What part do VALUES play in your assessment of a Leader?
advertisement

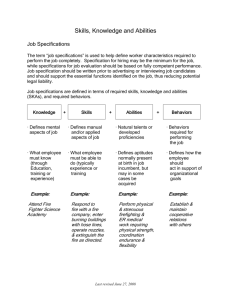
ADAPTIVE LEADERSHIP Leadership Basics Participant‘s Guide & Reference Pre-Course Leadership Self-Assessment Activity Notes: This survey is the short version. The long version can be found on http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/survlead.html If time permits complete this assessment prior to class start. This self-survey will provide you with feedback as to your feelings of leading others. Rate yourself on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being a definite YES and 1 being a definite NO. Be honest about your answers as this survey is only for you own self-assessment. Circle the number which you feel most closely represents your feelings about the task: NO YES 1. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy working on teams. 2. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am able to speak clearly to others. 3. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy relating to others on an interpersonal basis. 4. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am good at planning. 5. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I can interpret rules and regulations. 6. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I feel comfortable asking others for advice. 7. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy collecting and analyzing data. 8. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am good at solving problems. 9. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am comfortable writing memos to others. 10. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I can delegate work to others. 11. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am effective at handling employee complaints. 12. - 1 2 3 4 5 - Giving directions is comfortable for me. 13. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I know how to develop goals and carry them out. 14. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am comfortable at implementing new techniques. 15. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy appraising performance and giving feedback. 16. - 1 2 3 4 5 - If I made a mistake, I would admit it and correct it. 17. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am able to resolve conflict in the workplace. 18. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I believe in diversity in the workplace. 19. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I thrive on change. 20. - 1 2 3 4 5 - One of my greatest desires is to become a leader. Score the survey by adding the numbers that you circled: ________ A score of fifty or higher indicates a desire to become a leader and a perceived ability to perform the tasks required of a leader. A score of fifty or less indicates a general dislike of wanting to become a leader or a perceived inability to perform the tasks required of a leader. BUT, no matter what your score is, your commitment, desire, and determination are the biggest indicators of your ability to become a leader. Use this assessment to help you to determine what skills and abilities you can continue to improve (Strengths) and what skills and abilities you need to develop (Opportunities for growth). Once you know your weakness, use this course and others associated (listed in the reference section) to help develop those weaknesses. What are your strengths? What are your opportunities for growth? Participant’s Guide & Reference Larry C. Hale Phone 479.877.9672 A icsp aedrh B tvL Table of Contents Pre-Course Leadership Self-Assessment Activity .................. iii Objectives: ......................................................................................... 1 What defines a leader?.................................................................... 1 What defines the employee’s development level? ........................... 1 How do I and Why should I adapt my leadership style? .................. 1 Road Map .......................................................................................... 2 What defines a leader? ...................................................................... 3 What part does HONESTY play in your assessment of a Leader? ..... 5 How does having VISION impact your assessment of a Leader? ...... 6 What part do VALUES play in your assessment of a Leader? ............ 6 What is this thing called Leadership Style? ........................................ 7 Authoritarian (Autocratic) ................................................................. 7 Participative Leadership (Democratic) ............................................. 7 Delegative (Laissez-Faire) Leadership ............................................ 7 Defining Leadership behaviors into two categories: ........................... 9 Knowledge Skills and Abilities along with Motivation/Commitment 10 Telling .............................................................................................. 10 Coaching.......................................................................................... 10 Participating ..................................................................................... 11 Delegating........................................................................................ 11 Employee Development Path ........................................................... 12 Keys to understanding where the individual is in regard the task or tasks:13 Needs during the journey toward Star Performer .......................... 14 Development Level or Stage Activities ............................................. 