Chapter 12 problems
advertisement

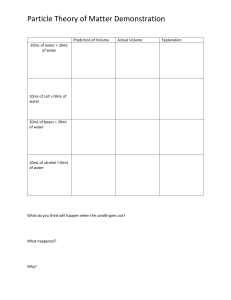
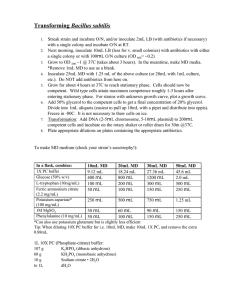
Chapter 12 problems What type of forces, intermolecular or intramolecular… • A) prevent ice cubes from adopting the shape of the container? • B) are overcome when the ice melts? • C) are overcome when liquid water vaporizes? • D) are overcome when gaseous water is converted to hydrogen and oxygen? When nitrogen gas is compressed to form liquid nitrogen, it cools to a very low temperature (around -200oC). Molecularly speaking, the nitrogen gas molecules released a lot of energy (as heat). Where did this energy come from? Which one will have a higher vapor pressure: a) ethanol or ethane? b) 10mL H2O in a 3-cm diameter vial or 10mL H2O in a 10-cm diameter culture plate? At which condition will a wet rag dry faster? a) 20oC or 40oC b) 33% humidity or 10% humidity Which one will have a higher melting point? a) cis-fat vs trans-fat b) CCl4 vs NaCl • The exceptionally high heat capacity of water is due to the number of H-bonding a single water molecule have. How many can it have? Show them. • Calculate the total heat needed to convert 22.00 g of ice at -6.00oC to liquid water at 0.500oC. • Given data: ΔHfus = 6.02 kJ/mol • Cice = 2.09 J/g-oC If a liquid has a ΔHvap of 35.5 kJ/mol, and a boiling point of 122oC, what is its vapor pressure at 113oC? Consider the phase diagram… ·E · B · ·A · C ·D F