Learning outcomes - Yaşar University | European Union Research
advertisement

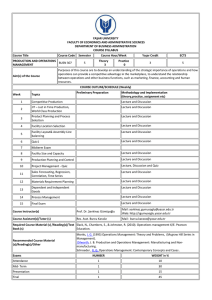
YASAR UNIVERSITY BOLOGNA SEMINARS Revision and Updates European Union Center November, 2013 Outline General Information on Bologna Process Road Map of Yasar University How to Write Programme and Learning Outcomes • Bologna Process intergovernmental European reform process aimed at establishing the European Higher Education Area (EHEA). Bologna Declaration was signed in 1999. • Aims: – Promoting mobility – Mutual recognition of degrees and other higher education qualifications, – transparency (readable and comparable degrees organised in a three-cycle structure) – Life Long Learning – European cooperation in quality assurance. 47 countries are participating to Bologna P. (Turkey: since 2001) Countries Participating to Bologna Process Countries following BP and attending to Bologna Policy Forum meetings since 2009. • Transparency Tools such as; – European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) – Diploma Supplement (DS) – Learning Agreement (LA) – Transcript of Records (ToR) European Qualifications Framework (EQF) National Qualifications Framework (NQF) by YÖK – 2009, Final Version 2010 Sectoral Qualifications by YÖK , 2011 Programme Outcomes by university Learning Outcomes by university TURKISH HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS FRAMEWORK • See NQF, Undergraduate, Level 6 (Link) • See Sectoral Qualifications (Link) • New Law: 6111 (2011) Credit System, minimum and maximum credits, graduation qualifications and NQF Yasar University Uses ECTS Credits since 2009 Updated university’s legal regulations, took Senate decisions on Recognition, LLL, placement, short courses, and credit transfer «Best Practice in ECTS Implementation» by National Agency (2009) Prepared ECTS Course Catalogue: http://bologna.yasar.edu.tr/ Prepared and published Prgramme Outcomes Gives DS Awarded «Diploma Supplement Label» in 2011. Awarded «ECTS Label» in 2012. Road Map of YU Stages Assigning ECTS to all courses (30 ECTS per semester arrangements) Determining the Programme Outcomes Completing the course syllabuses, determing the learning outcomes for each course Preparing the ECTS Course Catalogue; bologna.yasar.edu.tr Diploma Supplement Process ECTS Label Process Revision of Programme Outcomes by matching them with the National Qualifications and Sectoral Qualifications Framework X Updating the ECTS Catalogue, bologna.yasar.edu.tr X Revision of Course Syllabuses X 1. Revision of Programme Outcomes Match Software Engineering Programme Outcomes with; 1. National Qualifications Framework, Level 6 (undergraduate) 2. Sectoral Qualifications Framework of Engineering and Engineering Trades (ISCED 52) Example: Yasar University, Software Engineering Programme • Programme Outcomes: To determine the knowledge, skills and competences of Software Engineering graduates in line with the NQF and SQ • What are the qualifications of our graduates? Programme Outcomes of Software Engineering Upon the successful completion of this programme, the student will be able 1. To identify, formulate, and solve software engineering problems by applying knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering 2. To design and conduct scientific and engineering experiments; analyze and interpret data 3. To identify, formulate and validate user needs and system requirements 4. To develop large and complex software systems by applying software engineering principles and techniques 5. To use modern engineering techniques for analysis and design 6. To recognize the importance of abstraction and modeling 7. To use the efficient software engineering background for being able to follow up most recent developments in the field 8. To collect data regarding the special domain of knowledge in other fields and disciplines besides the computing discipline for the purpose of supporting software development 9. To demonstrate efficient communications in written and oral forms and work effectively individually and in teams 10. To adopt the ethical and professional responsibility and use them in professional life Matching Programme Outcomes with National Qualification Framework National Qualifications Framework Programme Outcomes 1. Alanında edindiği ileri düzeydeki kuramsal ve uygulamalı bilgileri kullanabilme 1,2,4 2. Alanı ile ilgili ileri düzeydeki bir çalışmayı bağımsız olarak yürütebilme. 4,9 3..... 8,1,3 4. 2,1 5. 4,6,1 6. 7,11 National Qualifications Framework http://tyyc.yok.gov.tr/?pid=33 Each article in NQF should be satisfied/matched by one or more of your Programme Outcomes Matching Programme Outcomes with Sectoral Qualification Framework Go to page http://tyyc.yok.gov.tr/?pid=48 for SQF Choose the main field Choose Level 6 as undergradute (Bachelor’s) Choose academic competences You will have the list of sectoral qualifications for Engineering and Engineering Trades. Each qualification in this list must match with your Programme Outcomes Matching Programme Outcomes with Sectoral Qualification Framework Sectoral Qualifications Framework Learning Outcomes of Software Engineering Programme 1-Matematik, fen bilimleri ve kendi dalları ile ilgili mühendislik konularında yeterli altyapıya sahiptir. 1,2 2- 3 3.... 5,7 4..... 6 5.... 4,2 6.... 11 7..... 9,10 8..... 8 9.... 7 10. Yaşam boyu öğrenmenin gerekliliği bilincindedir; bilim ve teknolojideki gelişmeleri izler ve kendini sürekli yeniler. 7 Road Map for YU 1. Matching; YU Programme Outcomes NQF SQF Revising of new Programme Outcomes by the Dep and approval by the Senate (2.12.2013-16.01.2014) 2. Revision of course syllabuses and updating the ECTS Course Catalogue Page (bologna.yasar.edu.tr) by the Departments (Send the updated info to euc@yasar.edu.tr ) (16.01.2014-30.01.2014) 3. Approval of course syllabuses by Head of Dep. (01.02.2014-08.02.2014) IMPORTANT NOTES • Please add one general article to your Programme Outcomes for matching the UFND courses • YÖK has not yet announced the NQF and SQF in English. We will work on the Turkish version. • Only the English version of course syllabuses are to be updated. • Each semester should have 30 ECTS course work load (Flexibility 29-31, however not recommended) Revision of Course Syllabuses Learning outcomes are statements of what a learner is expected to know, understand and/or be able to demonstrate after completion of a process of learning. (ECTS Users’ Guide) 1. 