Classical Conditioning
advertisement

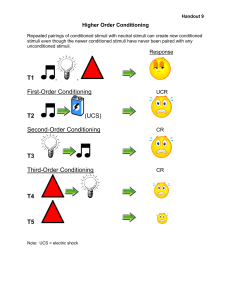
Classical Conditioning Learning Lesson 1 Objectives Define learning and provide examples. Identify John B Watson, BF Skinner, and Ivan Pavlov. Describe and apply the components of classical conditioning. Warm Up Identify some of the things you’ve learned in the past few months. Learning Learning IS… A process leading to relatively permanent change in behavior. Learning is NOT… Reflex: Simple, unlearned behavior controlled by the ANS Instinct: Inborn, complex pattern of behavior of a species Behaviorists John B. Watson Behaviorism Study of observable behaviors BF Skinner Behavior influenced by history of consequences Behavioral Psychology Study of how our behavior results from stimuli in the environment and within ourselves. (Stimulus-Response Learning) Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Cognitive or Social Learning Think-Pair-Share “When I’m driving and see a stoplight turn red, I stop” Stimulus – red light Reaction – stop Write down three more conditioned responses you do on a daily basis. Phone rings, pick it up Bell rings, you switch classes Teacher asks ?, you raise hand Classical Conditioning Stimulus in environment triggers response in subject. Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) Physiologist researching digestion in dogs Activity PsychSim 4.0 “Classical Conditioning” This activity provides a review of Pavlov’s famous experiment on the salivary response in dogs, as well as the basic processes of classical conditioning: acquisition, generalization, discrimination training, and extinction. http://www.worthpublishers.com/kolb/content/psychsim/ index.htm Pavlov’s Experiment Before Conditioning (Pre-Learning) During Conditioning (Learning) Ring tuning fork (NS) No response from dog Food (UCS) Dog salivates automatically (UCR) Ring fork (NS) Present food (UCS) Salivation (UCR) After Conditioning (Post-Learning) Ring fork (CS) Salivation (CR) Think-Pair-Share What other conditioned stimuli may have existed in Pavlov’s experiment? General Principles of C2 Acquisition Generalization Distinguishing between different stimuli Extinction Stimuli similar to CS cause CR Discrimination Time period it takes for NS to be associated with UCS Disappearance of CR to CS Spontaneous Recovery Previously extinguished CR returns suddenly Eye Blink Experiment UCS – puff of air in eye UCR – blink NS – tone CS – tone CR – blink Emotional Conditioning John B. Watson Prove human emotional reaction was result of conditioning Fear, rage, sadness Little Albert http://study.com/academy/lesson/watson-and-littlealbert.html Albert Activity Set up experimental design. Give examples of generalization in experiment. Cite criticisms of experiment Identify ways researchers could help Albert get over his fears. Albert Answers Before: Rat No Response Loud noise Fear During: Rat Noise Fear Generalization: Criticisms: After: Rat Fear Rabbit Fur Coat Screwed up kid Didn’t fix him Albert Answers Fixing Albert’s Fears Counter Conditioning: pleasant stimulus presented with fear object, re-condition Systematic Desensitization: gradually exposed to fear-evoking stimuli in pleasant circumstance Flooding: exposed to fear stimulus until response extinguished Other Examples Associate song with relationship…break up, song makes you sad Associate smells Taste Aversion – Got sick eating spaghetti, can’t eat it anymore