ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Material Behavior in Metal
advertisement

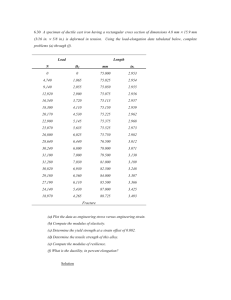
Introduction To Manufacturing Systems by Ed Red ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Fundamentals of Metal Forming • Metal forming is plastic deformation of metals into desired shapes • Deformation stresses may be tensile or compressive (usually compressive) • Metals must exhibit certain properties to be formed efficiently • Friction is an important factor in metal forming • Strain rate and temperature are important factors in metal forming ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Material Behavior in Metal Forming Engineering Stress and Strain (used by engineering designers): Engineering stress se = F/Ao Engineering strain e = (L - Lo)/Lo Hooke's Law (elastic region): se = E e ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Material Behavior in Metal Forming Stress - strain diagrams (tensile and compression): Ultimate strength se Plastic region Yield strength Elastic region 0.2% offset ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems e Material Behavior in Metal Forming Common parameter values: E Yield strength Ultimate strength ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Al Steel psi 10 x 106 30 x 106 MPa 70 x 103 210 x 103 psi 4000 60,000 MPa 28 400 psi 10,000 MPa 70 90,000 600 Material Behavior in Metal Forming True Stress and Strain (used by manufacturing engineers): True stress s = F/A True strain e= s Start of necking Plastic region Elastic region ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems e dL/L = ln(L/Lo) Material Behavior in Metal Forming Why do engineering designers base their design on engineering stress/strain, but manufacturing engineers use true stress-strain? ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Material Behavior in Metal Forming Strain hardening - Resistance to increasing strain. Stress-strain can be related in the plastic region by the form s = K en where K is the strength coefficient and n is the hardening exponent. A log-log diagram will show the linear behavior expected for a curve of this form. Note: The greater the n, the greater the strain hardening effect. Necking for many ductile materials begins approximately when the true strain reaches a value equal to n. ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Material Behavior in Metal Forming Material Strength coeff, K psi MPa Aluminum Steel ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems 30,000 125,000 210 850 Strain hardening exp, n 0.18 0.15 Material Behavior Example The following data are collected during a tensile test in which the initial gage length is 5 in. and the cross-sectional area is 0.1 in2: Load (lb) 0 4000 5180 6200 6500 6200 4600 Length (in) 5.000 5.009 5.25 5.60 5.88 6.12 6.40 Determine the yield strength Y, modulus of elasticity E, and tensile strength TS. Also determine the strength coefficient K and the hardening exponent n. ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems Some relations you need to know s = se (1 + e) e = ln (1 + e) Also note that it is often necessary to use a constant volume relationship for modeling process phenomena. In the case of a tensile test, the appropriate equation would be AL = Ao Lo ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems What have you learned? ME 582 - Manufacturing Systems