Chromosomes
advertisement

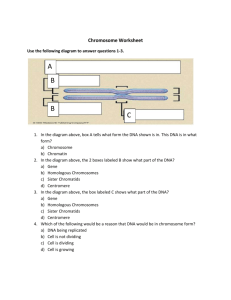
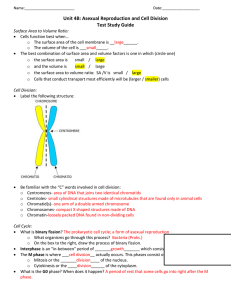
What is the link between these images? What is the common link? Down’s Syndrome can be caused where sufferers have three copies of chromosome 21. Trisomy 13, also called Patau syndrome, is a disorder in which an individual has three copies of genetic material from chromosome 13, rather than two. Jacobsen syndrome results from a loss of genetic material from the end of the long arm of chromosome 11. Sufferers of Klinefelter’s syndrome are born with an extra X chromosome, making them XXY. What is the common link? CHROMOSOMES DNA and chromosomes Aims: •How does DNA in prokaryotic organisms differ from the DNA in eukaryotic organisms? •What is a chromosome? •How are genes arranged on a DNA molecule? A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain a nucleus and other structures (organelles) enclosed within membranes The prokaryotes are a group of organisms whose cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus Eukaryote DNA larger Linear Associated with proteins Form Chromosomes Prokaryote DNA smaller Circular Not associated with proteins Plasmids https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q oERVSWKmGk Only visible during cell division. Each chromosome is one molecule of DNA Each species has a specific number of chromosome eg Humans :46 or 23 pairs Daughter cells contain an exact copy of the instructions in the parent cell –they are genetically identical Humans have 23 pairs of chromosome When visible, the DNA has replicated itself and chromosomes appear as two threads, joined at a single point called the centromere. Each replicated thread is called a chromatid. The DNA replicas are called sister chromatids Sister chromatids end up in different daughter cells The DNA in chromosomes is held in place by proteins. The molecules of DNA are wrapped around proteins called histones. (over 50%) DNA + histone are called chromatin fibres DNA carries the instructions A nucleosome DNA Helix Histone protein Core of 8 histone proteins Coiled Chromatin fibres Chromosome The chromatin is coiled up to form supercoiled chromosomes The supercoiled chromosomes can be moved around the cell during mitosis Supercoiled chromosomes can be stained and seen under the light microscope – 500nm thick As supercoiled chromosomes they cannot code mRNA so they remain as such for as little time as possible http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9kQpYdCnU1 4 Understanding checkpoint Turn to your partner. Number 1’s: Explain in as much detail as possible: What is a chromosome? Number 2’s: Define and explain the following key words: 1.Histone 2.Coiling 3.Chromosome 4.Chromatid Chromosomes occur in pairs called homologous chromosomes A homologous pair is always two chromosomes that determine the same genetic characteristics One of the pair is derived from the mother in the egg (maternal chromosome) The other is provided by the father in the sperm (paternal chromosome) The genes that code for a particular polypeptide are usually found at the same position in the DNA molecule of their chromosome in every cell in the body This position is called the locus (plural loci). In some cases the two genes that code for a particular polypeptide have exactly the same code. In others they are different although they still occur at the same position on the chromosome. These different forms of the same gene are called alleles 8.3 DNA and chromosomes Plenary 1: What is a gene? 2: What are homologous chromosomes? 3:What is a polypeptide? 4: What is a histone? 5: What is chromatid? 6: Name 2 things you have learned today.