15 Matching Leadership Style to Development Level ............................ 17 Match or Mismatched? Activities ................................................... 18 Next Chance to Learn! Activity .................................................... 20 What would you Say? .................................................................... 20 Partnering With your Employees for Development ........................... 23 When: Active leadership versus Reactive Leadership: ............... 23 SMARTT goal setting model ......................................................................................... 23 What: determine what is to be done and how it is to be done. .... 24 To what degree: Agreed on expectations; Agreed on Goals; ...... 25 Post-Course Leadership Self-Assessment Activity ............... 26 Scoring ......................................................................................... 26 References and Further Development Sources: .............................. 27 Index ................................................................................................ 28 A D A P T I V E Adaptive Leadership L E A D E R S H I P Objectives: From a Leader’s perspective we will explore: What defines a leader? What defines the employee’s development level? How do I and Why should I adapt my leadership style? In specific: Know the factors that impact a successful change, and know how to affect change in a team’s processes and priorities by affecting the individual employee’s knowledge and or motivation. Learn how to hold others accountable for their performance and generate a positive attitude toward the attainment of the organization’s goals. Demonstrate the ability to align the talents of the team to the requirements of the business. Demonstrate the enlisting of others in the successful accomplishment of business goals. Know when to coach, mentor and train to enhance others abilities. Learn to communicate from a Leader position. Adapt your style of support or directing to the appropriate development level for the employee. Explore the conditions of “buy-in” and “ownership” as they relate to projects and policies. Determine the most effective method of reward and recognition and will know the difference and their positive and negative aspects. 1 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Road Map What defines a leader? Explore the traits of a Good Leader and a Poor Leader. Explore different styles of leadership. Define Leadership behaviors Define styles of leadership What defines the employee’s development level? Define competence levels of the employee for a task Elements of development “Test” to determine the level How and Why do I adapt my leadership style? Explore “Matched and Mismatched” style and development levels. Mismatched Matched “What would you do/say?” How do I Lead? Partnering with Your Employees for Development. Planning for Success Coaching Evaluating 2 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Moving into a position of leadership and authority can be one of the most difficult transitions to make in the workplace. In addition to the new challenges you face and high expectations you must meet, it's imperative that you learn how to effectively communicate, motivate, and delegate to achieve success. You're judged not only on your performance and decision-making, but also on your ability to inspire and encourage your employees to achieve great things. Finding a balance between "being the boss" and maintaining positive relationships with your employees is the key to navigating your new duties and requires strong communication skills and the ability to adapt effectively. What defines a leader? Reflect back in your life on the behaviors that lead you to the conclusion that the leader was Good or Poor and record below. You may be asked to share your reflections with the rest of the class. Traits of a Good Leader. Traits of a Poor Leader In the table above list some traits of these leaders 3 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Traits of a Good Leader Compiled by the Santa Clara University and the Tom Peters Group: o Honest — Display sincerity, integrity, and candor in all your actions. Deceptive behavior will not inspire trust. o Competent — Base your actions on reason and moral principles. Do not make decisions based on childlike emotional desires or feelings. o Forward-looking — Set goals and have a vision of the future. The vision must be owned throughout the organization. Effective leaders envision what they want and how to get it. They habitually pick priorities stemming from their basic values. o Inspiring — Display confidence in all that you do. By showing endurance in mental, physical, and spiritual stamina, you will inspire others to reach for new heights. Take charge when necessary. o Intelligent — Read, study, and seek challenging assignments. o Fair-minded — Show fair treatment to all people. Prejudice is the enemy of justice. Display empathy by being sensitive to the feelings, values, interests, and well-being of others. o Broad-minded — Seek out diversity. o Courageous — Have the perseverance to accomplish a goal, regardless of the seemingly insurmountable obstacles. Display a confident calmness when under stress. o Straightforward — Use sound judgment to make a good decision at the right time. o Imaginative — Make timely and appropriate changes in your thinking, plans, and methods. Show creativity by thinking of new and better goals, ideas, and solutions to problems. Be innovative! 