Radioactive Decay - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

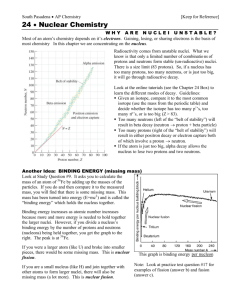
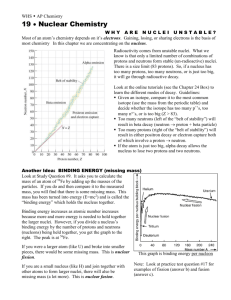
Radioactive Decay What do you know about Radioactivity? 1. All atoms are made up of __________. 2. What are some radioactive isotopes? 3. Why do some isotopes/atoms break down and decay? 4. What is given off as atoms break down and decay? 5. How can we manipulate and use this process to our advantage? The Nucleus • Recall that atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. • The nucleus of an atom contains the protons, which have a positive charge, and neutrons, which have no electric charge. The Strong Force • How do you suppose protons and neutrons are held together so lightly in the nucleus? • Another force, called the strong force, causes protons and neutrons to be attracted to each other. The Strong Force • Protons and neutrons have to be close together, like they are in the nucleus, to be attracted by the strong force. • The strong force is a short-range force that quickly becomes extremely weak as protons and neutrons get farther apart. Attractions and Repulsion • Some atoms, such as uranium, have many protons and neutrons in their nuclei. • These nuclei are held together less tightly than nuclei containing only a few protons and neutrons. Attractions and Repulsion • If a nucleus has only a few protons and neutrons, they are all close enough together to be attracted to each other by the strong force. Forces in a Large Nucleus • If nuclei have many protons and neutrons, each proton or neutron is attracted to only a few neighbors by the strong force. Radioactivity • When the strong force is not large enough to hold a nucleus together tightly, the nucleus can decay and give off matter and energy. Larger elements are more unstable and tend to decay. • This process of nuclear decay is called radioactivity. • All nuclei that contain more than 83 protons are radioactive. • However, many other nuclei that contain fewer than 83 protons also are radioactive. Radioactivity • Almost all elements with more than 92 protons don’t exist naturally on Earth. • They have been produced only in laboratories and are called synthetic elements. • These synthetic elements are unstable, and decay soon after they are created. Isotopes • Nuclei that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • These two isotopes of helium each have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Stable and Unstable Nuclei • Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons are radioactive and decay too. Nuclear Radiation • The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta and gamma radiation. • Alpha and beta radiation are particles. Gamma radiation is an electromagnetic wave. Nuclear Radiation • When an unstable nucleus decays, particles and energy called nuclear radiation are emitted from it. Alpha Particles • When alpha radiation occurs, an alpha particlemade of two protons and two neutrons is emitted from the decaying nucleus. • Notice that the alpha particle and its symbol is the same as a helium nucleus, • In alpha decay, two protons and two neutrons are lost from the nucleus or Helium gas is released. Beta Decay • Sometimes in an unstable nucleus a neutron decays into a proton and emits an electron. • The electron is emitted from the nucleus and is called a beta particle. Gamma Rays • They have no mass and no charge and travel at the speed of light. • The properties of gamma rays are summarized in the table. Gamma Rays • Thick blocks of dense materials, such as lead and concrete, are required to stop gamma rays. Radioactive Half-Life • Some radioisotopes decay to stable atoms in less than a second. • However, the nuclei of certain radioactive isotopes require millions of years to decay. • A measure of the time required by the nuclei of an isotope to decay is called the half-life. Radioactive Half-Life • The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the amount of time it takes for half the nuclei in a sample of the isotope to decay. • The nucleus left after the isotope decays is called the daughter nucleus. Radioactive Half-Life • Half-lives vary widely among the radioactive isotopes. • Some geologists, biologists, and archaeologists, among others, are interested in the ages of rocks and fossils found on Earth. Radioactive Dating • The number of half-lives is the amount of time that has passed since the isotope began to decay. Carbon Dating • Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years and is found in molecules such as carbon dioxide. • Plants use carbon dioxide when they make food, so all plants contain carbon14. • Only material from plants and animals that lived with the past 50,000 years contains enough carbon-14 to be measured. Common Isotopes • • • • Polonium-214 has a half life of .7 sec Uranium-238 = 4.5 billion years Carbon-14 = 5,730 years Lead-212 = 10.6 hours Problems • If a human body contained 50 grams of C14 and now had only 25 g, how old is the body? • ½ of 50 is 25 so 1 half-life elapsed and that is 5,730 years Problems • If the amount of C-14 is 12.5 g • 11,460 years • If the amount of C-14 is 6.25g • 17,190 years Graphs of Radioactive Decay Standard: SPS3a Students will differentiate between alpha, beta decay and gamma radiation What is Nuclear Radiation? Alpha Decay What is released? Radiation is made of… (Particles or electromagnetic waves) Interesting Fact (Use pgs 541-543) Beta Decay Gamma Radiation Reading Assignment • Please read pgs 544-545 on Radioactive Half-life. • As you read please make notes over the following sections: Section Radioactive half-life Radioactive Dating Carbon Dating Uranium Dating Your Notes