The American System
advertisement

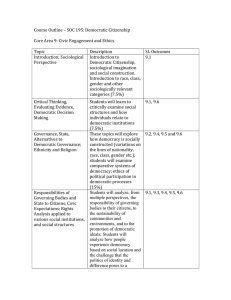
OQ: Describe legitimate authority. Give one example of legitimate and illegitimate authority and explain how they are different. Try to think of examples from the federal level of government. The American System Chapter 1 What is political power? Two great questions about politics Who governs -those who govern will affect us To what ends -how it will affect our lives Power [how does one know power is being exerted?] Definition- the ability of one person (group, etc.) to cause another person (group, etc.) to act a certain way Authority-the right to use power Legitimacy-that which makes a law or constitution a source of right struggles over what makes authority legitimate must be in some sense "democratic" in the US today What is democracy? Three different types Democratic Centralism defined: where the "true interests" of the people are served, whether or not those people are making decisions examples: China, Cuba, Soviet Union (past) and some dictatorships Participatory/Direct Democracy (Aristotle) defined: rule of the many examples: fourth century B.C. Greek city-states (well, the free, adult, male, landowners anyway), New England townships Representative Democracy: Elitist theory of democracy [why elitist?] power acquired by means of competitive elections Justification Direct democracy is impractical for many reasons The people make unwise decisions based on fleeting emotions (Demagogues) [Examples of fleeting emotions?] two types Presidential Parliamentary How is power distributed in a democracy? Majoritarian Politics Leaders try to follow the wishes of the majority very closely Applies best when issues are simple and/or clear Reduce energy costs Reduce the deficit Stop the threat of terrorism Democratic values, structure and processes Fundamental Democratic Values Popular sovereignty Respect for the individual. State serves individual, not vice versa. Liberty Equality of opportunity instead of equality of result [Explain.] Federalism Separation of powers Checks and balances Constitutional law Free and fair elections among competing persons and groups Majority rule with strong minority rights. Fear of “tyranny of the majority” led to protection of property rights. Freedom of expression Right to assemble and protest Fundamental Democratic Structure Fundamental Democratic Processes