4 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P The U.S. Army's Eleven Leadership Principles (Example for Historical Reference) — Be tactically and technically proficient — Know yourself and seek self-improvement — Know your soldiers and look out for their welfare — Keep your soldiers informed — Set the example — Ensure the task is understood, supervised and accomplished — Train your soldiers as a team — Make sound and timely decisions — Develop a sense of responsibility in your subordinates — Employ your unit in accordance with its capabilities — Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions What part does HONESTY play in your assessment of a Leader? What is the impact of your leader being honest with? : Our Customers Our employees You In the space provided, reflect on the impact a leader’s honesty has on each of the entities listed. Prepare to discuss with class. 5 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P How does having VISION impact your assessment of a Leader? How does your leader having a clear vision impact: Our Customers Our employees You In the space provided reflect on the impact a leader’s behaviors concerning vision (a clear path toward success aligned with the business and the participants in that business) have on each of the entities listed. Prepare to discuss with class. What part do VALUES play in your assessment of a Leader? What is the impact of your leader having aligned or matched values with? : Our Customers Our employees You In the space provided reflect on the impact a leader’s alignment of values has on each of the entities listed. Prepare to discuss with class. 6 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P What is this thing called Leadership Style? Many terms and titles have been given to the various styles of leadership. What are some that you are familiar with? Here are a few that are common place: Authoritarian (Autocratic) Authoritarian leaders, also known as autocratic leaders, provide clear expectations for what needs to be done, when it should be done, and how it should be done. There is also a clear division between the leader and the followers. Authoritarian leaders make decisions independently with little or no input from the rest of the group. Researchers found that decision-making was less creative under authoritarian leadership. Lewin also found that it is more difficult to move from an authoritarian style to a democratic style than vice versa. Abuse of this style is usually viewed as controlling, bossy, and dictatorial. (Lewin, K ref. 2) Participative Leadership (Democratic) Lewin’s study found that participative leadership, also known as democratic leadership, is generally the most effective leadership style. Democratic leaders offer guidance to group members, but they also participate in the group and allow input from other group members. In Lewin’s study, children in this group were less productive than the members of the authoritarian group, but their contributions were of a much higher quality. Participative leaders encourage group members to participate, but retain the final say over the decision-making process. Group members feel engaged in the process and are more motivated and creative. Delegative (Laissez-Faire) Leadership Researchers found that children under delegative leadership, also known as laissez-fair leadership, were the least productive of all three groups. The children in this group also made more demands on the leader, showed little cooperation and were unable to work independently. Delegative leaders offer little or no guidance to group members and leave decisionmaking up to group members. While this style can be effective in situations where group members are highly qualified in an area of expertise, it often leads to poorly defined roles and a lack of motivation. Which of these do you find yourself using the most often? 7 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P ___________________________________________________________ Have you asked yourself why? Have you found difficulty switching from one to the other? (If indeed you ever do switch) What has gotten in the way? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 8 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Defining Leadership behaviors into two categories: Breaking the styles down to their lowest details and placing the behaviors displayed two categories we find that being DIRECTING or SUPPORTING covers about all of the styles’ behaviors. Directing = Telling, Doing/Giving o The six most important words: "I admit I made a mistake." o The five most important words: "You did a good job." o The four most important words: "What is your opinion." o The three most important words: "If you please." o The two most important words: "Thank you," o The one most important word: "We" o The least important word: "I" ----How? What? When? Where” Supporting = Showing Watching/Listening -- Why? Is it Directing (D) These listed leader behaviors are either or Supporting (S)? Directing or Supporting. Which is Which? Place a “D” or “S” beside the behavior’s corresponding number. 