nutrients ppt
advertisement

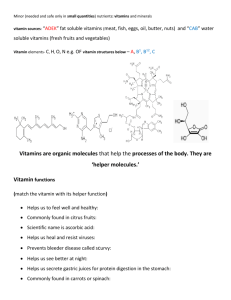
Essential Nutrients What Is Nutrition? The study of how your body uses the food you eat What is a Nutrient? A chemical substance in the body that helps maintain the body 6 Classes of Nutrients Your body needs over 50 different nutrients which can be divided into 6 classes: * Carbohydrates * Fats * Protein * Vitamins * Minerals * Water CARBOHYDRATES WHAT ARE THEY? * Essential nutrients * Make up the foundations of diets * Predominant in plant based foods * How much is recommened? A minimum of 130 grams of dietary carbohydrates * is needed daily Recommened 45-65% of your daily calories come * from carbohydrates * * * CARBOHYDRATES WHY DO YOU NEED THEM? (Functions) * Most desirable source of energy for the body * Main role is to supply fuel, primarily in the form * of glucose (predominant sugar in high-carb foods) * to your cells * Your brain and red blood cells rely on glucose to * function * 4 calories of energy per gram * EX. 10g of carbohydrates = 40 calories of energy * CARBOHYDRATES simple vs. complex Simple A category that contain a single sugar unit (monosacharide) or two sugar units combined (disaccharide) * * * * * * * * * * * * Monosacharides: Glucose Frutose Sweetest of the monosacharides AKA fruit sugar Galactose Links with glucose to create the sugar found in dairy foods Disaccharides: * Created from glucose, fructose, and galactose * Glucose+Fructose= Sucrose * Table Sugar * 2 Glucose=Maltose * Sugar found in grains * Glucose+Galactose=Lactose * Milk Sugar (Found in dairy foods) CARBOHYDRATES COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates that contain many sugar units combined (Polysaccharide) Starch (The storage form of glucose in plants), fiber (a non-digestible polysaccharide), and glycogen (the storage form of glucose in humans and animals are the three groups of polysaccharides CARBOHYDRATES Where to get them? * Breads * Cereal * Pasta * Fruits * Vegetables * Whole Grains FATS WHY DO YOU NEED THEM? They are... * A protective cushion for your bones, organs and nerves * Used for insulation and to maintain body temperature * Provide energy * Absorb certain nutrients * Carries fat-soluble vitamins * Provides essential fatty acids *9 Calories of energy per gram * It is recommended that 20-35% of your calories come from fat * * Fatty Acids FATS * Saturated- Raises LDL * Polyunsaturated- Decreases LDL * Monounsaturated- Decreases LDL and Increases HDL Cholesterol (Your body MAKES all the cholesterol it needs!) * LDL- Low Density Lipoprotein * Bad Cholesterol * Deposits cholesterol in the walls of the arteries Can lead to heart dise * HDL-High Density Lipoprotein * Good Cholesterol * Removes cholesterol from the tissues and delivers it to the liver to be used as a part of bile and/or be excreted from the body FATS Where to get them? * Cheese * Butter * Nuts * Meats * Dressings * Chocolate PROTEIN WHAT IS IT? * Compounds in your body that consist of numerous amino acids found in all living cells * Amino Acids- Building blocks of protein * 4 calories of energy per gram * How much is recommended? * Healthy adults should consume enough dietary protein to replace the amount they use each day * Pregnant women, people recovering from injury, and growing children need more to supply necessities for building new tissue PROTEIN WHY DO YOU NEED IT? (Functions) Provide structural and mechanical support Help maintain body tissues Needed by the body for growth and maintenance Help body make important substances Regulate body processes Supply energy PROTEIN * COMPLETE * Contains adequate amounts of all essential amino acids * Sources: * Meat * Milk * Eggs * Fish * * * * INCOMPLETE * Lacks some amino acids * Sources: Nuts Beans Peas What can happen if you… * EAT TOO MUCH PROTEIN * Increased risk for: * Heart Disease * Kidney Stones * Osteoporosis- (Brittle Bones) * Cancer * EAT TOO LITTLE PROTEIN * Increased risk for: Loss of bone mass Lack of sufficient protein and/or calories in the body. VITAMINS What Are They? * Tasteless organic compounds that you need in small amounts for growth, reproduction, and overall good health. * The DO NOT provide calories (energy) for your body but are essential for well-being. * There are 13 different vitamins and you get most of them from each of the food groups: * VEGETABLES FRUITS FOLATE VITAMIN A FOLATE VITAMIN C VITAMIN C VITAMIN E GRAINS PROTEIN DAIRY FOLIC ACID NIACIN VITAMIN B6 VITAMIN B12 (FORTIFIED RIBOFLAVIN) THIAMIN NIACIN THIAMIN VITAMIN B6 VITAMIN B12 RIBOFLAVIN VITAMIN A VITAMIN B12 VITAMIN D VITAMINS * Why do you need them? * They promote normal growth * Provide proper metabolism * Protect against certain diseases * Needed by your body to grow, reproduce, and maintain good health * Some function as antioxidants: * Substances that neutralize unstable molecules that can damage the cells of the body and possibly contribute to the risk of chronic diseases. * Vitamins A, C, and E and beta-carotene are antioxidants