liberalsim_and_constructivism
advertisement

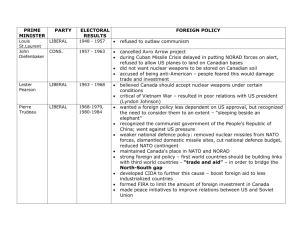
Why theories are important for foreign policy? Theories provide different policy options and contain different assumptions about how the world works Single world through multiple lenses Liberaslim Sees world as it should be Human rights, liberty, democracy, market, institutions Freedom of individual, laissez faire, social welfare Liberalism in foreign relations and establishment of peace- war is inevitable Use diplomacy to resolve conflicts Immanuel Kant “perpetual peace” Michael W. Doyle argues, claims that legitimate democratic domestic orders prevent the creation of conflict and war and sustain peaceful international orders Robert Keohane; complex interdependence Francis Fukuyama; end of history Imprudent aggressiveness- liberal states aggression against non-liberals Peace is only for liberals, liberal states fought wars with non-liberal states War is result of authoritarian states (Hitler, Napoleon, Mussolini, Stalin) Spread of liberal institutionalized norms and principles will create an environment as Doyle suggest in his Democratic Peace theory and there will be no use of force between countries that are democratic and it would eventually end international conflict. Liberals enter into war only with non-liberal states in order for self-defense and for humanitarian reasons However, Doyle suggests that they are prone to what he calls ‘liberal imprudence’, as well as ‘liberal imperialism’, seeking to ‘export’ their liberal democratic doctrine to the rest of the world Bosnian War is example how liberals failed to react HR violations and no strong commitment to democracy and war wars in Afghanistan and Iraq (example of imprudent liberalism)do not fit with the liberal theory because they are neither initiated for self-defense or for humanitarian reason. Bush administration highlights the promotion of democracy while largely neglecting the international institutions human right violations in Guantanamo Bay detention camp Liberals disagree with nature of anarchy (realist assumption of ‘state of war’, threat of other states) Three types of liberals 1-First image Lockean: human nature based on protection of life, liberty and property to preserve peace, mutual trust under the law (unlike Hobbes) 2-Second image commercial: societal, domestic forces, effects of market and commercial capitalism, instead of relative economic power (realist assumption) focuses on liberal market which reduces possibility of war (Adam Smith) ‘Invisible hand’ ‘harmony of interests’ Combination of democracy and capitalism is transformation of domestic state and social structure (free trade and peaceful foreign policy best policy of rational majorities in capitalist societies-democratic majoritanism) 3-Third image Kantian: republican internationalist ‘perpetual peace’ relations between liberals and with non-liberals To establish secure expectation of peace: peace between liberals and suspicion towards non-liberals Republican representation (rule of law and elected legislative); responsible to majority liberal respect (human rights); specify majority end’s and interests liberal strategy: defensive international community, protection of liberal community, expansion of liberal markets, multilateral institutions (UN, IMF, WTO,NATO), transnationalism Constructivism Appeared as a ‘third debate’ after the end of the Cold War due to the failure of dominant paradigms to predict end of the Cold War which is used to provide better explanations of the actions taken by states and other major actors as well as the identities that guide these states and actors Concern with how world works and aim to analyze state behaviors Failure of mainstream theories (realism&liberalism) to predict end of Cold War and spread of constructivist approach but not a paradigm (failed to addresses actors, problems or issues) it doesn’t’ offer solution for problems but offer alternative understanding concepts such as anarchy and balance of power It is a framework for foreign policy analysis/institutions, constructivism concern with specific questions: How old practices of rivalry and war-making can be changed through institutionalization which might over time change identities, interest, and practices Interaction across borders-establishment of security communities (NATO, EU) New relationship based on friendship and cooperation rather than rivalry, that identities and interest have been fundamentally changed in process that the structures of human association are determined primarily by shared ideas rather than material forces and that the identities and interests of purposive actors are constructed by these shared ideas rather than given by nature “anarchy is what states make of it“ (Alexander Wendt) which means that the anarchical structure is in fact a phenomenon that is socially constructed and reproduced by states interests and identities of the state are not primarily determined but socially constructed Social construction, importance of norms and ideas (basis of institutions), identity (constitutes interest, identity shaped the interest unlike liberalism and realism) NATO: security community, have headquarter but does not have military forces of its own, it constitutes common understanding, shared practices and interest between member states, establishing document is based on shared identity (Western) and values of members Its foreign policy against Soviet Union during the Cold War and new relationship after the end of the Cold War with former enemy NATO during the Cold War period: Realist view dominated defense alliance, “keeping Russians’ out, the Americans in, the Germans down.” NATO post Cold War period: still security provider based on common interest, identity and shared understanding between member states (almost same as before) BUT, relationship between self-other, rules and norms of alliance becomes stronger between states NATO and war in the Balkans-former Yugoslavia (1990s): test for its existence, new challenges political instability and uncertainty and also opportunity to practice new identity as European actor and foreign policy actor-new practices in new structural environment NATO’s new founding document: instead of defining protecting member’s territory refers to member’s security NATO-Russia relations (foreign policy) Cooperation on missile defense system and other defense related issues Cooperation and shared understanding about the missile defense Change of relations from rivalry to cooperation based on share interests and shared security concern In last two decade NATO adopted constructivist foreign policy by Establishing culture of anarchy based on friendship and cooperation among members Maintaining its role identity as defense alliance