1. Goal Setting 2 Praise and encourage 3 Clarify roles 4 Ask for input 5 Develop action plans 6 Sharing information about organization 7 Showing and telling why 8 Establishing timelines 9 Facilitating problem solving 10 Evaluating 11 Sharing information about self 12 Explain why 13 Identifying priorities 14 Listening and confirming you heard 9 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Knowledge Skills and Abilities along with Motivation/Commitment The behaviors of Directing primarily address a lacking in the areas of Knowledge, Skills or Abilities. The behaviors Commitment. of Supporting primarily address Motivation or We will discuss these more in-depth and in relationship to leadership style later in the lesson. For the purpose of clear communication and simplicity we will use the titles for our four leadership styles: Telling, Coaching, Participating and Delegating Telling Coaching 10 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Participating Delegating 11 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Employee Development Path If we explore and understand the development of our employees and most importantly understand where along that development “path” they are in relation to an individual task or group of tasks then we can adjust our behavior selection to have the most productive impact on their behaviors. *Use this diagram to capture the discussion on the development of your “typical” employee. Hired:______________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Novice:____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Rookie:____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Producer:___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 12 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Expert:_____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Definitions: Commitment is the measure of an individual’s motivation and confidence in relation to a specific goal or tasks. Commitment is attitudinal; it is inferred from one’s behavior. Knowledge- specific types of information people need in order to perform a job. Skills - acquired through practice. They often have physical and motor components and involve cognitive (thinking) components. Example: Skill at welding, operating a crane, typing, etc… Abilities - measurable attributes of an individual’s capacity to perform. Often time complex or multiple tasks are involved. Example: The ability to add subtract, multiply, and divide and use formulas. The ability to picture how a completed project will appear or operate. (Reference: Applied Measurement Methods in Industrial Psychology, Deborah L. Whetzel and George R. Wheaton, ppg. 65-66) Keys to understanding where the individual is in regard the task or tasks: Step 1 Step 2 • What is the specific task(s)? • Are they learning or doing? • Are they motivated/committed Yes or No? Step 3 13 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Needs during the journey toward Star Performer Development Level Max DePree The key elements in the art of working together are how to deal with change, how to deal with conflict, and how to reach our potential...The needs of the team are best met when we meet the needs of individual persons. NEEDS: Novice Rookie Producer Expert **Each Development Level requires: Clear Expectations, Accountability, and Feedback. How do you provide for the needs of your employees? Are expectations crystal clear and understood by each of your employees? How do you know? What part does assessments, audits, ride-a-longs and evaluations have on the development of your employee? How do you give feedback and is it causing a change? 14 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Development Level or Stage Activities Tom the Warehouse manager Has been asked to develop a plan to “slot” Which Level or the new customer’s inventory into the Stage? warehouse and staging for intermixing the new client’s inventory with the existing Learning or Doing client’s inventory for deliver. He will need to put in a good bit of time on the weekends just to get this done on time. It is Motivated or Not overwhelming. His manager has told him to Novice get this done and that he is the only one he can afford to put on this plan development. Rookie Tom is concerned that he does not have a good enough grasp of the situation and its Producer requirements. Tom wishes he could get some more information. Expert Kelly Team leader for new region relationships Has been asked to put together a team from Which Level or her region to look at developing Stage? relationships with other prospective customers in the South-West; including Learning or Doing Mexico. This is a great opportunity and she is excited. She does not have any experience in that market area and has no contacts in Motivated or Not that market. She tells you she isn’t sure who Novice to contact or where to start. Rookie Producer Expert Will the Evaluator His manager wants an evaluation of each of Which Level or his subordinates, their strengths and their Stage? weaknesses. One will be offered a fulltime position and take some of the duties from Learning or Doing Will, allowing Will to take on new responsibilities and challenges. Will has never written an evaluation before, but has Motivated or Not always been seen to be fair and consistent. Novice Will’s verbal assessments have always been “spot on.” Rookie Producer Expert 15 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Troy the Innovator Has seen the latest Profit & Loss and it has Which Level or shown a trend in higher personnel cost over Stage? production/profit. He must reduce personnel cost by 10%. He is concerned Learning or Doing that the loss of personnel or the reduction of income to his people will impact adversely the services he is providing to this Motivated or Not new client which has a large potential for Novice expansion in services needed from his business unit. Troy knows that if he can Rookie streamline some processes that he can avoid the personnel reduction or reduction in Producer wages with the increase in services to the new customer and more efficient scheduling Expert and routing. Troy’s manager has asked him to present his plan to the regional team next week. Troy is nervous. He ask you “What if I am not persuasive?” 