Chemistry CPA Unit 2 Test Study Guide Test Date: Wednesday
advertisement

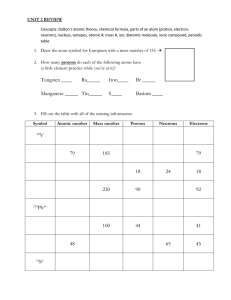
Chemistry CPA Unit 2 Test Study Guide Test Date: Wednesday, November 6, 2013 Unit 2 Materials – make sure you have the materials below completed and that you refer to them while you study: Do-Nows and Exit Passes (questions and answers on the website) Unit 2 notes – blue packet Unit 2 worksheet packet – purple packet Study Guide - Assignment 7 of purple packet (pp. 29-30) Textbook – Chapter 2 Labs – Atomic Target Practice, “Candium”, Flame Tests Topics: Atomic Theory – Know the scientists and their theories and atomic models Atomic Structure – Know the properties and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom Know that the atomic number identifies an atom and is also the same as the number of protons Isotopes and Ions – Know how and why they form Know the difference between the mass number and the average atomic mass Be able to calculate the average atomic mass given the mass numbers and percent abundance of multiple isotopes Electron Energy and the Electromagnetic Spectrumo Know the connection between electron energy and light o Know the Electromagnetic Spectrum and be able to correctly label each region, including where the energy, frequency, and wavelength is the greatest and the least Unit 2 Study Guide p. 1 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Practice – Answer the following questions. Do not use this as your only study guide. You must be reviewing your notes, the work you have done, and the labs you have performed in this unit. 1. Atomic Theory Fill in the Graphic Organizer below. Put the scientists into chronological order, starting with the earliest scientist: Scientist and Year Experiment Theory Model (Draw or Sketch) Unit 2 Study Guide p. 2 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Unit 2 Study Guide p. 3 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Atomic Structure 2. Define atomic number: 3. Define mass number: 4. Define average atomic mass: 5. Fill in the chart below: Particle Charge Location in Relative Mass atom Role in an atom 6. Fill in the chart below: Element Element Atomic # # name Symbol Mass # Neutrons Tellurium Isotope Hyphen Notation Notation 128 N 7 28 31 Potassium-39 F 19 7. When atoms differ by protons they are called: 8. When atoms differ by neutrons they are called: 9. When atoms differ by electrons they are called: Unit 2 Study Guide p. 4 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Electrons – Bohr and Lewis Dot Structures 10. Draw both the Bohr Model and Lewis Dot Diagram for the following elements below. Assume they are all neutral (equal number of protons and electrons): Element and Placement Bohr Lewis of electrons Argon Level 1:___ Level 2:___ Level 3:___ Silicon Level 1:___ Level 2:___ Level 3:___ Boron Level 1:___ Level 2:___ Level 3:___ Calcium Level 1:___ Level 2:___ Level 3:___ Magnesium Level 1:___ Level 2:___ Level 3:___ Unit 2 Study Guide p. 5 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Ions 11. Fill in the chart below: Ion Atomic Number Number of Protons Number of Electrons Ca+2 Ni+3 Br-1 Li+1 O-2 Ba+2 B+3 N-3 12. Write the chemical symbol (like above) for the ion with 12 protons and 10 electrons. 13. Write the chemical symbol for the ion with 53 protons and 54 electrons. 14. Write the chemical symbol for the ion with 88 protons and 86 electrons. 15. Write the chemical symbol for the ion with 15 protons and 18 electrons. 16. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in the 59Ni+2 ion? 28 17. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in the 91Zr+4 ion? 40 18. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in the 79Se-2 ion? 34 Unit 2 Study Guide p. 6 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 19. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in the 13C-4 ion? 6 20. Write the complete chemical symbol (like in the problems above) for the ion with 84 protons, 125 neutrons, and 80 electrons. 21. Write the complete chemical symbol for the ion with 27 protons, 32 neutrons, and 25 electrons. 22. Write the complete chemical symbol for the ion with 73 protons, 108 neutrons, and 68 electrons. 23. Write the complete chemical symbol for the ion with 31 protons, 39 neutrons, and 28 electrons. Unit 2 Study Guide p. 7 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Atomic Number, Isotopes, and Ions Identify the following sets of numbers as either different elements, isotopes, and/or ions: 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Atomic number: 9 Neutrons: 10 Electrons: 9 Atomic number: 9 Neutrons: 10 Electrons: 10 Atomic number: 31 Neutrons: 39 Electrons: 31 Atomic number: 31 Neutrons: 31 Electrons: 31 Atomic number: 6 Neutrons: 6 Electrons: 6 Atomic number: 7 Neutrons: 6 Electrons: 7 Atomic number: 30 Neutrons: 35 Electrons: 30 Atomic number: 30 Neutrons: 35 Electrons: 28 Atomic number: 8 Neutrons: 8 Electrons: 8 Atomic number: 8 Neutrons: 10 Electrons: 8 Unit 2 Study Guide p. 8 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 29. Which wave has the: highest energy? lowest energy? 30. Which wave has the: highest frequency? lowest frequency? 31. Which wave has the: longest wavelength? shortest wavelength? 32. Describe the three main properties of photons. 33. What change occurs within atoms when it emits light? 34. How does the modern electron cloud model of the atom differ from Bohr’s original planetary model of the atom? Unit 2 Study Guide p. 9 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013 Average Atomic Mass 35. Argon has three naturally occurring isotopes: argon-36, argon-38, and argon-40. Based on argon’s reported atomic mass, which isotope do you think is the most abundant in nature? Explain. 36. Copper is made of two isotopes. Copper-63 is 96.17% abundant and Copper-65 is 30.83% abundant. What is the average atomic mass of these two isotopes? 37. Gallium has two naturally occurring isotopes. Gallium-69 is 60.108% abundant and gallium-71 is 39.892% abundant. What is the average atomic mass of these two isotopes? 38. Calculate the average atomic mass of lead. The four lead isotopes with their percent abundances are: lead-204, 1.4% abundant; lead-206, 24.1% abundant, lead207, 22.1% abundant; and lead-208, 52.4% abundant. Unit 2 Study Guide p. 10 Callahan, Pengitore & Ricafort – Fall 2013