CHAPTER 8
advertisement

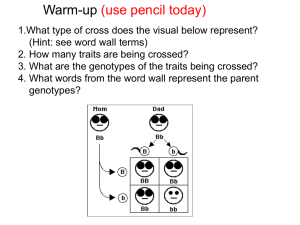
CHAPTER 8 INTRO TO GENETICS Gregor Mendel -FATHER OF GENETICS GENETICS-STUDY OF HEREDITY HEREDITY-PASSING OF CHARACTERISTICS FROM PARENT TO OFFSPRING TRAIT-INHERITED CHARACTERISTIC TRUE-BREEDING-PURE FOR A TRAIT Monohybrid Cross Crossed tall and short pea plants that were true-breeding for those traits Monohybrid cross -produced offspring whose parents differed by one trait (height) Offspring were called hybrids P1 Tall plants X short plants F1 Tall Pea Plants Monohybrid Cross P1 Tall plants X short plants F1 Tall Pea Plants F2 F1 x F1 3 Tall; 1 short EACH PERSON RECIEVES TWO COPIES OF A GENE -ONE FROM EACH PARENT -WHEN REPRODUCTION TAKES PLACE. ALLELES THERE ARE ALTERNATE FORMS OF A GENE CALLED ALLELES YOUR TRAITS ARE DETERMINED BY THE ALLELES YOU RECEIVE FROM YOUR PARENTS. WHEN TWO ALLELES OCCUR TOGETHER, ONE OF THEM MAY BE EXPRESSED (PHYSICALLY SEEN) WHILE THE OTHER MAY NOT BE OBSERVED IN THE ORGANISM’S APPEARANCE (HIDDEN) The expressed gene is called the dominant gene. (represent by capital letters) The hidden gene is called the recessive gene. (represented by lower case letters) Law of segregation When gametes are formed during meiosis, the alleles separate so that each gamete recieves only one allele for each trait. If the two alleles of a gene are the same the individual is said to be homozygous. TT -homozygous dominant tt -homozygous receive If the two alleles of a gene are different the individual is said to be heterozygous Tt The set of alleles an organism recieves from their parents is calle the. genotype genotype =type of gene The physical appearance of an organism (which is determined by the genotype) is called the phenotype. phenotype=physical Example Let's say that for the redthroated booby bird, red throat is the dominant trait and white throat is recessive. Since the "red-throat code" and the" white-throat code" are alleles (two forms of the same gene), we abbreviate them with two forms of the same letter. So we use "R" for the dominant allele/trait (red throat) and "r" for the recessive allele/trait (white throat). Our possible genotypes & phenotypes would be like so: Symbol Genotype name Phenotyp e RR Homozygou s pure dominant Red throat Rr Heterozygou Red s throat rr Homozygou s pure recessive White throat Punnet square Diagram that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring Use these parental genotypes: Tt x tt. Dihybrid crosses (DI=2) Cross that involves parents who differ by two traits Law of independent assortment-the inheritance of one trait had no effect on the inheritance of another trait. Seed color has no effect on seed shape. Dihybrid cross Cross involving parents that differ by two traits Law of independent assortment-genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other RRYY x rryy = RrYy RrYy x RrYy • R and r will separate; Y and y will separate • Recombine to produce 4 different gametes Example of a Dihybrid Cross Diagram of a Dihybrid Cross Images and examples are taken from various websites.