16 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Matching Leadership Style to Development Level Remember the Leadership Quiz you took prior to attending the class? What was your Style? During the Quiz did you have a “person or group” in mind as you were answering those questions? That is one of the problems with “shoot from the hip” selection of behaviors leaders often have. It seems we do this often: Shoot – Ready – Aim. We do not prepare ourselves; we do not select the target. We often miss! Forces that influence the style to be used included: How much time is available? Are relationships based on respect and trust or on disrespect? Who has the information — you, your employees, or both? How well your employees are trained and how well you know the task. Internal conflicts. Stress levels. Type of task. Is it structured, unstructured, complicated, or simple? Laws or established procedures such as OSHA or training plans. 17 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Match or Mismatched? Activities John, Building Specialist John is in his mid 30’s and has worked for Which Level or the company for over 3 years as an installer . Stage? He is your new Building Specialist. His or previous experience in the building trade Learning Doing was as a subcontractor to an apartment complex developer/builder as an installer. Motivated or Not John’s current position requires knowledge Novice of installation, delivery timing and staging, and the managerial skills to hold others Rookie accountable to standards of service John’s performance has had moments of success and opportunities as a manger of installers. You have just gotten off the phone with one of our customers, who is very dissatisfied with the install of over thirty double stacked washers and dryers. They are not level and the exhaust ducts are not securely fastened. Walls on the inside of the closet where the units sit are scratched and dirty. Producer Expert Which Leadership Style? Telling Coaching Participating Delegating Why is this the most effective style? 18 A D A P T I V E Mary the L E A D E R S H I P Customer Service Representative Mary is your Customer Service Which Level or Representative. She has worked with your Stage? company for about 3 months. Prior to this, she worked in the delivery scheduling Learning or Doing function of a Home Air Conditioning and Heating service. Motivated or Not Your Delivery Installers have brought up Novice numerous concerns; Customers were not aware of the time they were getting the Rookie delivery/install. The Customer expected a different service than what was on the Producer delivery sheet. Telephone numbers were wrong. Also some products were of the Expert wrong color or model. Delivery Installers could not get down the street to the home Which from any direction due to overhanging limbs Leadership Style? or narrow streets with on street parking. Telling Coaching Participating Delegating Why is this the most effective style? To sum this up, the obvious matching is Tell to Novice; Coach to Rookie; Participate to Producer; and Delegate to Expert. Reflect on the important aspect that we cannot assume the person is an Expert in everything nor are they a Rookie or Producer or Novice in everything. Our work environment does not allow us to see all the hidden talents and flaws of our employees. How are we going to discover with any sense of surety that we are using the most effective leadership style? Observe, ask others, test/assess, ask the individual, look for certifications etc… KNOW YOUR PEOPLE…..Know yourself….Adapt and LEAD! 19 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Next Chance to Learn! Activity What would you Say? Employee Development Level Leadership is influencing people — by providing purpose, direction, and motivation — while operating to accomplish the mission and improving the organization. 1 His manager wants an evaluation of each of his subordinates, their strengths and their weaknesses. One will be offered a fulltime position and take some of the duties from Will, allowing Will to take on new responsibilities and challenges. Will has never written an evaluation before, but has always been seen to be fair and consistent. Will’s verbal assessments have always been “spot on.” 2 Has seen the latest Profit & Loss and it has shown a trend in higher personnel cost over production/profit. He must reduce personnel cost by 10%. He is concerned that the loss of personnel or the reduction of income to his people will impact adversely the services he is providing to this new client which has a large potential for expansion in services needed from his business unit. Troy knows that if he can streamline some processes that he can avoid the personnel reduction or reduction in wages with the increase in services to the new customer and more efficient scheduling and routing. Troy’s manager has asked him to present his plan to the regional team next week. Troy is nervous. He ask you “What if I am not persuasive?” 20 Leadership Style A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P 3 Has been asked to develop a plan to “slot” the new customer’s inventory into the warehouse and staging for intermixing the new client’s inventory with the existing client’s inventory for deliver. He will need to put in a good bit of time on the weekends just to get this done on time. It is overwhelming. His manager has told him to get this done and that he is the only one he can afford to put on this plan development. Tom is concerned that he does not have a good enough grasp of the situation and its requirements. Tom wishes he could get some more information. 