DNA and RNA Review
advertisement

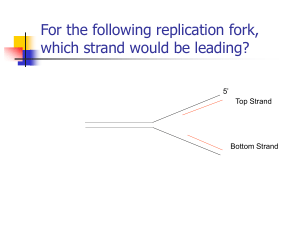
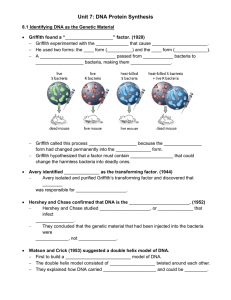
Name: _____________________________________ Date: ____________________ Block: _______________ Biology IB Unit 5 Test Review Sheet 1. What is DNA? What shape (structure) does this molecule have? Draw a sketch of DNA in the space provided. 2. What sugar is found in DNA and RNA? What else is different between DNA and RNA? 3. How did _______________________________ determine that adenine pairs with _________________ and guanine pairs with _________________? 4. Where is DNA located in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________ 5. Define: transcription, translation, replication, and transformation (**BE SURE to specify and describe what happens in each process**) 6. During DNA replication, the following DNA strands will produced what base pairs? a. TCGAAC c. AGCTTG e. TTGCGC b. GATCCA d. GAUCCA f. GTGTGC 7. What does RNA contain that DNA does not? 8. What are the three different types of RNA and what is the function of each? Where are each of these three copied from? a. b. c. 9. Where does transcription take place? (Where is RNA formed?) 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? 13. Using the information they contain, what do genes assemble? FIGURE 1 Name: _____________________________________ Date: ____________________ Block: _______________ 14. Why is mRNA considered to be the blueprint for the genetic code? 15. What are the 4 main types of mutations? 16. Define the following: substitution, insertion, and deletion 17. What is a promoter? How does it help with RNA polymerase? 18. What happens to the gene for a protein that is not continuously used by the cell… but still needed sporadically? 19. What are Hox Genes and what do they determine? 20. What are the three main parts of an RNA nucleotide? 21. Looking at FIGURE 2, which image illustrates tRNA? 22. Also looking at FIGURE 2, what does this tRNA molecule do? FIGURE 2 23. Using FIGURE 1 above, what codons specify for: a. ALANINE ____________________________________________________________________ b. LEUCINE ____________________________________________________________________ c. PHENYLALANINE ____________________________________________________________ d. ARGININE ___________________________________________________________________ e. LYSINE ______________________________________________________________________ 24. Where did “Sequence D” come from (A or B)? _________________ 25. What is “F” in this image? What does it specify? 26. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? 27. What is the relationship between “codons” and “anticodons”? How is this relationship important? 28. What is “deletion” and what is “duplication”? Draw an example of each.