CC presentation
advertisement

Introduction to
Computers
An electronic, programmable device that:
Accepts
data in the form of Input
Manipulates
Produces
that data by Processing
results in the form of Output
Stores
for future use through Storage
devices
Slide
2
Four basic operations:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Input
Processing
Output
Storage
Slide
3
Computers perform operations comprising
the information processing cycle to
manipulate data into information and
store for future use.
Data is a collection of facts, or
unprocessed items.
Information is the portion of those
facts that conveys meaning and is useful
to the user.
Slide
4
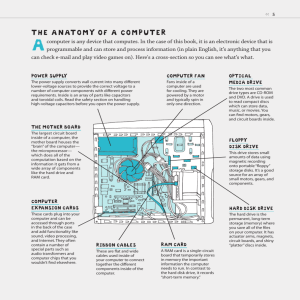
Hardware-the
physical components that make
up a computer system. Six primary components
include:
Input Devices
Output Devices
Processor
Storage devices
Memory
Communication
Software-detailed
set of instructions that tells
a computer exactly what to do. {aka Computer
Program}
Booting is the process that loads the operating
system into RAM (Random Access Memory).
Slide
5
Allow you to enter data, programs, commands, and user
responses into a computer.
Keyboard-contains keys you press to enter data.
Mouse-pointing device that controls the pointer.
Microphone-a device that converts sound waves into
electrical energy to be broadcast, recorded or
amplified.
Scanner-light-sensing device that reads printed text
and graphics and translates the results into digital
form.
Digital Camera-records photographic images,
sound and/or video in digital form.
Slide
6
Graphics/Digitizing Tablet-uses a stylus to sketch
drawings or images on surface.
Stylus-resembling a pen, uses pressure to input
data.
Touchpad-controls pointer movements by sliding
your fingertip on the pad.
Touch Screens –LCD display capable of sensing
multiple points of contact.
Game Controllers-consist of game pads, joysticks,
gloves, steering wheels, trackballs, etc.
Slide
7
Case that contains electronic components of the
computer used to process data. The Motherboard
is the main circuit board and includes the processor,
memory and expansion slots.
Slide
8
Processor,
aka Central Processing Unit
(CPU)-is the brain of the computer that
interprets and executes the instructions that
operate a computer.
Control Unit-interprets the instructions
Arithmetic/Logic Unit-performs the logical and
arithmetic processes.
Memory,
aka Random Access Memory(RAM)consists of the electronic components that
temporarily store instructions waiting to be
executed by the processor.
Slide
9
The amount of memory in computers is
measured in bytes.
Terabyte
(TB)- one trillion memory locations
Gigabyte
(GB)-one billion memory locations
Megabyte
Kilobyte
Byte-one
(MB)-one million memory locations
(K)-one thousand memory locations
memory location
Slide 10
Make information resulting from processing
available for use.
Printers-produce
a hard copy also called a
printout and classified as either Impact or
Nonimpact.
Monitors-produce
a soft copy that visually
conveys text, graphics, and video information.
Speakers-converts
electrical signals into sounds
loud enough to be heard at a distance.
Projectors-an
optical instrument that projects
an enlarged image onto a screen.
Slide 11
Impact
Printers-print by striking an inked
ribbon against the paper.
Dot-Matrix
Printer-produces printed images
when tiny pins strike
an inked ribbon on
continuous form paper.
Slide 12
Nonimpact
Printers-form characters by means
other than striking a ribbon against paper.
Ink-jet
Printers (DeskJet or Photo
Printers)-produce images by using a
nozzle that sprays tiny drops of ink
onto a page.
Laser
Printers-high-speed,
highest- quality printers that form
images to be printed from a beam of
light focused on a photoconductor
drum similar to a copying machine.
Slide 13
Monitors are composed of individual picture
elements called Pixels that form parts of a
character or graphic shape on the screen.
Panel Monitors-take up much less desk
space.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)-Monitors use a
Flat
liquid display crystal, similar to a digital watch,
to produce images on the screen.
Ray Tube (CRT)-display graphics
through technology used in most televisions.
Cathode
Slide 14
Used to store instructions, data, and
information when they are not being used in
memory.
Four
basic types of storage media include:
Magnetic Disks
Optical Discs
Tape
Miniature Mobile Storage Media
Slide 15
Use magnetic particles to store items such as data,
instructions, and information on a disk’s surface.
Hard
Disk-contains one or
more inflexible, circular
platters that magnetically
store data, instructions, and
information.
Floppy
Disks (Diskette)inexpensive portable storage
medium.
3.5” only stores 1.44 MB
Slide 16
Process of preparing a disk to be read from or
written on by dividing the disk into tracks and
sectors.
narrow recording
band that forms a full
circle on the surface of a
disk.
Track-a
Sector-pie-shaped
storage
section, which breaks the
tracks into small arcs
storing up to 512 bytes of
data.
Slide 17
Flat, round, portable storage medium that
reads and records data using laser technology.
CD-ROM
& DVD-ROM (Read-Only Memory)-can
read but not write on (record) or erase.
CD-R
& DVD-R (Recordable)-record on each part
only one time but cannot erase.
CD-RW
& DVD-RW (Rewritable)-erasable optical
discs you can write on multiple times.
DVDs (Digital Versatile Discs) are the highest
capacity optical discs capable of storing 4.7-17 GB.
Slide 18
Optical Disc
CD-ROM
CD-R
CD-RW
DVD-ROM
DVD-R
DVD-RW
Read
Slide 19
Write Erase
Magnetically coated ribbon of plastic housed in a
tape cartridge capable of storing large amounts
of data at a low cost. Primarily used for longterm storage and Backup.
A
Backup is a duplicate
of a file, program, or
disk that you can use in
case the original is lost,
damaged, or destroyed.
Slide 20
Flash Memory Cards-solid-state media
that consist entirely of electronics and contain
no moving parts.
USB Flash Drive-flash memory storage
device that plugs into a USB port on a
computer or mobile device.
Smart Card-stores data on a thin
microprocessor embedded in the card.
Slide 21