VITAMINS Fat Soluble vs. Water Soluble Fat-Soluble Vitamins Dissolve in fats Can be stored in fatty tissues of the body NUTRIENT Vitamin A FUNCTIONS SOURCES Keeps skin and mucus Butter, dark green and membrane healthy yellow fruits and Prevents night vegetables, egg yolk, blindness Promotes liver, whole and fortified growth milk Vitamin D Builds strong bones and teeth Egg yolk; fortified butter, margarine, and milk, the sun Vitamin E Acts as an antioxidant to protect cell membranes Eggs, liver, salad oils, whole grain cereals Heps blood clot Cauliflower, egg yolk, organ meats Vitamin K VITAMINS Fat Soluble vs. Water Soluble * Water-Soluble Vitamins *Dissolve in water *Not stored in the body NUTRIENT FUNCTIONS SOURCES Vitamin C Helps wounds heal Helps fight infection Broccoli, citrus fruits, tomatoes Thiamin Keeps nervous system healthy Release energy from food Pork, whole grain breads and cereals Riboflavin Helps cells use oxygen, Breaks down carbohydrates Cheese, eggs, milk, poultry Niacin Keeps nervous system healthy Helps cells use other nutrients Dried beans and peas, peanuts Folate Helps protect brain and spinal cord of unborn babies Bananas, fortified breads and cereals ARE SUPPLEMENTS A HEALHTY SUBSTITUTE? * Americans spend more than $11 Billion on vitamin and mineral supplements annually * Why is it called a supplement? Because it should do just that... SUPPLEMENT your diet, not replace a healthy diet. * Supplements are useful for people who cannot meet their needs through a regular, varied diet, such as: * Women who may become pregnant (Folic Acid) * Pregnant and breastfeeding women * Older individuals * Individuals who do not drink enough milk Individuals on low-calorie diets * Strict vegetarians with limited dietary options for certain vitamins and nutrients Overconsumption can become poisonous HOW SHOULD YOU GET YOUR VITAMINS? Foods are the best way to meet your vitamin needs * Provide more than just vitamins * Substances and nutrients in foods all work together to keep you healthy * Fortified Foods (foods with added nutrients) can be an option for individuals whose diets fall short of some nutrients. * MINERALS WHAT ARE THEY? * Elements essential to the nutrition of humans * Work with other nutrients, such as protein and carbs, to enable your body to function properly. * WHY DO YOU NEED THEM? * Electrolytes (minerals that are charged ions in your body fluids) help maintain fluid balance * Can work with your immune system * Play a role in structural growth * MINERALS Macrominerals VS. Trace Elements * MACROMINERALS * Needed in amounts of * 100mg or more per day * Sodium * Chloride * Potassium * Calcium * Phosphorus *Magnesium * Sulfur * TRACE ELEMENTS * AKA Microminerals Needed in amounts less than 20mg * Iron * Zinc * Selenium * Fluoride * Chromium * Copper * Manganese * Molybdenum MINERALS… WHERE CAN YOU GET THEM? VEGETABLES FRUITS GRAINS POTASSIUM SODIUM POTASSIUM CALCIUM PHOSPHORUS CALCIUM (fortified MAGNESIUM MAGNESIUM juice) IRON ZINC PROTEIN DAIRY SODIUM PHOSPHORU POTASSIUM S CALCIUM MAGNESIUM PHOSPHORUS IRON ZINC MACROMINERALS NUTRIENT FUNCTIONS SOURCES Calcium Builds bone and teeth Helps muscles and nerves work Dairy products, leafy green vegetables Magnesium Helps cells use energy nutrients Regulates body temperature Beans, dark green leafy vegetables, whole grains Phosphorus Builds bones and teeth Regulates bodily activities Proteins and calcium foods sources Sodium, Chlorine, Potassium Folate Sodium and chlorine: Control osmosis Maintain acidTable salt base balance in the body Potassium: Bananas Helps protect brain and spinal cord of unborn babies Bananas, fortified breads and cereals MICROMINERALS NUTRIENT FUNCTIONS SOURCES Fluorine Helps teeth resist decay Maintains bone health Fluoridated drinking water, toothpaste Promotes normal function of thyroid gland Iodized table salt, saltwater fish and shellfish Helps cells use oxygen Dried beans and fruits, egg yolk, lean meats, whole grains Zinc Helps wounds heal Promotes normal growth Legumes, meat, poultry, seafood, whole grains Folate Helps protect brain and spinal cord of unborn babies Bananas, fortified breads and cereals Iodine Iron WATER WHY DO YOU NEED IT? * Average healthy adult is about 60% water Aids digestion and cell growth and maintenance * Facilitates chemical reactions * Lubricates joints and cells * Regulates body temperature * Needed for overall well being * * WATER How much do you need and what are the best sources? HOW MUCH DO YOU NEED? * Depends on physical activity, environmental factors * (ex: temperature), and diet * BEST SOURCES: Milk * Fruits and Vegetables Some foods * Other liquids can also provide it such as coffee, tea, * and soft drinks, but they are not always the best choices. * EXCESS NUTRIENTS * Too much of any one nutrient is not good for you * Excess energy nutrients (Carbs, fats, and proteins) can lead to an unhealthy weight gain * Excess of some vitamins and minerals can lead to toxicity (poisoning) and other complications