The Knee: Injuries Notes Objectives Identify pathologies that occur

The Knee: Injuries
Objectives
Identify pathologies that occur in the knee, differentiating their signs & symptoms
Bony pathologies
Ligamentous pathologies
Musculotendinous pathologies
Other structural/functional pathologies
Structural Malalignments
Leg alignment
Genu valgum –
Genu varum – bow-legged
Genu recurvatum – Hyperextension
Patella alta – high patella
Patella baja – low patella
Squint eye patella – points
Frog eye patella – points laterally
Q-angle – degree of valgus alignment between anterior hip & tibia
Skeletal pathologies
Knee fractures
Femur, Tibia, Fibula o Diaphysis o o Avulsion
Epiphyseal fractures o Skeletally immature o o Proximal tibia or fibula
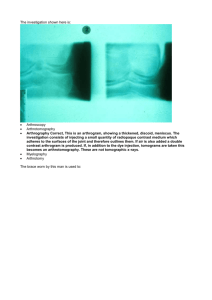
Osteochondral defect
Fracture of o Can involve the underlying bone
MOI: & shear force
Medial & Lateral femoral condyle, tibial articulating surface, & patella
S&S: o Diffuse pain, “ ,”
“popping,” “clunking,” “giving way” o “ ” o Often mimics meniscal tears
Patellar fractures
Relatively rare o MOI: Direct trauma; rapid flexion force; eccentric load o May or may not require surgery o Can be acute or stress related
Chondromalacia Patella
Degeneration of
Chronic condition
Possible predisposing factors o Recurrent subluxations or dislocations o Direct trauma
Notes
o Patellar malalignment
Often involves
Pain after prolonged sitting (“movie sign”)
Traction apophysitis
Defined as: of a large tendon that causes damage to the unfused apophysis
(junction) to which it is attached
Can occur at any site where tendon attaches to bone
Common in two places in the knee o o Sinding-Larsen-Johansson
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Most common growth related knee pain in young people o Rapid growth, increased strength, or both
Repetitive traction on
Minor avulsion at tibial tuberosity o Leads to inflammatory reaction
Sinding-larsen-johansson disease
Inflammation at the of the patella resulting from avulsion or stress fracture o Repetitive traction on inferior patella
Common in skeletally immature individual & males
Soft tissue pathologies
Sprains
Lateral collateral (LCL) o force or internal rotation of tibia o Relatively uncommon o May involve ACL or PCL o Be aware of secondary avulsion injury to fibular head
Medial collateral (MCL) o force or external rotation of tibia o May be contact or non-contact injury o Often involve medial meniscus and/or
ACL o Must be wary of patellar dislocations with valgus force
Posterior cruciate (PCL) o Tibia hyperext or hyperflex o Often involves edema o Mechanism
Anterior cruciate (ACL) o Tibia
on femur,
on femur, rotation of tibia, & w/ o Many are non-contact injuries o Often involves a “ ” & edema
The Knee: Injuries o Be aware of secondary injuries o o Know predisposing factors!
Potential ACL Injury Components high velocity force
Tibiofemoral dislocations
Direction, complete/partial, open/closed, low or
Severe pain, spasm, and deformity o Consider if 3 of ACL, PCL, MCL, or LCL are damaged without deformity
Probable (~30%) pathology to vessels and nerves o Consider if these symptoms are present w/out deformity o MUST o Medical emergency
Patellar dislocation/subluxation
May be described as “just gave out”
Acute or chronic; more common in females
Tight lateral tissues, weak medial musculature,
↑ Q-angle
MOI:
(~20-30°) and external rotation of tibia o May involve avulsion fracture or muscle tearing o May involve MCL tear; consider effect of
ACL
Meniscal tears
Typically caused with o Varus or valgus forces
May be chronic or acute
Type – based on orientation & etiology of defect
Lateral meniscus tears o Often ; often secondary to repeated stress o Can go undetected
Medial meniscus tears o Firm fixation and attachment to o More likely to be torn?
S & S: o o Joint line pain, effusion o May or may not involve pain
Patellar tendonitis
Typically a chronic injury w/ insidious onset o May start with acute trauma
Notes o Moderate to severe pain w/
= better indicator than mild pain
Quadriceps tendonitis
Typically a chronic injury w/ insidious onset o May start with acute trauma o Moderate to severe pain w/
= better indicator than mild pain
Bursitis
13 bursae commonly around the knee joint
MOI: o Be aware of infection
Swelling may be extreme (“water on the knee”)
Onset may be acute or chronic
Most common bursitis in athletes o Prepatellar o Infrapatellar o o Deep infrapatellar o Anserine & Semimembranosus
IT band friction syndrome
Often seen in runners, cyclists, rowing o Often seen when “over-striding” o Running downhill, going down stairs, etc.
Inflammation as I-T Band repeatedly crosses over
Often associated with tight or inflexible IT Band
Typically chronic, insidious onset o Repetitive microtrauma of knee flex/ext o May develop bursitis or periostitis
S&S: o “ ”; often radiates distal from lateral femoral condyle o Pain w/ knee flexion & extension o May describe “popping” sensation o General IT band tightness
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Catch all term involving abnormal
Malalignment & instability issues present
Chondromalacia patella
Lateral tracking of patella o Tight hamstrings & gastrocnemeus o Increase Q angle o Tight & lateral patellar tissues o Patella alta or baja o ______ weakness or imbalance compared to vastus lateralis o Weak hip adductors o Change in footwear, surface, activity level/intensity