Failure Effect Mode Analysis
advertisement

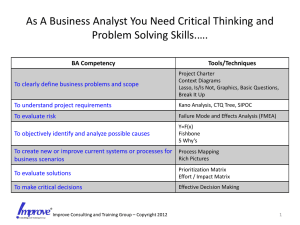
Failure Effect Mode Analysis By Rajeev Kishore Uros Great question; a confusion in estimation How a raw egg bounce? Tacoma Bridge Collapse Gondola FMEA Introduction to FMEA • To introduce new products or manufacturing processes successfully in a cost-effective manner, resources should be allocated upfront to prevent problems. • Fixing the problem after a product is manufactured is more expensive than it is to prevent them. Benefits of FMEA • • • • • Reduce the number of engineering changes Reduce product development time Lower start-up cost, and reduces warranty Greater customer satisfaction Increased cooperation and teamwork between various functions • A well-documented project history and information database Do you know? “Failure Modes...” is a misnomer — some sources now call FMEA by another name: “Fault Hazard Analysis.” Reliability • Failures are expensive • System flakiness is a major source of user frustration - 25% in survey have seen peers kicking their computers - 2% claim to have hit the person next to them in their frustration Failures are not very well understood No Publicly available data on failures on real systems WHY? Different types of FMEA • Design (DFMEA): technique used primarily by a Design Responsible Engineer/Team as a means to assure potential failure modes, causes and effects have been addressed for design related characteristics • Process (PFMEA): technique used primarily by a Manufacturing Engineer/Team as a means to assure potential failure modes, causes and effects have been addressed for process related characteristics The Pre-work Process or Product Name _____ Prepared By ____________ Page ________of ________ Person Responsible __________________ FMEA Date (Orig.) _______ Revised _______ Guide to do FMEA STEP 1 STEP 2 • Scope Project STEP 3 • Identify potential effects of failures STEP 4 • Determine severity rankings STEP 5 • Identify causes of failures STEP 6 • Determine occurrence rankings STEP 7 • Define current control methods STEP 8 • Determine detection rankings STEP 9 • Calculate Risk Priority Numbers STEP 10 • Prioritize corrective actions • Brainstorm all potential failures FMEA Worksheet Funct Failure Failure S Failure O Current D R Rec. ion mode effect Cause Control P Actions N 1. 2. S O D R P N Terms and Definitions • • • • Fault Failure Function/Process Examples – 1. Pencil Sharpener 2. Oil changing process Def. Cont… Failure Mode • The way failure occurs • Can cause a failure mode in another item • Identify and list possible failure modes • Examples – 1. Frequently breaking the graphite 2. Wrong type of oil or No oil added Def. Cont… Failure Effect • Immediate consequence of a failure • Effects can range from very small to major disasters. • Examples – 1. Improper writing 2. Engine wear or Engine Failure Def. Cont… Severity (SEV) • Worst consequence of a failure • How is it determined? • Standard scale from 1 (no danger) to 10 (very severe) • Prioritize the failures modes and their effects Def. Cont… Failure Cause • Design weakness - How the failure could occur? • Listed in technical terms and are documented • Examples – 1. Improper mixture of Graphite and Clay 2. Misread oil chart or Hurrying Def. Cont… Occurrence (O) • Probability of the cause occurring • Look for similar products or processes • Probability number scale from 1 (not likely) to 10 (inevitable) • Detailed development section of FMEA Process Def. Cont… Current Controls • Current controls that prevent the failure cause (before causing effects) • Examples – 1. improve quality of graphite 2. No control or engine light Def. Cont… Detection (D) • Assessment of the likelihood that the current controls will detect failure cause or failure, before it reaches the customer. • Different techniques are used by an engineer • Identify the detection number ‘D’, ranging from 1 (easily detectable) to 10 (cannot detect) Def. Cont… Risk Priority No (RPN) • RPN = S * O * D • Risk that has greatest concern can be identified • Failures are prioritized according to: - Severity - Occurrence - Detection • Requires additional planning or action Pareto Diagram Recommended Actions and Results • Address potential failures that have a high RPN • Are any further actions required? • Assign new value for S, O and D, and calculate new RPN value • Update the FMEA as the design or process changes Development Team • Crucial step in FMEA • FMEA is a team function - Formulate cross functional team - Understand customer requirements – both internal and external inputs - All team members walk and observe the process - Make notes or observations Link with continuous improvement Component Proving Process Mistake Proofing Techniques Continuous Improvement Programs FMEA FMEA Timing • FMEA should be updated whenever: - At the conceptual stage - Changes are made in the design - New regulations are instituted - Customer feedback indicates a problem Uses of FMEA • Development of methods to design • Test systems to ensure that the failures are eliminated • Tracking and managing potential risks • Ensuring that failure will not injure customer or impact a system • Evaluation of customer reviews on the problems indicated TQM Principles •Continuous Improvement Process •Continued building and prevention of failure on the process •Employee Involvement and Empowerment •Employees can feel empowered and involved if they correct an error in a process or part. •Leadership •There needs to be a team leader for every group, which is assigned to one part of the process. TQM Principles •Performance Measurement •RPN, lower the better •Supplier Partnership •If one supplier has bad parts, it directly affects your products, by creating failure in your company. •End Customer Satisfaction •Reliability meets customer requirements Limitations • FMEA is limited by the team experience • FMEA may only identify and avoid major failure modes • Multiplication of rankings may result in rank reversals FMEA Conclusion • Purpose of FMEA, is the process of identifying potential failure modes and their associated causes, assigning severity, Occurrence, and Detection ratings, and calculating RPN • RPNs should be used for continuous improvement activities Resources http://www.pehwhk.com/Flyers/FAILURE%20MODE%20EFFECT%20 ANALYSIS%20_FMEA_.pdf http://www.fmeainfocentre.com/handbooks/fmeamanual.pdf http://www.fmeainfocentre.com/handbooks/umich.pdf. http://www.aluminiumville.co.uk/images/lightbox/aluminium_process.jp g www.nitrd.gov/subcommittee/hec/workshop/20060816/Data/HECIWGFSIO-2006-Data-Failure-Schroeder.pdf http://www.npd-solutions.com/fmea.html http://www.sigmazone.com/gondola_lift_fmea.htm http://www.suppliermanageronline.com/training/corporation/fmea_training.pdf