal, adult critical care, trauma burns – Strategic clinical networks i.e. cancer, cardiovascular, maternity and children and mental health, dementia and neurological conditions – Local networks, locally determined. SCNs and ODNs • Operational delivery networks are focussed on coordinating patient pathways between providers over a wide area to ensure access to specialist resources and expertise. Provider clinicians dominate their membership, though work closely with patients and other stakeholders. – In future they will be provider hosted and funded • Strategic clinical networks define evidence based best practice pathways, and operate as engines for change across complex systems of care, maintaining and or improving quality and outcomes. They bring primary, secondary and tertiary care clinicians together with partners from social care the third sector and patients. – In future they will be NHS CB hosted and receive national commissioning funding for their core functions – Criteria for SCNs set out in ‘The Way Forward’ Current Situation • Existing provider delivery networks – With national coverage: Critical Care, Adult, paediatric, Neonatal, Burns, Trauma. – Variable coverage: adult congenital heart disease, paediatric congenital cardiac surgery, paediatric neuroscience. • Variable funding mechanisms and scope. Eg 11/12 baseline survey £8.5m on provider delivery networks, with £4m on adult critical care. Trauma networks just being established. • Range per network £84k to £621k pa. • Mainly PCT hosted Proposal • Move to align to senate geography -12 in England • Include membership of ODN in commissioning specifications for inclusion in 13/14 contacts. • Over time funded through tariff • Nationally set strategy coordinated through NHS CB specialised commissioning programme of care leads and clinical reference groups. • Continued patient and family engagement • Close alignment with SCNs , local senates, AHSNs, LETB, research networks, HWBs, CCGs etc Purpose of ODNs • • • • • • • Ensure effective clinical flows Facilitate system wide collaboration Multi professional engagement Consistent application of standards Quality assurance Capacity planning Activity and quality monitoring Benefits of ODNs • Improved outcomes and efficiency • Stronger collaborative provision • Increased consistency of care and patient and family experience • Additional risk sharing opportunities • More accurate costing, leading to better resource utilisation • Development of ‘prime contracting’ focus • Increased speed of innovation adoption • Rapid learning and development • Improved system resilience including major incident planning Success factors for ODNs • Improved access and egress to and from services at the right time. • Improved operating consistency. • Improved outcomes. • Increased productivity. • Improved collaboration between providers in a pathway. Operating Principles • Hosted by lead provider • Chaired by experienced clinical leader • Link member to relevant national Clinical Reference Group • Use NHS Change Model www.changemodel.nhs.uk • In accordance with pathway in contract specification • Governance within host provider Links to commissioning policy development • 60 National Clinical Reference Groups linked to Specialised commissioning definition set • CRGs support development of national contracting products, quality monitoring tools, developing clinical innovation • Coordinated through Regional Programme of Care Leads, within Regional Specialised commissioning teams Proposed funding mechanisms • Long term- tariff funded. Providers will not be able to provide these services without being in an appropriate network and will need to agree with each other how this is resourced. • Transitional arrangement ( 13/14 and 14/15): c0.1% CQUIN for relevant specialised services will be retained by specialised commissioners • Nationally 0.1% CQUIN worth c£9m compared to current estimated £8.5m cost Proposed contractual arrangements • Local LAT Specialised Commissioning teams will agree a host provider for each network and a locally agreed quality and outcome related service specification. • Host provider receives locally agreed CQUIN funds • All relevant providers will have a service specification requiring networked pathways through an ODN approach • Host provider may or may not be tertiary provider; may be economies of scale to host more than one ODN Accountability • ODN hosted by and accountable to a lead provider • Governance arrangements agreed between members, to include clear escalation and risk management arrangements • Subject to specification in the contract • Annual report highlighting quality outcomes to be produced HR issues • In future, staff will be employed by the host provider, within provider determined structures • TUPE principles apply. • Specialised commissioning teams will negotiate transfers with host providers within a national HR framework • National timescales apply ie staff to know destination by December 12 • Further consultation with staff to follow Next steps • NHS CB sign off of ODN operating model ( by end of November 12) • Communications and engagement plan • Organisational development arrangements • Managing transition • Local negotiation between specialised commissioning teams and providers • Development of national model specifications for ODNs