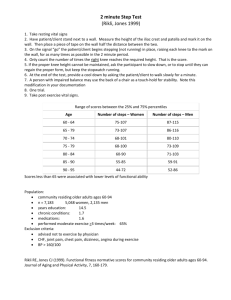
Knee
advertisement
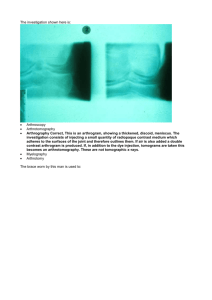
Knee The Views AP Lateral Internal Oblique External Oblique Things You Should Know • • • • • • • Cassette Size 10 x 12 lengthwise One view per cassette Shield Marker Measures 11 Hold Still 70@5 Part Position for AP • • • • Done in the table bucky Patient in Supine position on table Align knee mid-line of table Rotate foot internally 3 -5 degrees for true AP CR perpendicular Tibial platea 40 SID ½” Distal to apex of patella CR ANGLE DIFFERENCE • Measure the distance from ASIS to table • 19-24 Average Patient perpendicular • 25-up Above average Patient 5 degrees cephalad • Below 19 Below Average 5 degrees caudad. Our CR Angle • For our comp we will shoot straight in • So our distance will be 40 • DON’T FORGET TO LINE BUCKY Seen on Radiograph • • • • The distal femur The proximal tib/fib The femorotibial joint open The intercondylar eminence in its fossa. • The fibular head imposed by tibia Lateral Knee • • • • 10 x 12 cassette lengthwise Shield Marker Measure 10 Part Position for Lateral • • • • Roll patient up on affected side Flex knee 20 degrees Align knee to mid-line of table. Align the epicondyles perpendicualr to film so they are superimposed. • Patella plane perpendicular to Film. CR 5-7 degrees cepalad 1 inch below epicondyles SID 40 Distance 39 Seen on Radiograph • The distal femur and patella in profile • The femoral epicondyles superimposed. • Proximal tib/fib Medial oblique • • • • • 10 x 12 cassette lengthwise Shield Marker Hold still Measures 10 Part position for medial • Patient supine • Align center knee with mid-line to table • Internally rotate leg 45 degrees. CR Perpendicular SID 40 ½ in distal to patella apex Seen on Radiograph • The proximal tib/fib with no imposition of head and neck of fibula. • Patella imposing the medial condyle of femur • Lateral and medial joint spaces open. • Lateral condyle of femur and tibia are seen Lateral Oblique • • • • 10 x 12 cassette lengthwise Shield Marker Hold still Part Position for lateral • Patient supine on table • Knee align to mid-line of table • Rotate knee 45 degrees externally. CR Perpendicular SID 40 ½ in distal to apex of patella Seen on Radiograph • Proximal fibular imposed by the tibia • Half of patella free of imposition from lateral condyle. • Medial condyle and tibia in profile • Distal femur The lower leg Tib/fib the Views • AP • Lateral Things to know • Cassette size: 14 X 17 turned diagonally • one cassette per view • Shield • Marker • Measures 10 Part position for AP • • • • Patient Supine on table Place shield over lap leg fully extended place leg in true AP position for knee and ankle • Femoral condyles parallel to IR • foot flexed to 90 degree (TOES up) • include both joints (knee & ankle) IR. Central Ray • 40 SID • perpendicular to mid-leg • Collimate to skin borders on lateral and medial sides. • Leave collimation open from top to bottom • ** can go up to 44 or 48 SID to include more of part** Seen on Radiograph • The entire tibia and fibula • both ankle and knee joint • the condyles of tibia and femur in profile • the intercondylar eminence centered in the intercondylar fossa • some imposition of distal and proximal tib/fib Lateral Tib/Fib • 14 X 17 diagonally • shield • Marker Part position for lateral • Patient on side with injured side down • flex knee about 45 degree to ensure true lateral • plane of patella should be perpendicular to IR • opposite leg behind injured one • both joints included on IR •40 SID Central Ray • • • • perpendicular to mid-leg collimation to skin borders on sides open fully top to bottom ** can go up to 44 or 48** Seen on Radiograph • • • • • Entire tib/fib both joints tibial tuberosity in profile fibula head imposed by tibia distal fibula imposed on posterior portion of tibia • femoral condyles superimposed. !!!Important Note!!!! • If you can not fit entire leg on on film... • You must include the joint nearest the injury on the film and take a separate picture of the other joint.