Student Presentation
advertisement

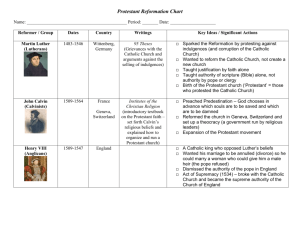
Weber and the Protestant Work Ethic Origin Weber proposed a theory to help explain the development of capitalism in Western Europe. First proposed his theory in a two part paper published in 1904 & 1905. Stressed the role of ascetic Protestantism in the development of modern captialism and the growth seen in parts of Western Europe during the 1500 ’s and beyond. Theory Weber stated that Protestantism, specifically Calvanism, played a large role in the development of capitalism. However, it had no part in sustaining it, rather capitalism grew on its own once in place. Protestantism was singled out as the catalyst, however Weber believed that it could potentially be another force. His only criteria was that it be a radical cultural force that broke through traditional beliefs and attitudes. This was of course contingent on other factors being present, such as economic, technical and political factors. ‘Spirit of Capitalism’ and the growing accumulation of wealth. Cultural shift under capitalist rationalization. Capitalism becoming the culture. Weber was curious about the source of this culture. He did not accept a purely materialistic view. Led him to the connection between the Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism.‘ Protestantism Why the Protestants? Salvation, doctrinal shifts and the growth of personal wealth. Calvinists as the first. Opposite of Catholics. The blending of Protestand Ethic and Spirit of Capitalism into one. Criticism Weber’s incomplete theory helped fuel criticism. Two main criticisms. Middle ground? Catholicism Catholic community vs. Protestant community. One’s path to salvation. Charity and poverty. Present Day Weber’s theory in present day economics. Reluctance by economists to blend disciplines. Source: Howard, Michael C. One Hundred Years From Today: Max Weber’s the Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism. History of Economics Review, vol. 0, no. 42, Summer 2005, pp. 100-103. Max Weber Roman Catholics are assured of their salvation from their belief in the sacraments and by following the authority of the Church’s hierarchy. He believed that the protestant ethic had removed such assurances of salvation. Salvation By lacking their assurance of salvation, protestants were led abroad for new answers Success as a new medium to salvation Out of this emerges Calvinism Calvinism Calvinism is a theological system and an approach to Christian life that emphasizes God’s sovereignty in all things. It falls within the realm of Protestant Christianity and is sometimes called the Reformed tradition or Reformed theology. Reformation Rising importance of Reformed Churches belongs to the second phase of the Protestant Reformation Evangelical churches began to form A spread across Europe His ideas about the reformed church across Europe and began to emerge in countries such as Germany, France, Hungary… Calvinism Continued… Concept of Predestination No longer can good/faithful acts automatically lead to the path of heaven Either among the ‘elect’ or not Wealth taken as a sign of the ‘elect’ Continued Some more… A clear incentive for acquiring wealth Thus, Calvinism (so also, the protestant ethic) led to a religious outlook that placed emphasis on discipline that encouraged men to acquire wealth Why is this important? I don’t know… Just kidding Weber’s intention was to demonstrate a relationship between Calvinism and a form of capitalism, deeming it important. Barro and McCleary Costs include not only time but resources expended on buildings, precious objects and so on. Believing (values) relative to belonging (or attending) is the main channel through which religion matters for economic and other outcomes Blum and Dudley Europe Today Economic Networks Protestant Europe created a distributed economic network that spread across state borders. new arbitrage opportunities available in cities bordering on the Atlantic Information available from Protestant printing centers-Catholic ones were censored Divergence Between North/South Growth of real wage and population Urban population growth 5x greater in protestant regions than Catholic ones Literacy Protestant now (1750) more literate English males 60% vs. French males 40% Catholic Urban Literacy Network (1750) The Protestant Urban Literacy Network (1750) Blum and Dudley’s Conclusions European economic growth prior to 1750 was actually not Malthusian Weber’s individual protestant work ethic not strongly supported Literacy along with a higher honoring of contracts created a close knit network of Protestants Religion in China Traditional Chinese religions: Confucianism system of social and ethical philosophy Daoism indefinable, unifying force at the centre of the universe Buddhism Buddha taught that in life there exists sorrow/ suffering which is caused by desire and it can be cured by following the Noble Eightfold Path Non-Traditional Religions Islam Christianity History of Christianity in China Developed since at least 7th century AD 1807: Chinese translation of Bible by missionary Divided into 2 main categories: Protestant (基督教徒) Catholic (天主教徒) Communism Era Communist Party discouraged the practice of religion not only because it was atheist, but also believed religion was a dangerous alternative set of beliefs to communism 1982 constitution amended thanks to Deng Xiaoping's views, and freedom of religion was allowed. Catholics worship through the Chinese Catholic Patriotic Association rather than the Roman Catholic Church Question: Where do you think China stands? Do you think religion has had any impact on its economic growth?