4 Kelly has been asked to put together a team from her region to look at developing relationships with other prospective customers in the SouthWest; including Mexico. This is a great opportunity and she is excited. She does not have any experience in that market area and has no contacts in that market. She tells you she isn’t sure where to start. 5 During an audit/check ride your employee was found to not be following policy in that he was not wearing a seat belt. 6 Marty has taken on a very negative attitude toward the new employees. Doing only what’s asked of him and only when he is ready to do so. He had difficulty with the revised tracking and reporting system recently installed. He was the expert in the previous system and was always willing to share his knowledge and demonstrate his skills. People want someone to believe in and want someone to believe in them . 21 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P 7 You have noticed that Tom has been “surfing the internet” a lot toward the end of the daily shift. He never “chit chats” with his nearby coworkers. His work is always done and done well. He is meeting the goals set for him. The computer security says he is visiting a lot of job listing sites. 8 A Carrier Sales Coordinator is not meeting the percent to market goals for the past two months. Prior to this she was on target for 6 months straight. She has been late to work for two occasions and has had to leave work early twice this week. Her coworkers have seen a definite change in her attitude toward work and how she speaks to the prospective carriers. 9 Brad is your supervisor of the warehouse. Freight is not getting on the delivery trucks as it should. It is not loaded according to the planned stops every time. The night shift lead is new to the position (2 months). This has been brought to Brad’s attention by the installers before today 10 Customers are complaining about the abrupt behavior of your employee. You have received four complaints this week. Prior to this month you have never had any complaints with this employee (three years with company) This employee is now delivering for our newest client “Have it Your Way.” 22 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Partnering With your Employees for Development How do we go about leading? This section discusses the execution of leadership. When: Active leadership versus Reactive Leadership: Planning to be Successful “Failing to Plan is Planning to Fail” New Employee: New Process: Questions to be answered by the leader and by the employee: 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the goals each employee is going to be expected to reach? How are they to reach them? When are they to reach them? What is in it for them to attain the goals? Goals must be ______________ to the individual; if not they may ____________. SMARTT goal setting model S M A R T T ________________and ______________ ____________________ (Exact) (What’s in it for them) _____________________ (Can be Done - reachable) _____________________ (Impacts the business) ______________________ (What is used to measure your progress) _____________________ (Specific deadlines) This process is ____________________to setting the path to success. It is your plan and theirs. This is an agreement between two individuals. One representing a business entering into an agreement with another, an employee, which agrees to ______________and behave in a certain manner to sustain the _________________ and its growth according to this plan. 23 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P What: determine what is to be done and how it is to be done. “With your team members” You cannot do it all! You cannot monitor it all! Coaching A Safety Net and a Guide for the Journey What purpose would you doing a “job shadow” serve? Audits; Active or Reactive? What comes of an audit results? Do we coach everyone the same? What about consistency and fairness? How important is it to have the plan in- place and the plan tailored/designed with the employee in mind prior to having an assessment? 24 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P To what degree: Agreed on expectations; Agreed on Goals; Partnering and holding each other accountable. Reward and Recognition – Good or Bad Evaluating Without Evaluating; how do you know how far you have come or how much farther you must go? Performance Evaluations: On what do you use to base your conclusion? Potential Evaluations: On what do you base your conclusion? How does the Plan fit into this evaluation? How do Honesty, Fairness, Values, Consistency, and Vision impact this process? 25 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P Post-Course Leadership Self-Assessment Activity Notes: Remember this survey? Now take it with a slightly different perspective now that you have participated in the Foundations of Leadership course. How do you feel now about these? Take the survey one more time and see if your assessment of yourself has changed. o This survey is the short version. The long version can be found on http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/survlead.html This self-survey will provide you with feedback as to your feelings of leading others. Rate yourself on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being a definite YES and 1 being a definite NO. Be honest about your answers as this survey is only for your own self-assessment. Circle the number which you feel most closely represents your feelings about the task: NO YES 1. