Kimz - Wikispaces
advertisement

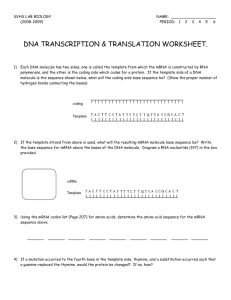
Section 3 Definitions RNA- ribonucleic acid, a natural polymer that is present in all living cells and that play a role in protein synthesis. Gene expression- the manifestation of the genetic material of an organism in the form of specific traits. Transcription- the process of forming a nucleic acid b y using another molecule as a template. Translation- the portion of protein synthesis that takes place at ribosomes and that used the codons in Mrna molecule to specific the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides chains Codon-In DNA and mRNA, a three-nucleotide sequence that encodes an amino acid or signifies a start signal or a stop signal. Section 3 Questions 1. What are the structural differences between RNA and DNA? Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid –a molecule made of nucleotide subunits liked together. Like DNA, RNA has four bases and carries information in the same way that DNA does. 2. What is the role of a promoter? Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to the specific DNA sequence in the gene that is called the promoter. The promoter site the ‘start’ location. 3. How do codons and anticodons differ? An anticodon is a three-nucleotide sequence that is complementary to an mRNA codon. Each codon is matched to 1 of 20 amino acids or acts as a start or stop signal for the translation stage.