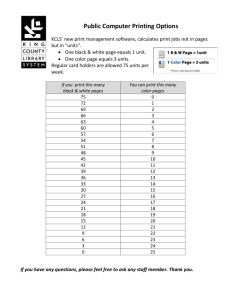
File
advertisement

1. Computer: Electric devices, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory, that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules (process), produce results (output), and store the results (storage) for future use. 2. Information Processing Cycle: Four basic operations that a computer performs. (Input, Process, Output, and Storage). 3. Data: A collection of unprocessed items, which can include text, numbers, images, audio, and video. 4. Information: Conveys meaning and is useful to one or more people. 5. Computer Users; End Users; Users: People who use the computer directly or use the information it provides. 6. Computer Program- or Software: A detailed set of instructions that tells it exactly what to do. 7. Keyboard: An input device that contains keys you press to enter data into the computer. 8. System Unit: The processor, memory, and storage devices are housed in this box-like case. 9. Input Device: Any hardware component that allows you to enter data, programs, commands, and user responses into a computer. 10. Mouse: A pointing device that fits comfortably under the palm of your hand. 11. System Unit: A case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data. 12. Processor: Also called the Central Processing Unit (CPU), interprets and carries out the basic instructions that operate a computer. 13. Arithmetic/logic Unit: Performs the logical and arithmetic process. 14. Control Unit: Interprets the instructions. 15. Memory: Also called Random Access memory (RAM), consist of electronic components that temporarily store instructions waiting to be executed by the processor, data needed by those instructions, and the results of processed data (information). 16. Kilobyte (K or KB): Equals approximately 1,000 memory locations. 17. Megabyte (MB): Equals approximately one million memory locations. 18. Gigabyte (GB): Equals approximately one billion memory locations. 19. Memory Location –or- Byte: Usually stores one character such as a letter A. 20. Output Device: Make the information resulting from processing available use. 21. Impact Printer: Prints by striking an inked ribbon against the paper. 22. Nonimpact Printers: Form characters by means other than striking a ribbon against paper. 23. Photo Printers: Produce photo-quality pictures and are ideal for home or small-business use. 24. Display Device: An output device that visually conveys text, graphics, and video information. 25. Monitor: A display device that is packed as a separate unit. 26. Flat Panel Monitor and CRT: Two basic types of monitors. 27. LCD monitor: the most popular type of flat panel monitors. 28. CRT (cathode ray tube): television-like monitor. 29. Pixels- monitor composed of individual picture elements 30. Storage device- an item used to store info. 31. Magnetic discs- these items use magnetic particles to store info like media, instruction and other important info. 32. Formatting-the process of dividing the disc into tracks and sectors so the computer can search for data. 33. Track- a narrow recording band on a disc 34. Sectors- storage locations that consist of pie-shaped sections. 35. Portable storage medium- you can remove the medium from one computer and carry it to another computer using a floppy disc or hard disc. 36. Hard disc- a storage device that contains one or more inflexible, circular patterns that magnetically store data. 37. Head crash38. Back-up: 39.