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy working on teams. 2. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am able to speak clearly to others. 3. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy relating to others on an interpersonal basis. 4. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am good at planning. 5. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I can interpret rules and regulations. 6. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I feel comfortable asking others for advice. 7. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy collecting and analyzing data. 8. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am good at solving problems. 9. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am comfortable writing memos to others. 10. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I can delegate work to others. 11. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am effective at handling employee complaints. 12. - 1 2 3 4 5 - Giving directions is comfortable for me. 13. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I know how to develop goals and carry them out. 14. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am comfortable at implementing new techniques. 15. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I enjoy appraising performance and giving feedback. 16. - 1 2 3 4 5 - If I made an mistake, I would admit it and correct it. 17. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I am able to resolve conflict in the workplace. 18. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I believe in diversity in the workplace. 19. - 1 2 3 4 5 - I thrive on change. 20. - 1 2 3 4 5 - One of my greatest desires is to become a leader. Scoring Score the survey by adding the numbers that you circled: ________ 26 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P A score of fifty or higher indicates a desire to become a leader and a perceived ability to perform the tasks required of a leader. A score of fifty or less indicators a general dislike of wanting to become a leader or a perceived inability to perform the tasks required of a leader. BUT, no matter what your score is, your commitment, desire, and determination are the biggest indicators of your ability to become a leader. Use this assessment to help you to determine what skills and abilities you can continue to improve (Strengths) and what skills and abilities you need to develop (Opportunities for growth). One you know your weakness, use this course and others associated (listed in the reference section) to help develop those weaknesses. What are your strengths? What are your opportunities for growth? Now take control of your future….Develop yourself! References and Further Development Sources: 1. Leadership Job Interview Questions by Susan M. Heathfield, About.com Guide http://humanresources.about.com/od/leadership/a/leader_question.htm 2. Leadership Style Theories, Which Leadership Style is the Most Effective? Melissa Bushman, Yahoo Contributor Network, Jan 15, 2007 http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/117884/leadership_style_theories.html 3. Leadership Style, Big Dog & Little Dog’s Performance Juxtaposition. http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/leadstl.html 4. Get Them On Your Side, Samuel B. Bacharach Ordering site: http://www.amazon.com/ThemYour-Side-Samuel-Bacharach/dp/1593377363/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid=1296848373&sr=8-1 5. Leadership and the Language of Integrity posted by Samuel b Bacharah on Feb 4, 20011. http://sambacharach.com/bacharachblog/leader/leadership-and-the-language-of-integrity/ 6. 3 Reasons to Be Obsessed with Influence. Blog posting of June 28, 2010 From “Saying What You Mean.” 27 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P http://nicoledefalco.wordpress.com/2010/06/28/3-reasons-to-be-obsessed-withinfluence/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+wordpress%2F gQyV+%28Saying+What+You+Mean%29 7. Four Leadership Behaviors That Build or Destroy Trust, Blanchard LeaderChat., A forum to Discuss Leadership and Management issues. http://leaderchat.org/2010/07/07/four-leadership-behaviors-that-build-or-destroy-trust/ Our “In House” library has an extensive listing of Leadership Development support books and pamphlets. Please while here at the Lowell Training & Development Department browse through the collections and if you wish to “Check It Out” contact our administrator in the front office area or contact any of the staff members of Training & Development. Index Abilities, 10, 13 Accountability, 14 Active leadership versus Reactive Leadership, 23 Agreed on expectations; Agreed on Goals, 25 Audits, 24 Authoritarian (Autocratic), 7 Broad-minded, 4 Clear Expectations, 14 Coaching, 10 Commitment, 13 Competent, 4 consistency, 24 Courageous, 4 Delegating, 11 Delegative (Laissez-Faire) Leadership, 7 determine what is to be done and how it is to be done., 24 Directing, 9 Employee Development Path, 12 Expert, 14 Fair-minded, 4 fairness, 24 Feedback, 14 Forward-looking, 4 Honest, 4 Imaginative, 4 Inspiring, 4 Intelligent, 4 Keys to understanding, 13 Knowledge, 10, 13 Leadership Quiz, 17 Novice, 14 Participating, 11 Participative Leadership (Democratic), 7 Partnering, 23 Performance Evaluations:, 25 Potential Evaluations, 25 Producer, 14 Ride –A –Longs, 24 Rookie, 14 Skills, 10, 13 SMARTT goal setting model, 23 Straightforward, 4 Supporting, 9 task or group of tasks, 12 Telling, 10 28 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P 29 A D A P T I V E L E A D E R S H I P 30