2. 3. Knowledge/understanding Skills Competences • A shift from intentions of teacher (aims of a module/course) to achievement of learner • From teacher based to student based learning • The learning outcomes are student-focused and conveys the learning success of the student, not the aim of education Student Based Approach (Outcome based approach) what the students are expected to be able to do at the end of the module or programme Learning outcomes: what it is expected that students should be able to do at the end of the learning period. Focus to gain these learning outcomes Assestment: How much of these outcomes are succesfully gained? What students can do at the end of a learning opportunity defines the learning outcome How to Write Learning Outcomes? • The Programme and Learning Outcomes should be written by using Bloom’s Taxonomy (1956). • Bloom (1956) proposed that knowing is composed of six successive levels arranged in a hierarchy. • Bloom suggested certain verbs that characterise the ability to demonstrate these processes. 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge 1. Knowledge - ability to recall or remember facts without necessarily understanding them 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: Arrange, collect, define, describe, duplicate, enumerate, examine, find, identify, label, list, memorise, name, order, outline, present, quote, recall, recognise, recollect, record, recount, relate, repeat, reproduce, show, state, tabulate, tell. 24 24 2. Comprehension - ability to understand and interpret learned information 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: Associate, change, clarify, classify, construct, contrast, convert, decode, defend, describe, differentiate, discriminate, discuss, distinguish, estimate, explain, express, extend, generalise, identify, illustrate, indicate, infer, interpret, locate, predict, recognise, report, restate, review, select, solve, translate. 25 25 3. Application: ability to use learned material in new situations, e.g. put ideas and concepts to work in solving problems • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension Apply, assess, calculate, change, choose, complete, compute, construct, demonstrate, develop, discover, dramatize, employ, examine, experiment, find, illustrate, interpret, manipulate, modify, operate, organise, practice, predict, prepare, produce, relate, schedule, select, show, sketch, solve, transfer, use. 1. Knowledge 26 26 4. Analysis: ability to break down information into its components, e.g. look for inter-relationships and ideas (understanding of organisational structure) 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: Analyse, appraise, arrange, break down, calculate, categorise, classify, compare, connect, contrast, criticise, debate, deduce, determine, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, divide, examine, experiment, identify, illustrate, infer, inspect, investigate, order, outline, point out, question, relate, separate, sub-divide, test. 27 27 5. Synthesis - ability to put parts together • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge Argue, arrange, assemble, categorise, collect, combine, compile, compose, construct, create, design, develop, devise, establish, explain, formulate, generalise, generate, integrate, invent, make, manage, modify, organise, originate, plan, prepare, propose, rearrange, reconstruct, relate, reorganise, revise, rewrite, set up, summarise. 28 28 6. Evaluation: Ability to judge value of material for a given purpose 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge • USE ACTION VERBS LIKE: Appraise, ascertain, argue, assess, attach, choose, compare, conclude, contrast, convince, criticise, decide, defend, discriminate, explain, evaluate, interpret, judge, justify, measure, predict, rate, recommend, relate, resolve, revise, score, summarise, support, validate, value. 29 29 While writing PO and LO… • Avoid verbs like “know”, “understand”, “be familiar with”, “be exposed to” (Osters and Tiu) • “Try to avoid ambiguous verbs such as “understand”, “know”, “be aware” and “appreciate”. (Sheffield Hallam Guide). • “Care should be taken in using words such as ‘understand’ and ‘know’ if you cannot be sure that students will understand what it means to know or understand in a given context” (Univ NSW). • Certain verbs are unclear and subject to different interpretations in terms of what action they are specifying…… These types of verbs should be avoided: know, become aware of, appreciate, learn, understand, become familiar with. (American Association of Law Libraries). Programme and Learning Outcomes should: • • • • • • • identify important learning requirements be achievable and assessable use clear language easily understandable to students Avoid vague terms like know, understand, learn, be familiar with, be exposed to, be acquainted with, and be aware of. These terms are associated with teaching objectives rather than learning outcomes. Ensure that the learning outcomes of the module relate to the overall outcomes of the programme. The learning outcomes must be observable and measurable. Ensure that the learning outcomes are capable of being assessed. At the end of this module/course the student will be able to … Then follow with a verb. Useful ones include: analyse, appraise apply, calculate, choose, compare, contrast, create, criticise, demonstrate, derive ,describe ,design, develop, differentiate, discuss, explain, evaluate, extrapolate, formulate ,identify ,list, measure, name, plan, plot, postulate, predict, present, propose, recall, recognise, use, utilise Links for Keys Documents • European Qualifications Framework for LLL (EU) http://ec.europa.eu/education/pub/pdf/general/eqf/leaflet_en.pdf • National Qualifications Framework (YÖK) http://tyyc.yok.gov.tr/?pid=33 • Sectoral Qualifications Framwork (YÖK) http://tyyc.yok.gov.tr/?pid=48 • «66 Soruda Bologna Süreci»: https://bologna.yok.gov.tr/files/ce63c4b383ae852dce0a9b17bac57c6e.pd f • Türkiye Yükseköğretim Yeterlilikler Çerçevesi Genel Bilgi: http://tyyc.yok.gov.tr/ THANK YOU Yasar University EU Center euc@yasar.edu.tr Gökay Özerim, 5012 Umut Pamuk, 5011